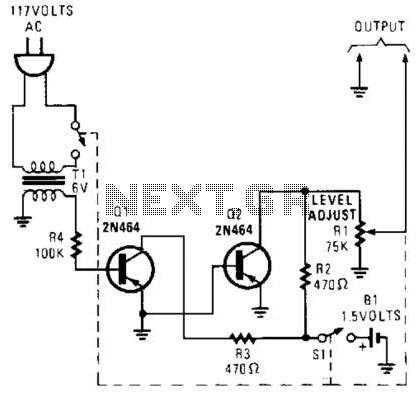
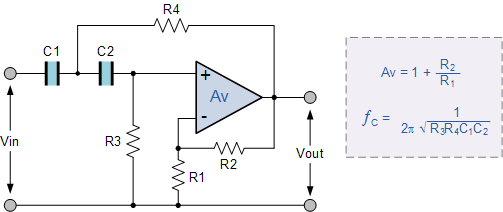
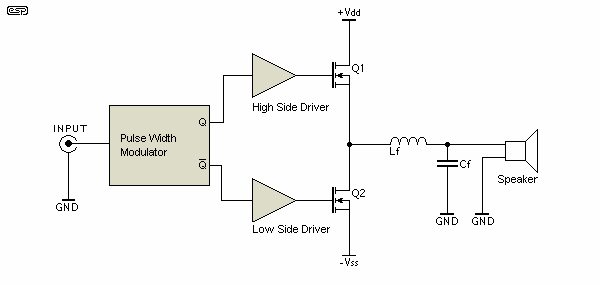
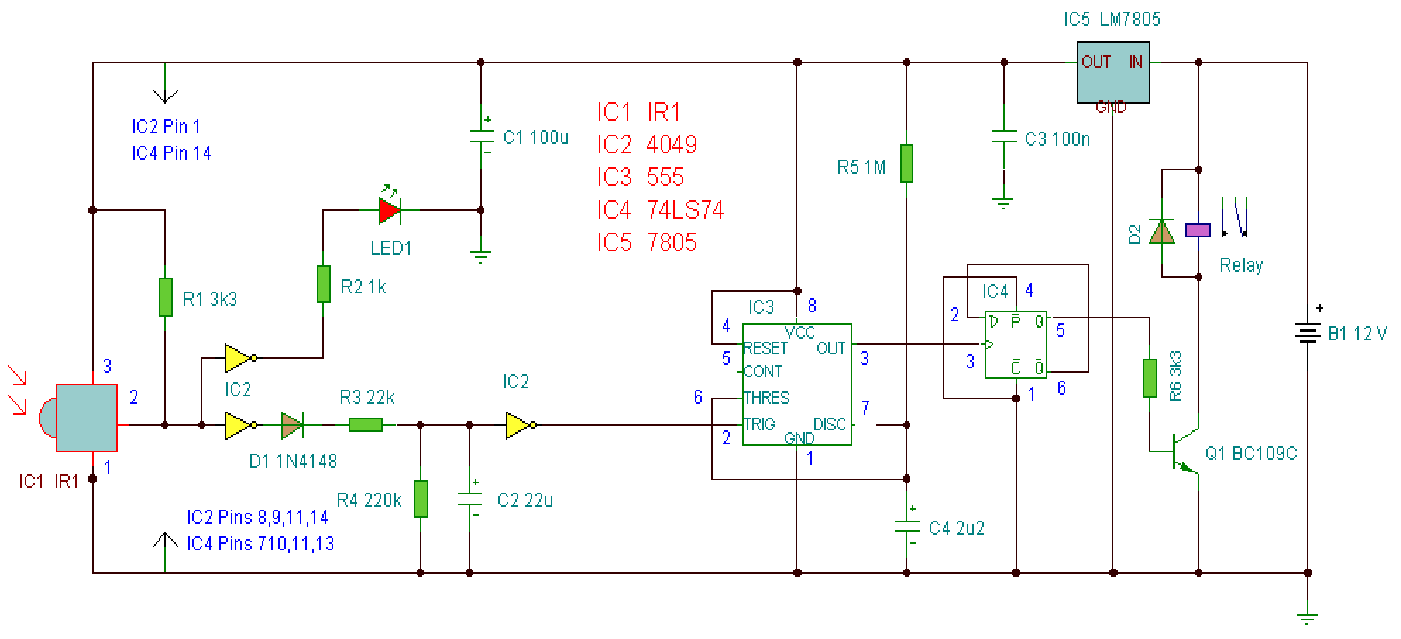
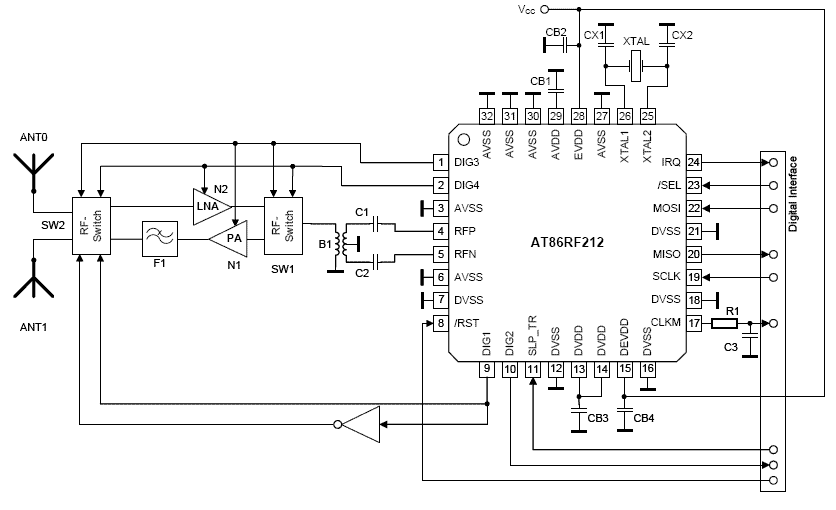
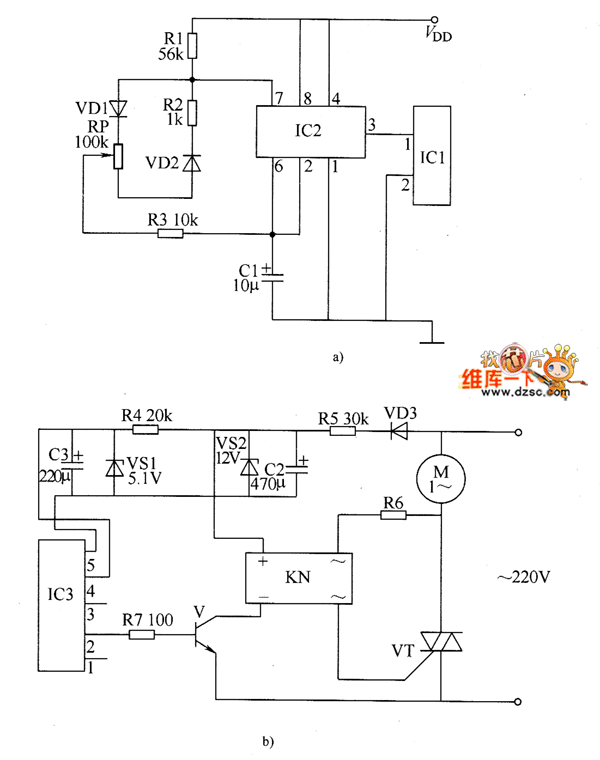
Second-order active band stop filter circuit
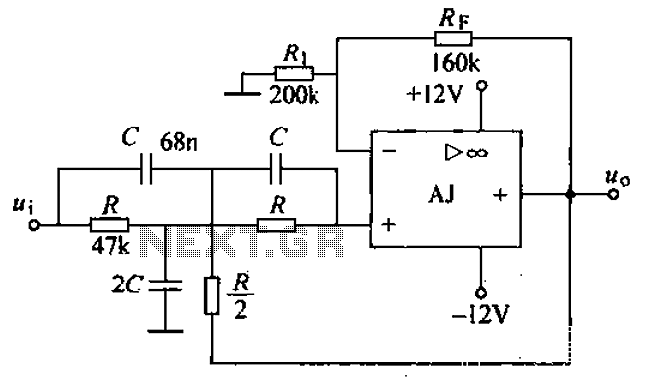
A band-stop filter (BSF) utilizing an integrated operational amplifier is designed to suppress signals within a specific frequency band, allowing signals outside this band to pass with minimal attenuation. This configuration is achieved through a two-stage network, which employs a T-phase ratio arithmetic circuit to form a basic second-order active band-stop filter. The filter is represented in the accompanying figure, which illustrates the integrated operational amplifier configuration using a dual op-amp setup.
