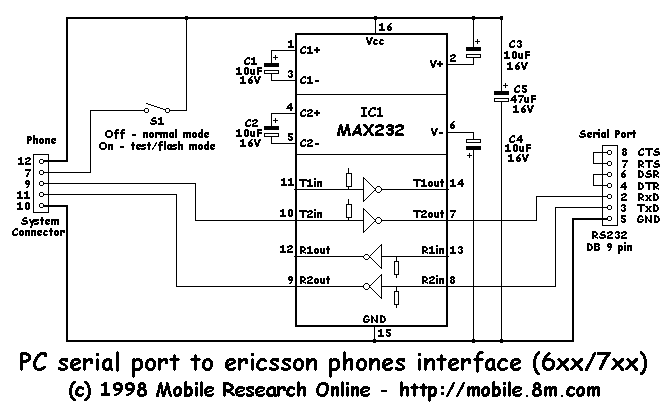
RS-232 Serial Interface Status Indicator Circuit

RS-232 Serial Interface Status Indicator Circuit. This circuit utilizes a single logic integrated circuit (IC) to indicate the transmission (TXD) and reception (RXD) statuses of a serial interface.
The RS-232 Serial Interface Status Indicator Circuit is designed to provide visual feedback regarding the status of data transmission and reception in RS-232 communication. The circuit primarily employs a logic integrated circuit (IC), which simplifies the design while ensuring reliable operation.
The circuit typically includes two LED indicators: one for TXD (transmit data) and another for RXD (receive data). These LEDs illuminate when the respective data lines are active, providing a clear visual indication of communication activity.
The operation of the circuit is based on monitoring the voltage levels on the TXD and RXD lines. When data is being transmitted, the TXD line will exhibit a change in voltage, which is detected by the logic IC. The IC then drives the TXD LED, turning it on to indicate that data is being sent. Similarly, the RXD line is monitored for incoming data, and when activity is detected, the RXD LED is illuminated.
Power supply considerations are crucial for the circuit's performance. The circuit can be powered by a standard voltage supply, typically 5V or 12V, depending on the specifications of the logic IC used. Proper decoupling capacitors should be employed near the power pins of the IC to minimize noise and ensure stable operation.
In summary, the RS-232 Serial Interface Status Indicator Circuit is a practical solution for visualizing data transmission and reception in serial communications, leveraging a simple logic IC to drive LED indicators for effective status monitoring. This design is particularly beneficial in debugging and monitoring serial communication systems.RS-232 Serial Interface Status Indicator Circuit. I designed this circuit many years ago and have used it several times since. It uses a single logic IC to indicate the TXD and RXD. 🔗 External reference
The RS-232 Serial Interface Status Indicator Circuit is designed to provide visual feedback regarding the status of data transmission and reception in RS-232 communication. The circuit primarily employs a logic integrated circuit (IC), which simplifies the design while ensuring reliable operation.
The circuit typically includes two LED indicators: one for TXD (transmit data) and another for RXD (receive data). These LEDs illuminate when the respective data lines are active, providing a clear visual indication of communication activity.
The operation of the circuit is based on monitoring the voltage levels on the TXD and RXD lines. When data is being transmitted, the TXD line will exhibit a change in voltage, which is detected by the logic IC. The IC then drives the TXD LED, turning it on to indicate that data is being sent. Similarly, the RXD line is monitored for incoming data, and when activity is detected, the RXD LED is illuminated.
Power supply considerations are crucial for the circuit's performance. The circuit can be powered by a standard voltage supply, typically 5V or 12V, depending on the specifications of the logic IC used. Proper decoupling capacitors should be employed near the power pins of the IC to minimize noise and ensure stable operation.
In summary, the RS-232 Serial Interface Status Indicator Circuit is a practical solution for visualizing data transmission and reception in serial communications, leveraging a simple logic IC to drive LED indicators for effective status monitoring. This design is particularly beneficial in debugging and monitoring serial communication systems.RS-232 Serial Interface Status Indicator Circuit. I designed this circuit many years ago and have used it several times since. It uses a single logic IC to indicate the TXD and RXD. 🔗 External reference