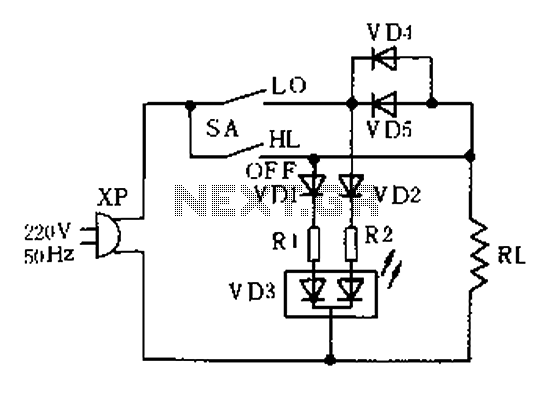
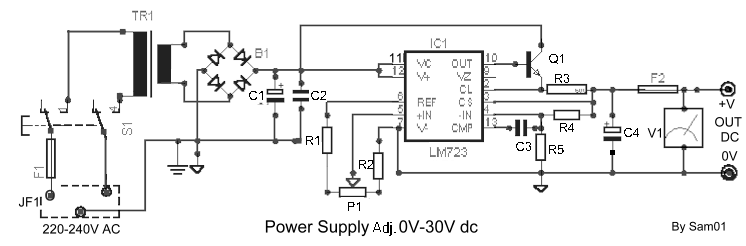
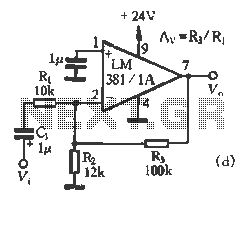
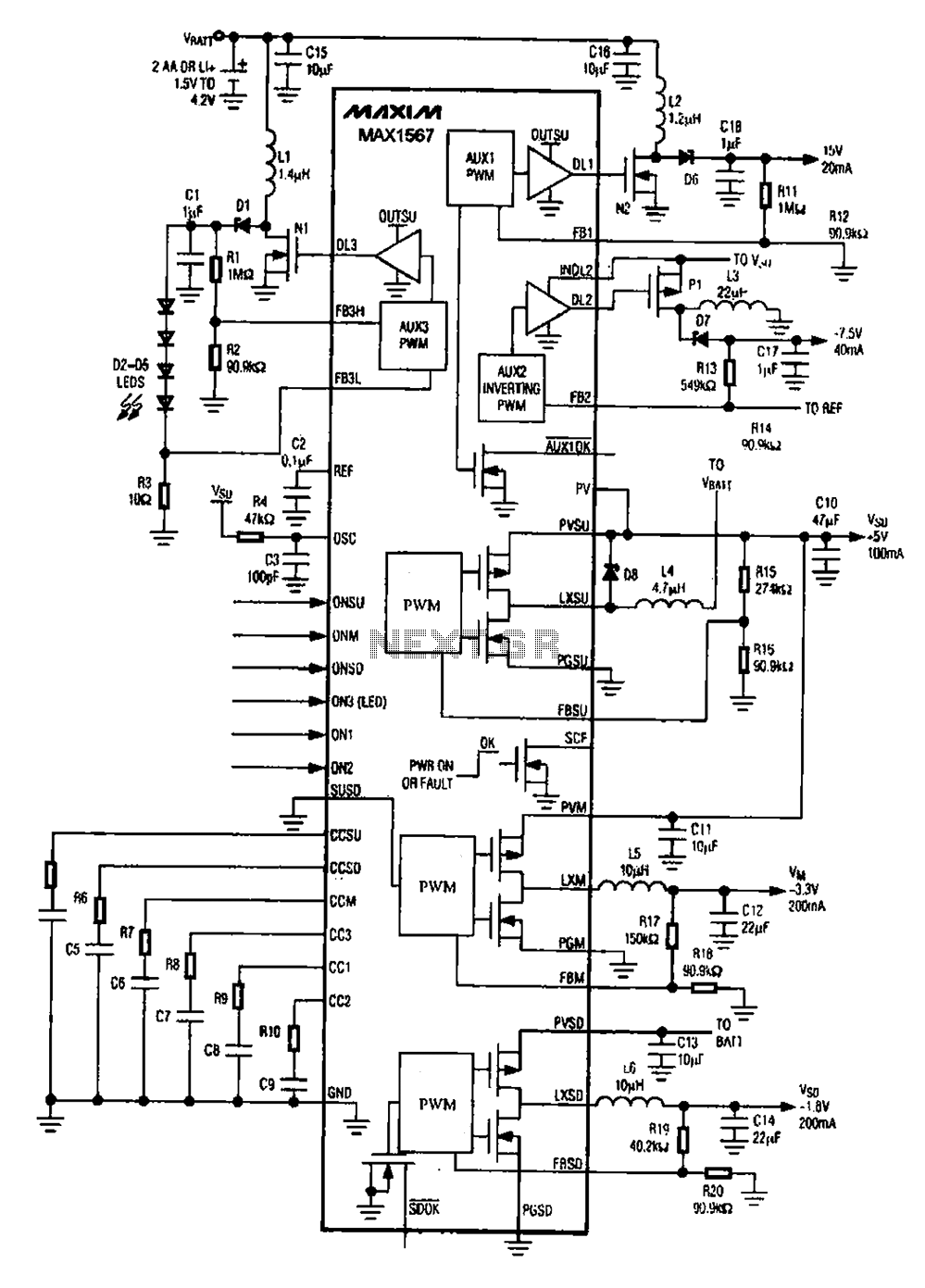
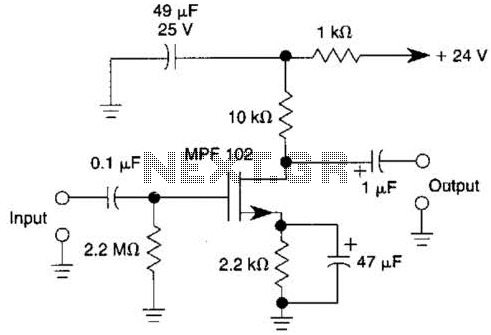
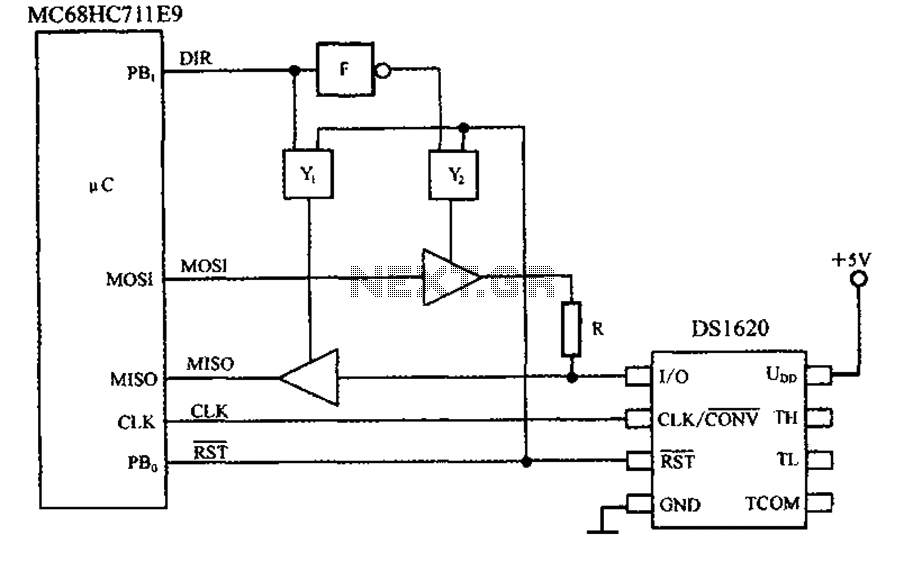
SBC Power overvoltage protection circuit diagram
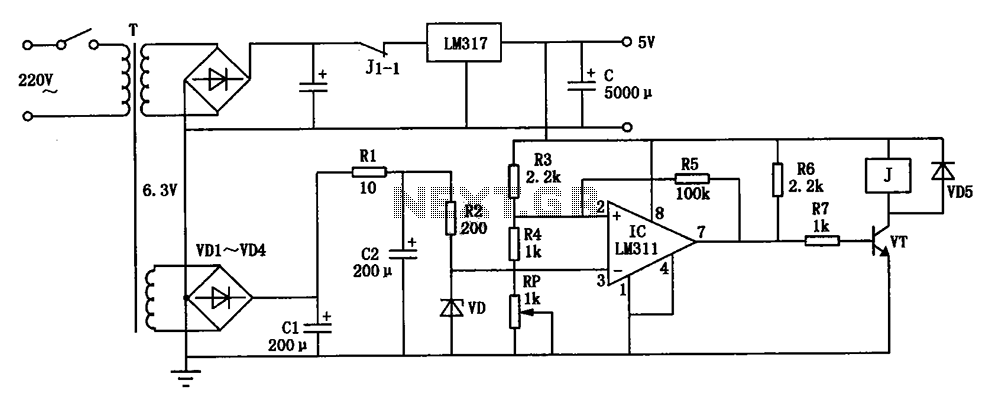
The circuit depicted can be utilized to operate at a voltage of +5V for Single Board Computer (SBC) power, preventing damage caused by over-voltage from the power supply throughout the SBC.
This circuit serves as a protective mechanism for Single Board Computers (SBCs) by regulating the input voltage to a safe level of +5V. It is essential to prevent over-voltage conditions that could potentially damage sensitive electronic components within the SBC.
The circuit typically includes a voltage regulator, which is designed to maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. Commonly, a linear regulator or a buck converter may be employed, depending on the efficiency requirements and the input voltage range.
