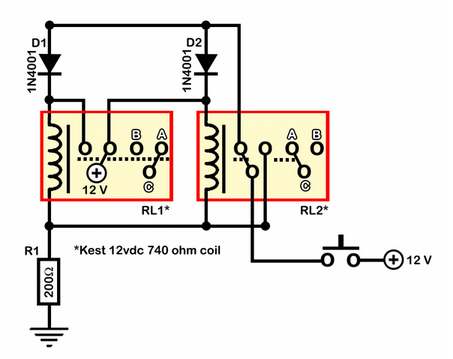
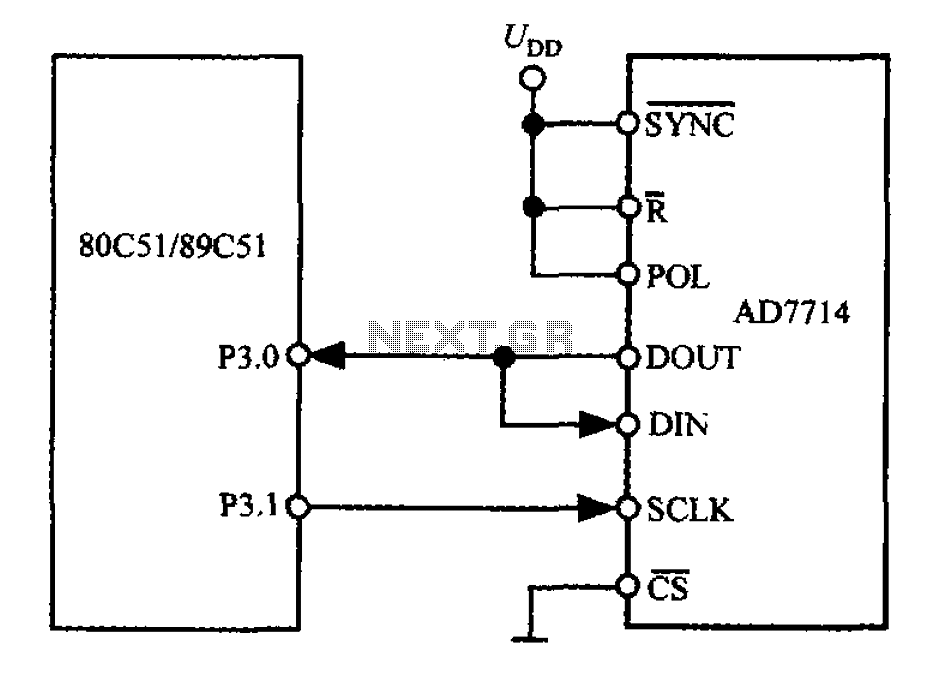
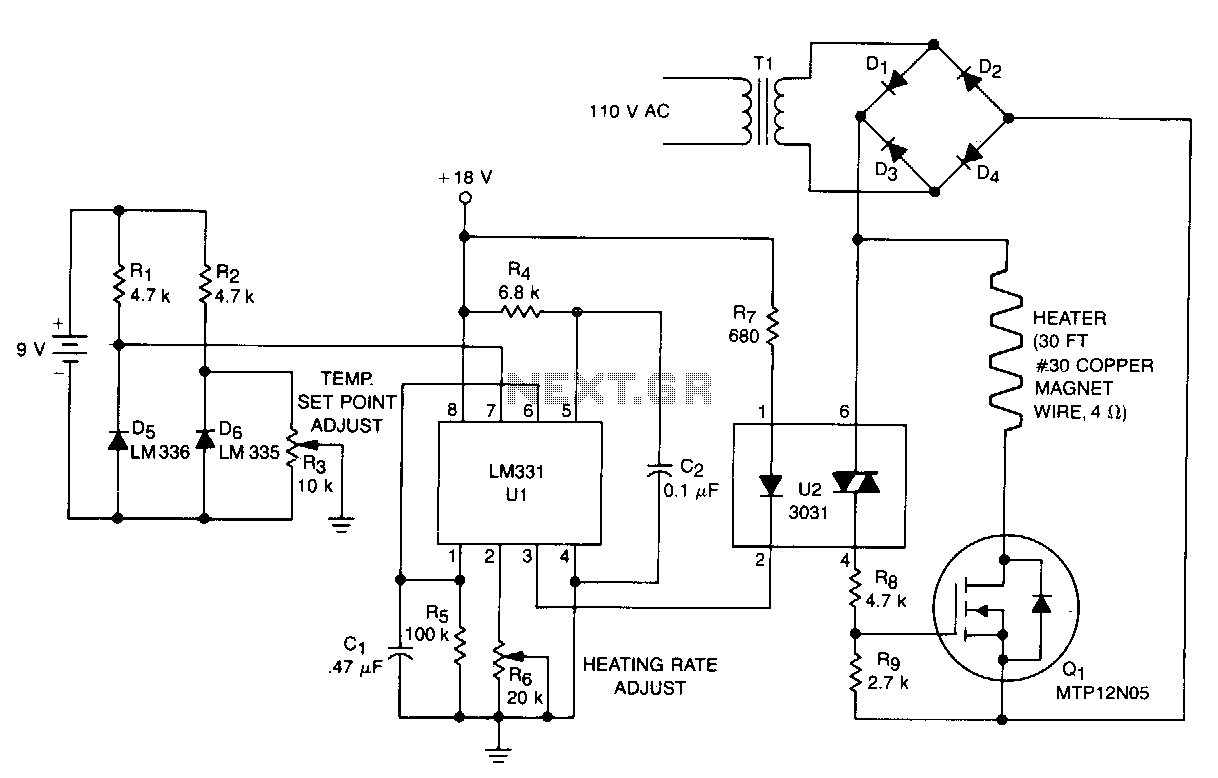
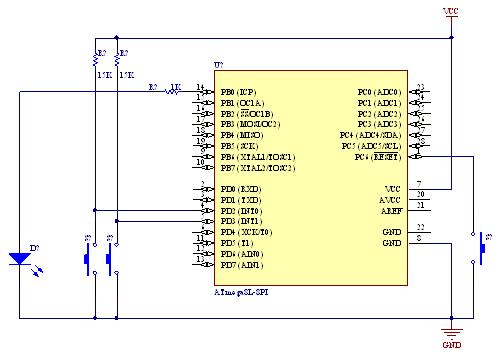
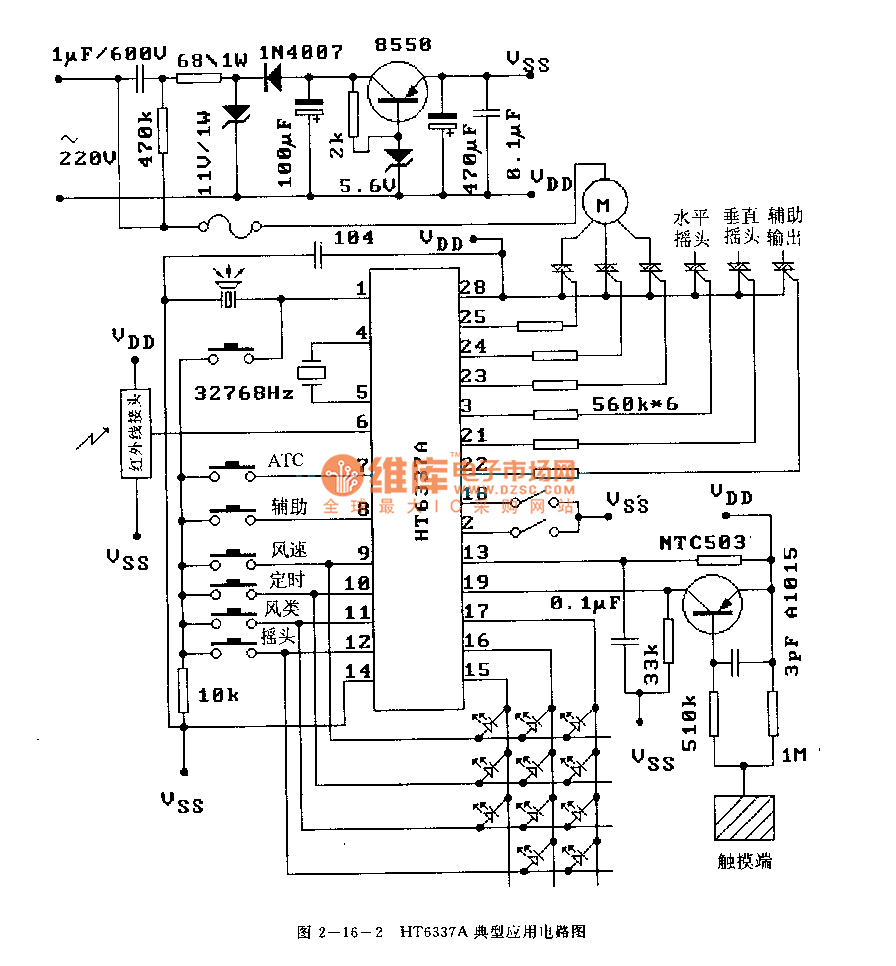
RF Based Wireless Remote Control Switch
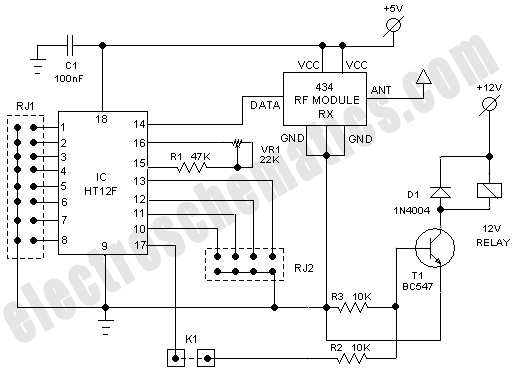
It is often necessary to control electrical appliances remotely, even when there is no direct line of sight between the transmitter and receiver.
In modern electronic applications, remote control systems are increasingly utilized for various purposes, including home automation, industrial control, and consumer electronics. These systems typically consist of a transmitter, which sends control signals, and a receiver, which executes the commands to operate the connected devices.
The transmitter can be designed using a microcontroller or a dedicated remote control IC, which encodes the control signals into a suitable format for transmission, such as infrared (IR), radio frequency (RF), or even Bluetooth. When using IR, the transmitter emits modulated light signals that are detected by the receiver's photodiode or phototransistor. In contrast, RF systems utilize radio waves to transmit signals over greater distances and through obstacles, making them ideal for applications requiring non-line-of-sight operation.
