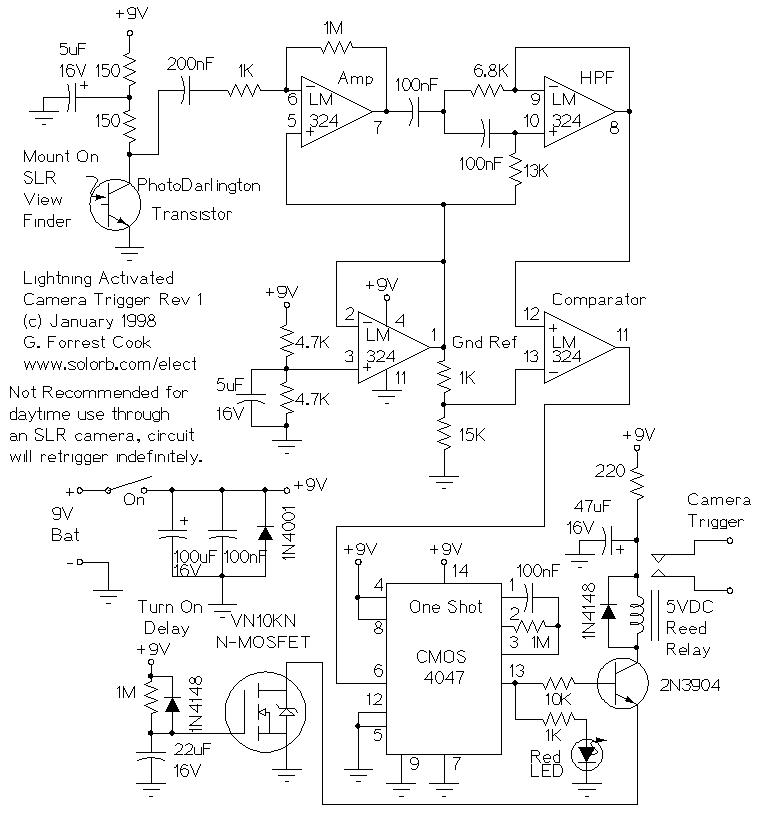
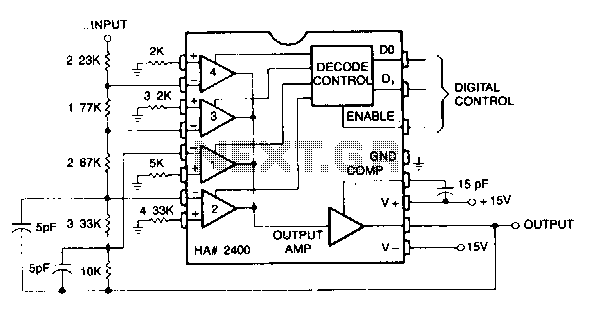
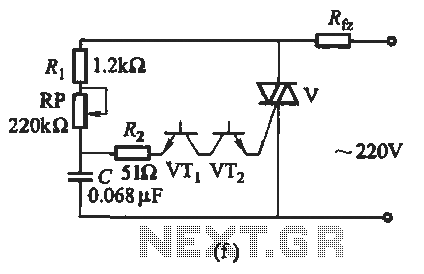
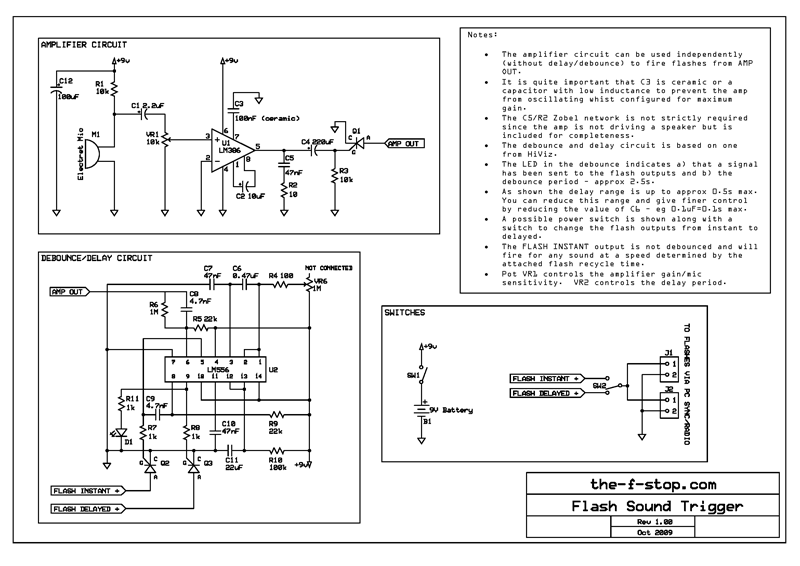
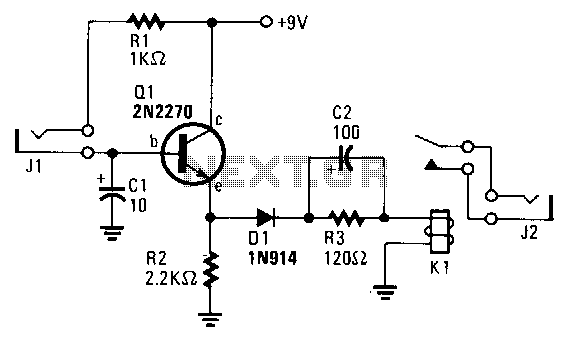
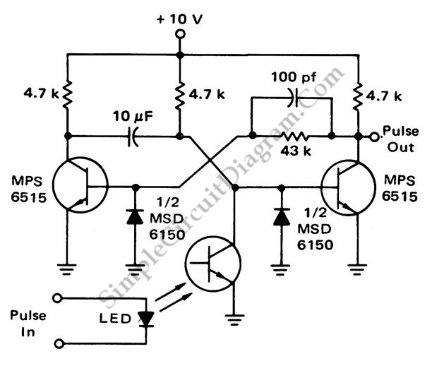
Schmitt trigger with programmable hysteresis
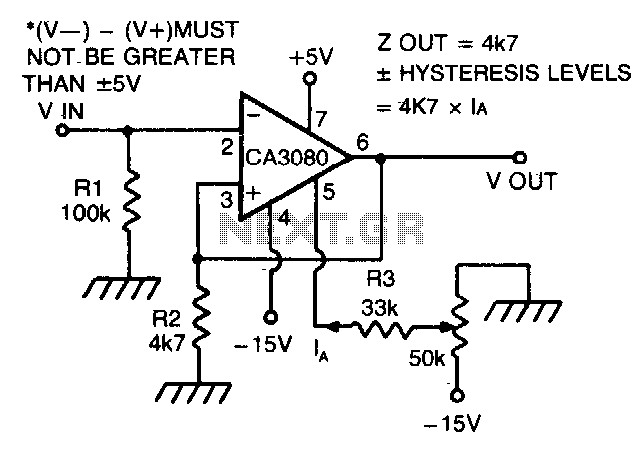
The CA 3088 is utilized as a versatile Schmitt trigger. The magnitude of the hysteresis levels is determined by the current (Ia) flowing out of the amplifier's output and through resistor R2. An increase in Ia results in an increase in hysteresis, and conversely, a decrease in Ia results in a decrease in hysteresis. Furthermore, the positive and negative hysteresis levels are symmetrical around 0 V.
The CA 3088 is a dual operational amplifier that can be configured to function as a Schmitt trigger, which is a type of comparator circuit with hysteresis. Hysteresis is a property that prevents the circuit from responding to small fluctuations or noise in the input signal, thereby providing stable switching behavior. The hysteresis levels are defined by the feedback network, which typically includes resistors that determine the threshold voltages for switching.
In this configuration, Ia represents the output current from the amplifier, which flows through resistor R2 and impacts the feedback loop. The feedback network, composed of resistors R1 and R2, sets the upper and lower threshold voltages for the input signal. By adjusting R2, the designer can fine-tune the amount of hysteresis, allowing for greater control over the circuit's response to varying input conditions.
The symmetrical nature of the hysteresis levels about 0 V indicates that both the positive and negative thresholds are equidistant from the zero voltage level. This characteristic is beneficial in applications where balanced switching behavior is required, such as in digital signal processing or waveform shaping.