The band-stop filter (BSF) is a critical component in various electronic applications where it is necessary to eliminate unwanted frequencies while preserving the integrity of other signals. The design typically consists of a combination of resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers that work together to create a notch in the frequency response at the desired frequency range.
In this configuration, the operational amplifier serves as the active element, providing gain and allowing for precise control over the filter characteristics. The dual op-amp arrangement enhances the filter's performance by enabling the implementation of more complex filtering techniques, such as feedback and feedforward paths, which can improve stability and selectivity.
The two-stage network in the band-stop filter consists of a series of reactive components that define the filter's cutoff frequencies and the depth of attenuation at the notch frequency. The T-phase ratio arithmetic circuit plays a vital role in determining the phase response of the filter, ensuring that the output maintains the desired characteristics over the specified frequency range.
Overall, the integrated operational amplifier band-stop filter is an essential tool in signal processing, audio engineering, and communication systems, where it is crucial to eliminate specific interference while allowing other signals to pass through unaffected. The design's effectiveness is largely dependent on the precise selection of component values and the configuration of the operational amplifiers used in the circuit. Band-stop filter (BEF) integrated operational amplifier, such electrical road performance and a bandpass filter contrary, that in a certain band, the signal can not be (or has been greatly attenuated or suppressed), while in the remaining frequency Fan Wai, signals can be passed. After two-plus network level T-phase ratio arithmetic circuit, it constitutes the basic second-order active band-stop filter BEF.
Band stop filter as shown in FIG. FIG integrated operational amplifier AJ dual op amp
The band-stop filter (BSF) is a critical component in various electronic applications where it is necessary to eliminate unwanted frequencies while preserving the integrity of other signals. The design typically consists of a combination of resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers that work together to create a notch in the frequency response at the desired frequency range.
In this configuration, the operational amplifier serves as the active element, providing gain and allowing for precise control over the filter characteristics. The dual op-amp arrangement enhances the filter's performance by enabling the implementation of more complex filtering techniques, such as feedback and feedforward paths, which can improve stability and selectivity.
The two-stage network in the band-stop filter consists of a series of reactive components that define the filter's cutoff frequencies and the depth of attenuation at the notch frequency. The T-phase ratio arithmetic circuit plays a vital role in determining the phase response of the filter, ensuring that the output maintains the desired characteristics over the specified frequency range.
Overall, the integrated operational amplifier band-stop filter is an essential tool in signal processing, audio engineering, and communication systems, where it is crucial to eliminate specific interference while allowing other signals to pass through unaffected. The design's effectiveness is largely dependent on the precise selection of component values and the configuration of the operational amplifiers used in the circuit. Band-stop filter (BEF) integrated operational amplifier, such electrical road performance and a bandpass filter contrary, that in a certain band, the signal can not be (or has been greatly attenuated or suppressed), while in the remaining frequency Fan Wai, signals can be passed. After two-plus network level T-phase ratio arithmetic circuit, it constitutes the basic second-order active band-stop filter BEF.
Band stop filter as shown in FIG. FIG integrated operational amplifier AJ dual op amp