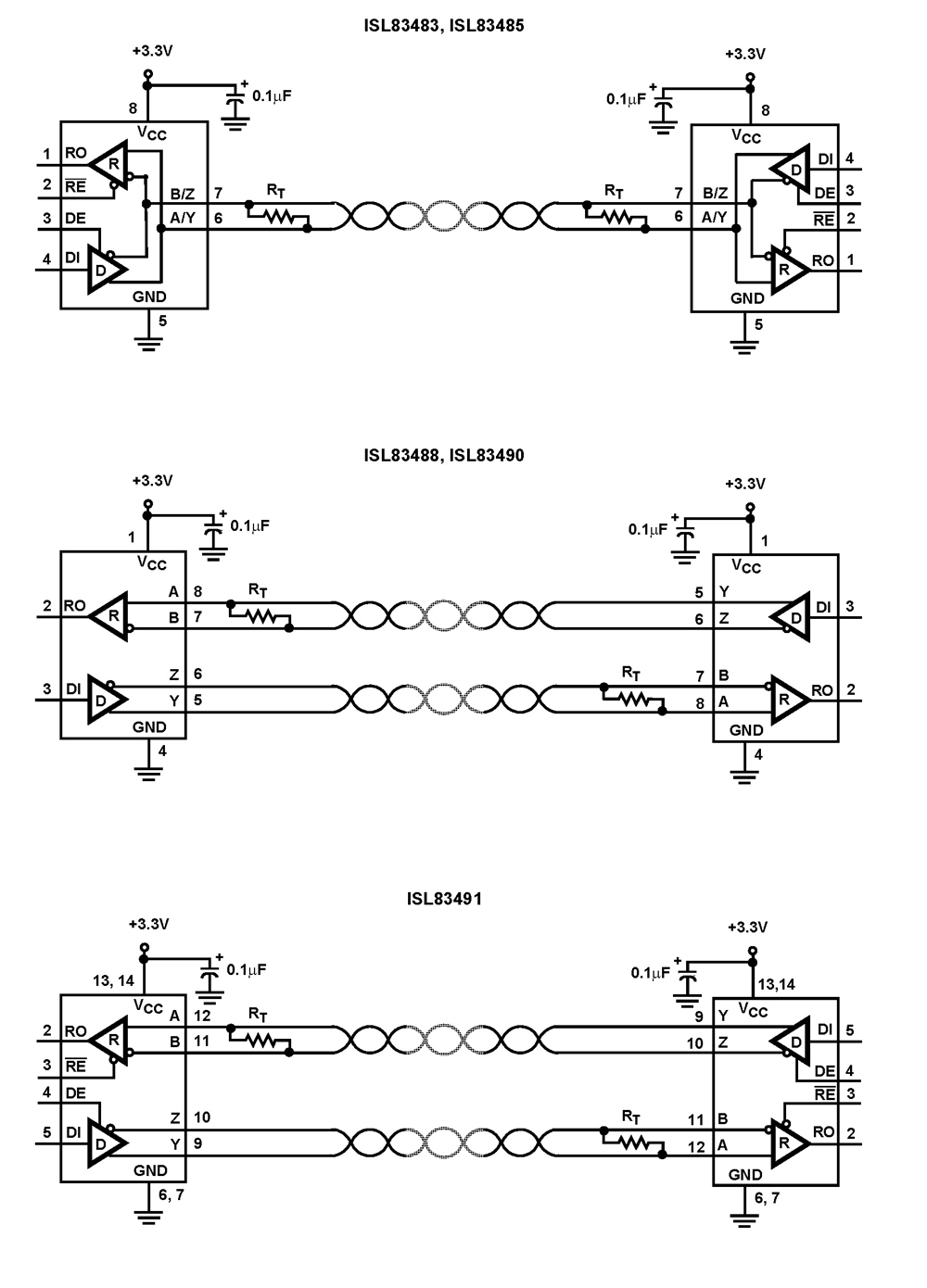
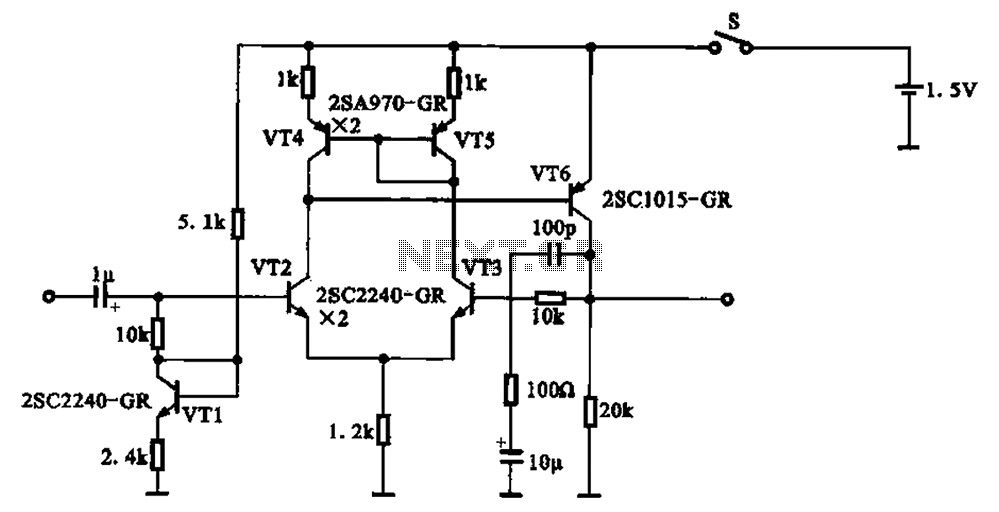
RS-485 Signal Loss Detection
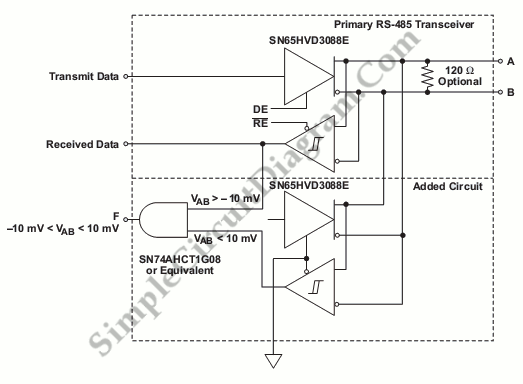
The safety shutdown and fault isolation protocol is critical in various telecommunication, industrial, and data processing systems. It is essential for data sharing.
The safety shutdown and fault isolation protocol serves as a fundamental component in ensuring the reliability and safety of telecommunication, industrial, and data processing systems. This protocol is designed to prevent damage to equipment and protect personnel during fault conditions. It encompasses a series of steps that are triggered when a fault is detected, allowing for the immediate isolation of the affected system components.
In a typical implementation, the protocol initiates a safety shutdown sequence that systematically powers down non-essential systems while maintaining critical operations. This can involve the activation of circuit breakers, relay systems, or software-based controls that monitor system health. The protocol also includes mechanisms for fault detection, which may utilize sensors or software algorithms to identify anomalies in system performance.
Furthermore, the fault isolation aspect of the protocol ensures that any detected fault does not propagate through the system, potentially leading to widespread failure. This is achieved through the use of redundant pathways, isolation switches, or automated systems that can reroute data and power as necessary.
In telecommunication systems, the protocol is particularly vital as it safeguards against data loss and service interruptions. It allows for the seamless continuation of service by isolating faulty components while maintaining operational integrity. In industrial applications, it protects machinery and personnel from hazardous conditions that may arise due to equipment failure.
Overall, the safety shutdown and fault isolation protocol is an indispensable feature in modern electronic systems, contributing to enhanced safety, reliability, and efficiency in data sharing and processing across various sectors.The safety shutdown and fault isolation protocol are critical in many telecommunication, industrial, data processing system and industrial. To share data.. 🔗 External reference