In practical applications, the CA 3088 Schmitt trigger can be employed in various circuits, including oscillators, timers, and pulse-width modulation systems. The ability to modify the hysteresis levels through Ia and the resistor values makes it a flexible choice for designing reliable and noise-immune electronic systems.CA 3088 is used as a versatile Schmitt trigger. The size of the hysteresis levels is determined by Ia that flows out of the amplifier"s output and through R2. Increasing Ia increases hysteresis and vice versa The positive and negative hysteresis levels are symmetrical about 0 V. 🔗 External reference
The CA 3088 is a dual operational amplifier that can be configured to function as a Schmitt trigger, which is a type of comparator circuit with hysteresis. Hysteresis is a property that prevents the circuit from responding to small fluctuations or noise in the input signal, thereby providing stable switching behavior. The hysteresis levels are defined by the feedback network, which typically includes resistors that determine the threshold voltages for switching.
In this configuration, Ia represents the output current from the amplifier, which flows through resistor R2 and impacts the feedback loop. The feedback network, composed of resistors R1 and R2, sets the upper and lower threshold voltages for the input signal. By adjusting R2, the designer can fine-tune the amount of hysteresis, allowing for greater control over the circuit's response to varying input conditions.
The symmetrical nature of the hysteresis levels about 0 V indicates that both the positive and negative thresholds are equidistant from the zero voltage level. This characteristic is beneficial in applications where balanced switching behavior is required, such as in digital signal processing or waveform shaping.
In practical applications, the CA 3088 Schmitt trigger can be employed in various circuits, including oscillators, timers, and pulse-width modulation systems. The ability to modify the hysteresis levels through Ia and the resistor values makes it a flexible choice for designing reliable and noise-immune electronic systems.CA 3088 is used as a versatile Schmitt trigger. The size of the hysteresis levels is determined by Ia that flows out of the amplifier"s output and through R2. Increasing Ia increases hysteresis and vice versa The positive and negative hysteresis levels are symmetrical about 0 V. 🔗 External reference