The receiver, which can also incorporate a microcontroller or dedicated IC, demodulates the incoming signals and translates them into actionable commands. These commands can then be used to control various types of electrical appliances, such as lights, fans, or motors, through relay or transistor switching circuits.
In addition to basic functionality, advanced remote control systems may include features such as feedback mechanisms, allowing the user to receive status updates from the controlled devices, and security protocols to prevent unauthorized access. Overall, the design and implementation of such systems require careful consideration of factors such as range, power consumption, and signal integrity to ensure reliable operation in all intended environments.It is often required to switch electrical appliances from a distance without being a direct line of sight between the transmitter and receiver. As you may.. 🔗 External reference
In modern electronic applications, remote control systems are increasingly utilized for various purposes, including home automation, industrial control, and consumer electronics. These systems typically consist of a transmitter, which sends control signals, and a receiver, which executes the commands to operate the connected devices.
The transmitter can be designed using a microcontroller or a dedicated remote control IC, which encodes the control signals into a suitable format for transmission, such as infrared (IR), radio frequency (RF), or even Bluetooth. When using IR, the transmitter emits modulated light signals that are detected by the receiver's photodiode or phototransistor. In contrast, RF systems utilize radio waves to transmit signals over greater distances and through obstacles, making them ideal for applications requiring non-line-of-sight operation.
The receiver, which can also incorporate a microcontroller or dedicated IC, demodulates the incoming signals and translates them into actionable commands. These commands can then be used to control various types of electrical appliances, such as lights, fans, or motors, through relay or transistor switching circuits.
In addition to basic functionality, advanced remote control systems may include features such as feedback mechanisms, allowing the user to receive status updates from the controlled devices, and security protocols to prevent unauthorized access. Overall, the design and implementation of such systems require careful consideration of factors such as range, power consumption, and signal integrity to ensure reliable operation in all intended environments.It is often required to switch electrical appliances from a distance without being a direct line of sight between the transmitter and receiver. As you may.. 🔗 External reference