rising pitch siren

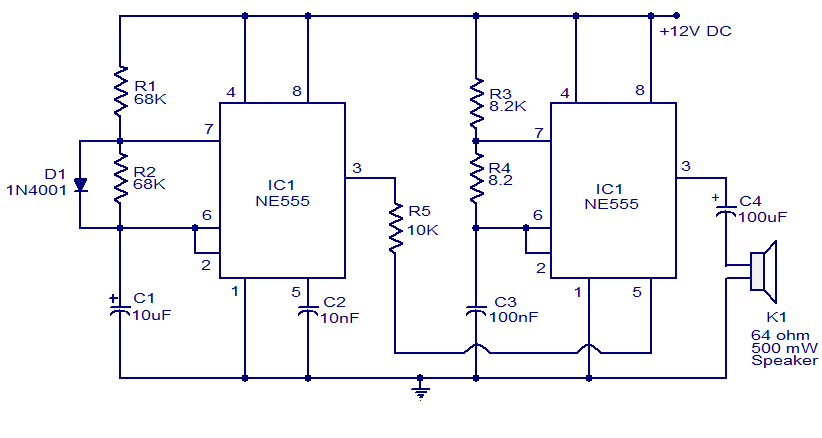
A two-transistor electronic siren breadboard circuit that produces an audible rising pitch on a loudspeaker. This circuit serves as a tutorial for beginners in electronics.
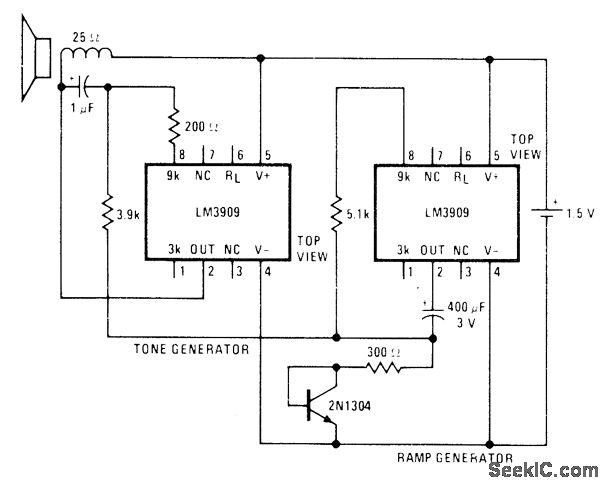
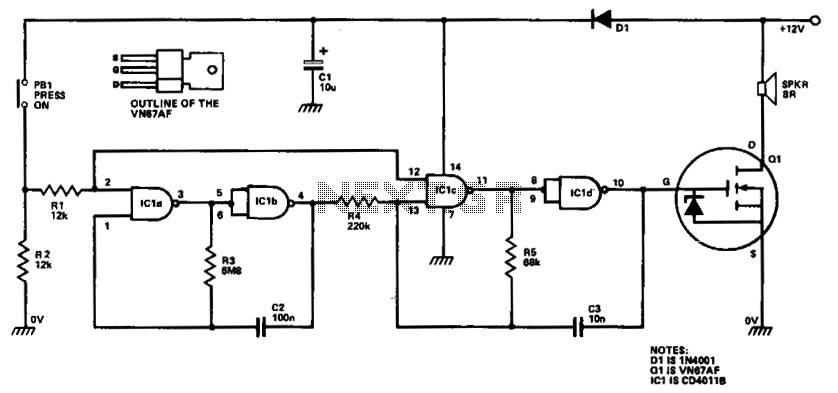
The two-transistor siren circuit operates by utilizing the properties of transistors to create an oscillating signal that drives a loudspeaker. The basic components of the circuit include two NPN transistors, resistors, capacitors, and a loudspeaker.
In this configuration, the first transistor is connected in a feedback loop with the second transistor. The circuit is designed to charge and discharge a capacitor, which results in a changing frequency of oscillation. As the capacitor charges through a resistor, it eventually reaches a threshold voltage that turns on the second transistor. This action causes the first transistor to switch off, leading to a rapid discharge of the capacitor and a corresponding drop in voltage. This cycle repeats, creating an audible sound that increases in pitch over time.