The safety shutdown and fault isolation protocol serves as a fundamental component in ensuring the reliability and safety of telecommunication, industrial, and data processing systems. This protocol is designed to prevent damage to equipment and protect personnel during fault conditions. It encompasses a series of steps that are triggered when a fault is detected, allowing for the immediate isolation of the affected system components.
In a typical implementation, the protocol initiates a safety shutdown sequence that systematically powers down non-essential systems while maintaining critical operations. This can involve the activation of circuit breakers, relay systems, or software-based controls that monitor system health. The protocol also includes mechanisms for fault detection, which may utilize sensors or software algorithms to identify anomalies in system performance.
Furthermore, the fault isolation aspect of the protocol ensures that any detected fault does not propagate through the system, potentially leading to widespread failure. This is achieved through the use of redundant pathways, isolation switches, or automated systems that can reroute data and power as necessary.
In telecommunication systems, the protocol is particularly vital as it safeguards against data loss and service interruptions. It allows for the seamless continuation of service by isolating faulty components while maintaining operational integrity. In industrial applications, it protects machinery and personnel from hazardous conditions that may arise due to equipment failure.
Overall, the safety shutdown and fault isolation protocol is an indispensable feature in modern electronic systems, contributing to enhanced safety, reliability, and efficiency in data sharing and processing across various sectors.The safety shutdown and fault isolation protocol are critical in many telecommunication, industrial, data processing system and industrial. To share data.. 🔗 External reference