In addition to the voltage regulator, the circuit may incorporate protective elements such as diodes, capacitors, and fuses. Diodes can be used to prevent reverse polarity, ensuring that the SBC receives power only in the correct direction. Capacitors can smooth out voltage fluctuations, providing stability to the power supply. Fuses or resettable polyfuses can protect against overcurrent conditions, disconnecting the power supply in the event of a fault.
The layout of the circuit should be designed to minimize noise and interference, which can adversely affect the performance of the SBC. Proper grounding techniques and decoupling capacitors should be employed to enhance the reliability of the power supply circuit.
Overall, this circuit is critical for maintaining the integrity and longevity of SBCs by ensuring that they receive a stable and safe operating voltage. Circuit as shown, can be used for operating voltage of + 5V SBC power to prevent damage due to over-voltage power supply throughout the SBC.
This circuit serves as a protective mechanism for Single Board Computers (SBCs) by regulating the input voltage to a safe level of +5V. It is essential to prevent over-voltage conditions that could potentially damage sensitive electronic components within the SBC.
The circuit typically includes a voltage regulator, which is designed to maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. Commonly, a linear regulator or a buck converter may be employed, depending on the efficiency requirements and the input voltage range.
In addition to the voltage regulator, the circuit may incorporate protective elements such as diodes, capacitors, and fuses. Diodes can be used to prevent reverse polarity, ensuring that the SBC receives power only in the correct direction. Capacitors can smooth out voltage fluctuations, providing stability to the power supply. Fuses or resettable polyfuses can protect against overcurrent conditions, disconnecting the power supply in the event of a fault.
The layout of the circuit should be designed to minimize noise and interference, which can adversely affect the performance of the SBC. Proper grounding techniques and decoupling capacitors should be employed to enhance the reliability of the power supply circuit.
Overall, this circuit is critical for maintaining the integrity and longevity of SBCs by ensuring that they receive a stable and safe operating voltage. Circuit as shown, can be used for operating voltage of + 5V SBC power to prevent damage due to over-voltage power supply throughout the SBC.