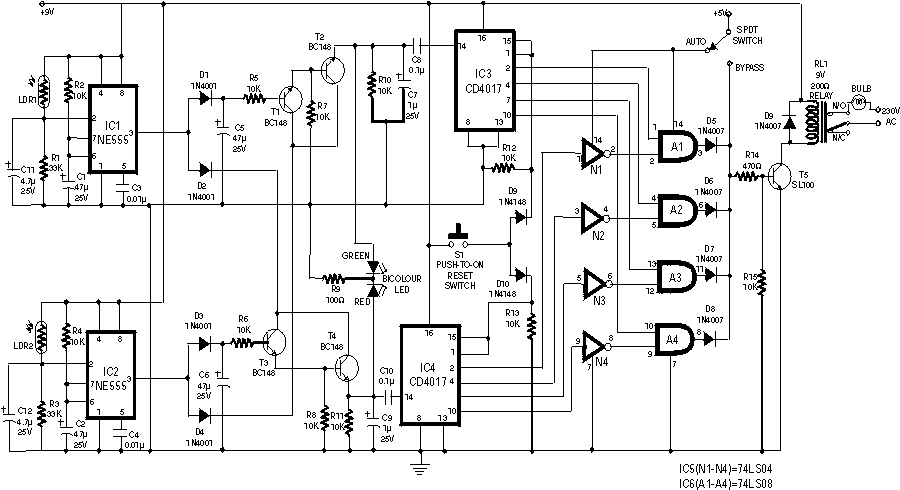
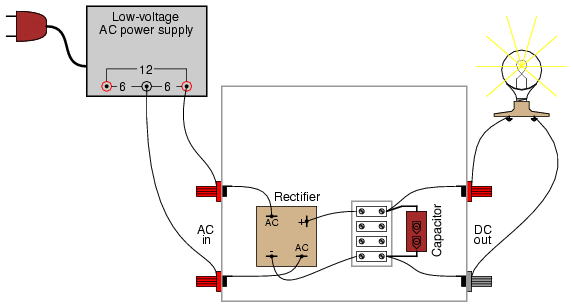
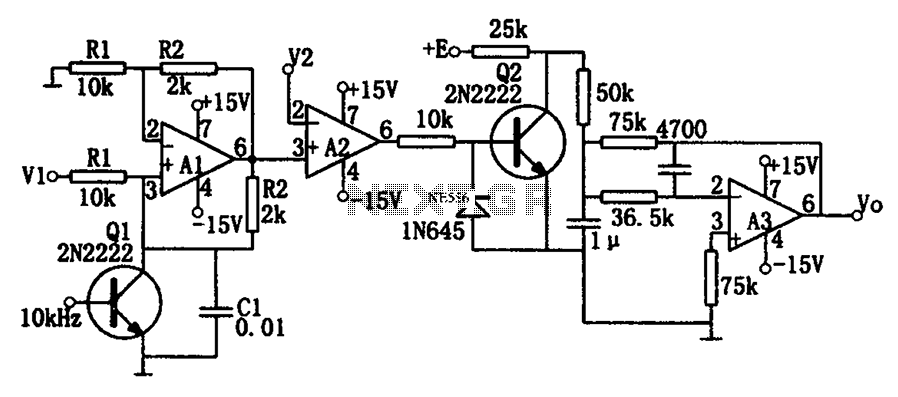
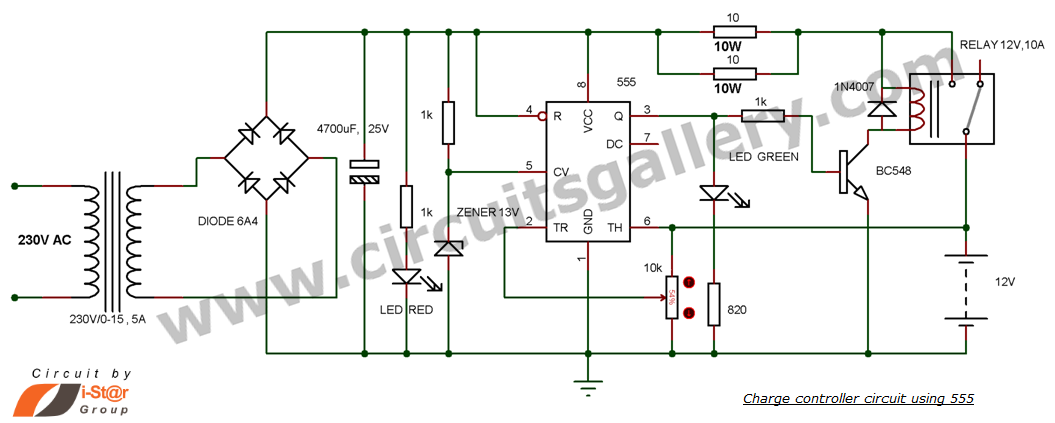
60Hz Square-Wave Generator Circuit
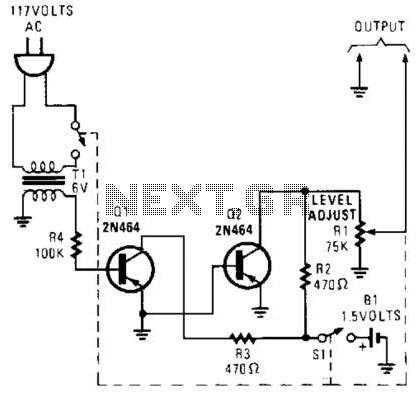
This generator circuit utilizes an overdriven amplifier to generate a 60 Hz square wave from the 60 Hz AC line. The circuit is suitable for line-operated applications as a clock source.
The generator circuit operates by leveraging an overdriven amplifier configuration, which is capable of producing a square wave output. The input to the circuit is derived from the standard 60 Hz AC line voltage, which is a common frequency for electrical power distribution in many regions. The overdriven amplifier takes this input and amplifies it beyond its linear operational range, resulting in a clipped output that approximates a square wave.
In practical applications, this square wave output can serve as a reliable clock source for various digital circuits, timing devices, and synchronous systems. The circuit may include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to stabilize the output waveform and improve its characteristics, ensuring that the square wave maintains its desired frequency and amplitude.
It is important to note that the performance of the circuit can be affected by external factors such as load impedance and power supply variations. Therefore, careful design considerations should be taken into account to ensure the circuit operates effectively in the intended application. Overall, this generator circuit is a versatile solution for generating clock signals in line-operated electronic systems. This generator circuit uses an overdriven amplifier to produce a 60-1 Iz square wave from the 60-Hz ac line. The circuit can be used in line- operated applications as a clock source. 🔗 External reference
The generator circuit operates by leveraging an overdriven amplifier configuration, which is capable of producing a square wave output. The input to the circuit is derived from the standard 60 Hz AC line voltage, which is a common frequency for electrical power distribution in many regions. The overdriven amplifier takes this input and amplifies it beyond its linear operational range, resulting in a clipped output that approximates a square wave.
In practical applications, this square wave output can serve as a reliable clock source for various digital circuits, timing devices, and synchronous systems. The circuit may include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to stabilize the output waveform and improve its characteristics, ensuring that the square wave maintains its desired frequency and amplitude.
It is important to note that the performance of the circuit can be affected by external factors such as load impedance and power supply variations. Therefore, careful design considerations should be taken into account to ensure the circuit operates effectively in the intended application. Overall, this generator circuit is a versatile solution for generating clock signals in line-operated electronic systems. This generator circuit uses an overdriven amplifier to produce a 60-1 Iz square wave from the 60-Hz ac line. The circuit can be used in line- operated applications as a clock source. 🔗 External reference