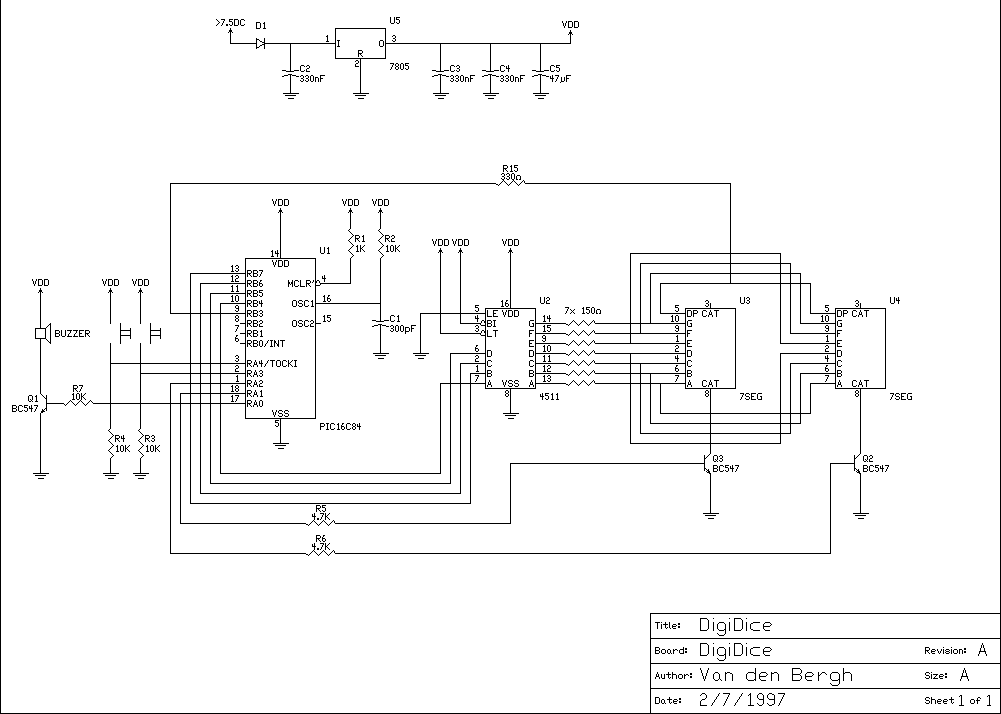
Electronic thermostat circuit
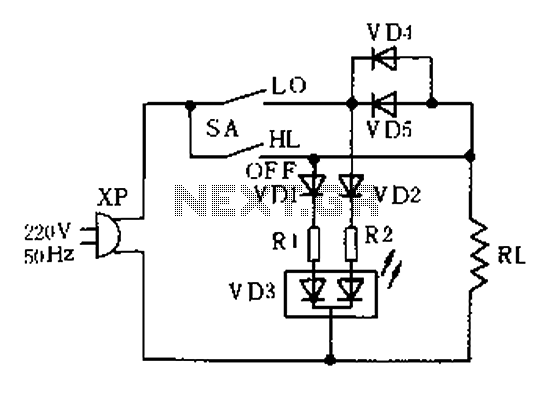
The thermostat electric circuit operates as depicted in the figure. It has three settings: off, low power (Lo), and high power (Peru HL). When the DIP switch SA is set to the Lo position, 220V AC is directed through diodes VD4 and VD56 to the load RL. This configuration results in a half-wave rectification, which reduces the effective voltage across RL compared to the full 220V AC. Consequently, the temperature of RL decreases.
The thermostat circuit is designed to control the temperature of a system by switching between different power levels. The circuit includes a DIP switch (SA) that allows the user to select between three operational modes: off, low power (Lo), and high power (Peru HL).
In the low power mode, when the switch is set to Lo, the circuit allows 220V AC to flow through diodes VD4 and VD56. These diodes serve as rectifiers, converting the AC voltage to a pulsating DC voltage through half-wave rectification. This process effectively reduces the voltage supplied to the load (RL), which is crucial for applications requiring lower heat output. The reduction in voltage results in a significant decrease in the power dissipated by the load, thereby lowering its temperature.
The circuit's design ensures that in the high power mode (Peru HL), the load receives the full 220V AC, allowing for maximum heating capability. The off position completely disconnects the load from the power supply, ensuring that no current flows and the load remains inactive.
This thermostat circuit is commonly used in heating applications where precise temperature control is necessary. By utilizing the DIP switch to select the desired power level, users can effectively manage the thermal output of the system, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.Thermostat electric circuit as shown in FIG. It points to off (off), Lo (low power), Peru HL (high power) third gear. When DIP switch SA to Lo gear, 220V electricity through the diode VD4, VD56 added to the load RL ends; half-wave rectified by a diode so that RL was significantly lower than when the operating voltage 220v straight, so RL temperature drops.
The thermostat circuit is designed to control the temperature of a system by switching between different power levels. The circuit includes a DIP switch (SA) that allows the user to select between three operational modes: off, low power (Lo), and high power (Peru HL).
In the low power mode, when the switch is set to Lo, the circuit allows 220V AC to flow through diodes VD4 and VD56. These diodes serve as rectifiers, converting the AC voltage to a pulsating DC voltage through half-wave rectification. This process effectively reduces the voltage supplied to the load (RL), which is crucial for applications requiring lower heat output. The reduction in voltage results in a significant decrease in the power dissipated by the load, thereby lowering its temperature.
The circuit's design ensures that in the high power mode (Peru HL), the load receives the full 220V AC, allowing for maximum heating capability. The off position completely disconnects the load from the power supply, ensuring that no current flows and the load remains inactive.
This thermostat circuit is commonly used in heating applications where precise temperature control is necessary. By utilizing the DIP switch to select the desired power level, users can effectively manage the thermal output of the system, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.Thermostat electric circuit as shown in FIG. It points to off (off), Lo (low power), Peru HL (high power) third gear. When DIP switch SA to Lo gear, 220V electricity through the diode VD4, VD56 added to the load RL ends; half-wave rectified by a diode so that RL was significantly lower than when the operating voltage 220v straight, so RL temperature drops.