To construct this circuit on a breadboard, the following steps should be followed:
1. Place the two NPN transistors on the breadboard. The collector of the first transistor should be connected to the base of the second transistor, while the emitter of the first transistor connects to ground.
2. Connect a resistor from the power supply (typically 9V) to the collector of the first transistor. This resistor limits the current flowing through the transistor.
3. Connect a capacitor between the collector of the first transistor and ground. This capacitor will charge and discharge, facilitating the oscillation.
4. Connect the loudspeaker in parallel with the capacitor to convert the oscillating signal into sound.
5. Ensure that all connections are secure and that the power supply is correctly connected to avoid damaging the components.
By adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors, the frequency and pitch of the siren can be modified, allowing for experimentation and learning about electronic components and their behavior in a circuit. This circuit not only serves as a practical application of basic electronic principles but also provides an engaging project for beginners to enhance their understanding of oscillators and sound generation.A two transistor electronic siren breadboard circuit that produces an audible rising pitch on a loudspeaker. Tutorial and circuit for beginners in electronics.. 🔗 External reference
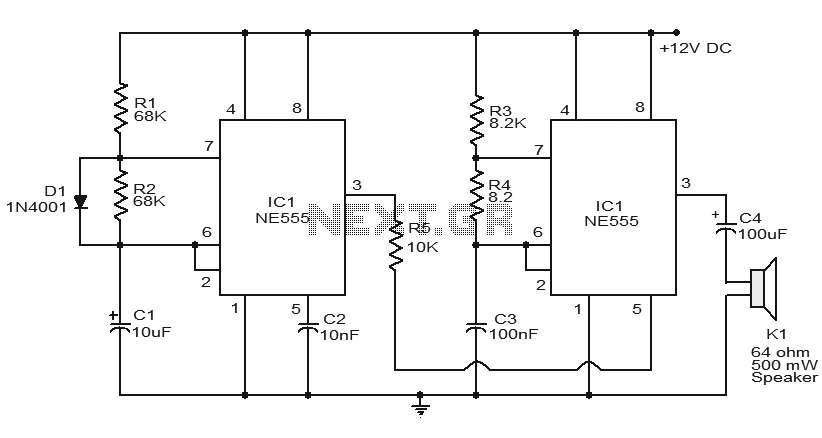
The two-transistor siren circuit operates by utilizing the properties of transistors to create an oscillating signal that drives a loudspeaker. The basic components of the circuit include two NPN transistors, resistors, capacitors, and a loudspeaker.
In this configuration, the first transistor is connected in a feedback loop with the second transistor. The circuit is designed to charge and discharge a capacitor, which results in a changing frequency of oscillation. As the capacitor charges through a resistor, it eventually reaches a threshold voltage that turns on the second transistor. This action causes the first transistor to switch off, leading to a rapid discharge of the capacitor and a corresponding drop in voltage. This cycle repeats, creating an audible sound that increases in pitch over time.
To construct this circuit on a breadboard, the following steps should be followed:
1. Place the two NPN transistors on the breadboard. The collector of the first transistor should be connected to the base of the second transistor, while the emitter of the first transistor connects to ground.
2. Connect a resistor from the power supply (typically 9V) to the collector of the first transistor. This resistor limits the current flowing through the transistor.
3. Connect a capacitor between the collector of the first transistor and ground. This capacitor will charge and discharge, facilitating the oscillation.
4. Connect the loudspeaker in parallel with the capacitor to convert the oscillating signal into sound.
5. Ensure that all connections are secure and that the power supply is correctly connected to avoid damaging the components.
By adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors, the frequency and pitch of the siren can be modified, allowing for experimentation and learning about electronic components and their behavior in a circuit. This circuit not only serves as a practical application of basic electronic principles but also provides an engaging project for beginners to enhance their understanding of oscillators and sound generation.A two transistor electronic siren breadboard circuit that produces an audible rising pitch on a loudspeaker. Tutorial and circuit for beginners in electronics.. 🔗 External reference