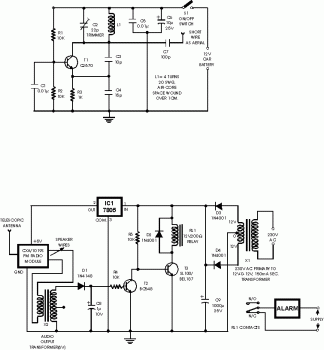
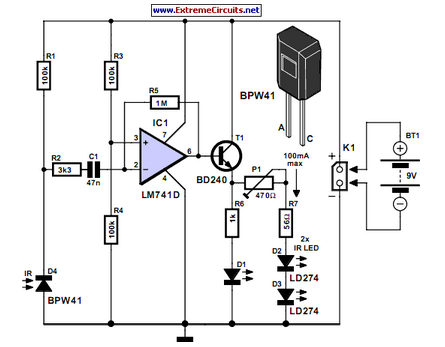
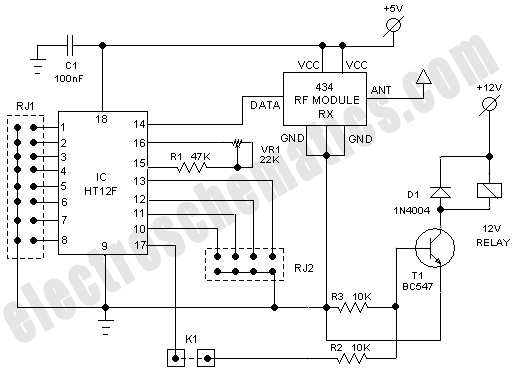
Schematic of The Infrared Rays Wireless Headphone
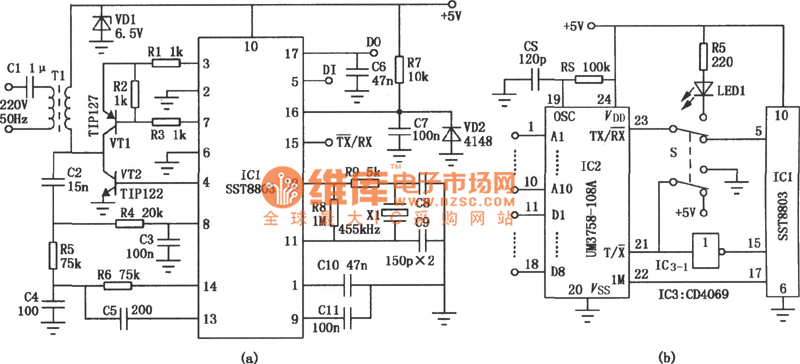
The transmitter circuit for inductive headphones must be installed on a wall or ceiling, limiting their use outdoors. This is a significant drawback of inductive headphones. In contrast, infrared wireless headphones do not have this limitation; their flexible infrared transmitter circuit allows for use in various environments.
The inductive headphone system operates by creating a magnetic field that transmits audio signals to a receiver within the headphones. This setup requires a fixed installation of the transmitter, which restricts mobility and outdoor use. The transmitter typically consists of an oscillator circuit that generates a carrier frequency, which is then modulated with audio signals. The resulting magnetic field is picked up by the inductive receiver in the headphones, converting the magnetic signals back into audio.
In contrast, infrared wireless headphones utilize infrared light waves to transmit audio signals. The infrared transmitter can be positioned flexibly, allowing for a broader range of application, including outdoor settings where line-of-sight is maintained. The transmitter emits modulated infrared light, which is detected by a photodiode in the headphone receiver. This infrared communication provides a reliable audio link without the constraints imposed by physical installations required for inductive systems.
Both systems have their unique advantages and disadvantages. Inductive headphones are typically more secure from interference, as they operate on a principle that is less susceptible to environmental factors. However, the limitation of fixed installation makes them less versatile compared to infrared headphones, which offer greater flexibility and portability.Because of the transmitter circuit of the inductive headphone must installed on the room wall or on the ceiling, so the inductive headphone can not be used outdoor, this is the main weak point of the inductive headphone. But the infrared rays wireless headphone is not in this case, for the flexible infrared rays transmitter circuit, it can be used in electro..
🔗 External reference
The inductive headphone system operates by creating a magnetic field that transmits audio signals to a receiver within the headphones. This setup requires a fixed installation of the transmitter, which restricts mobility and outdoor use. The transmitter typically consists of an oscillator circuit that generates a carrier frequency, which is then modulated with audio signals. The resulting magnetic field is picked up by the inductive receiver in the headphones, converting the magnetic signals back into audio.
In contrast, infrared wireless headphones utilize infrared light waves to transmit audio signals. The infrared transmitter can be positioned flexibly, allowing for a broader range of application, including outdoor settings where line-of-sight is maintained. The transmitter emits modulated infrared light, which is detected by a photodiode in the headphone receiver. This infrared communication provides a reliable audio link without the constraints imposed by physical installations required for inductive systems.
Both systems have their unique advantages and disadvantages. Inductive headphones are typically more secure from interference, as they operate on a principle that is less susceptible to environmental factors. However, the limitation of fixed installation makes them less versatile compared to infrared headphones, which offer greater flexibility and portability.Because of the transmitter circuit of the inductive headphone must installed on the room wall or on the ceiling, so the inductive headphone can not be used outdoor, this is the main weak point of the inductive headphone. But the infrared rays wireless headphone is not in this case, for the flexible infrared rays transmitter circuit, it can be used in electro..
🔗 External reference