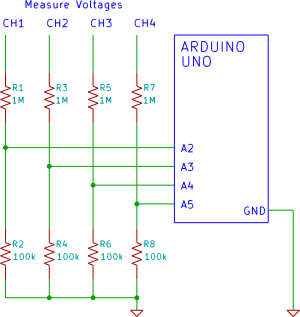
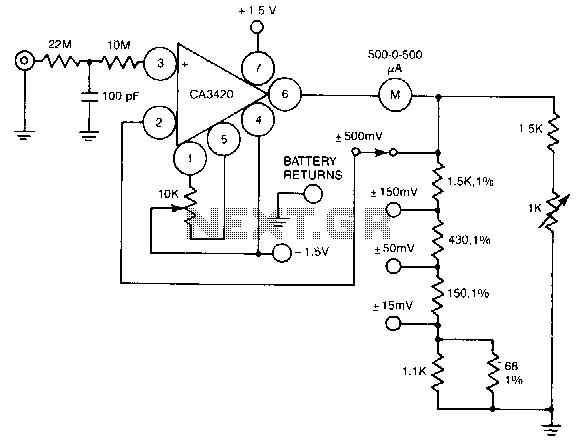
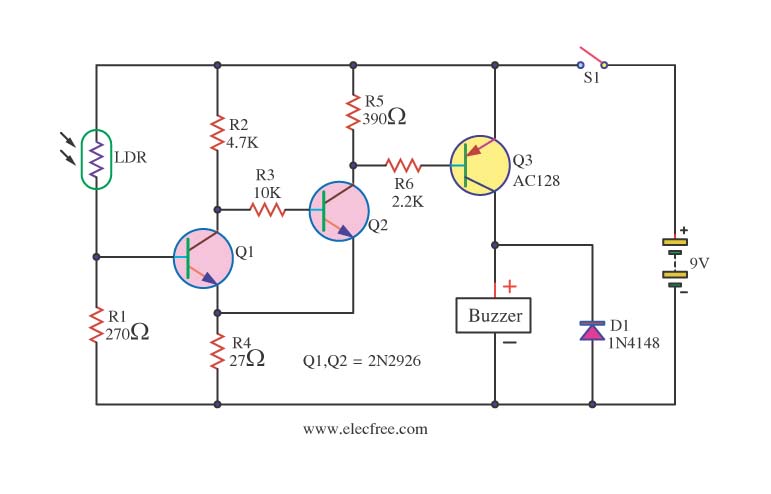
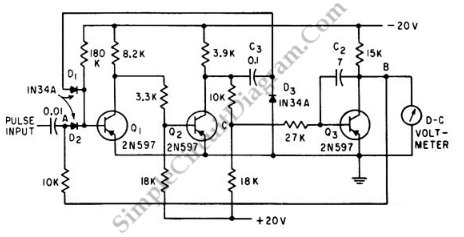
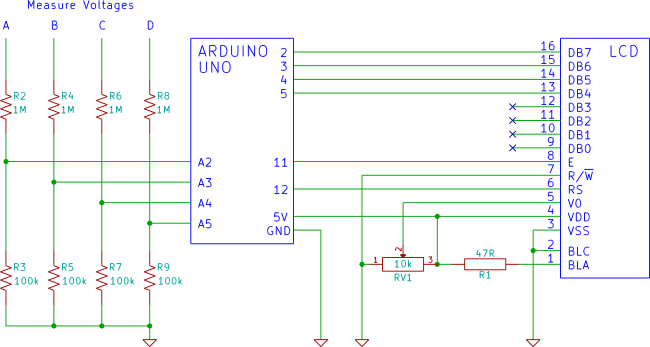
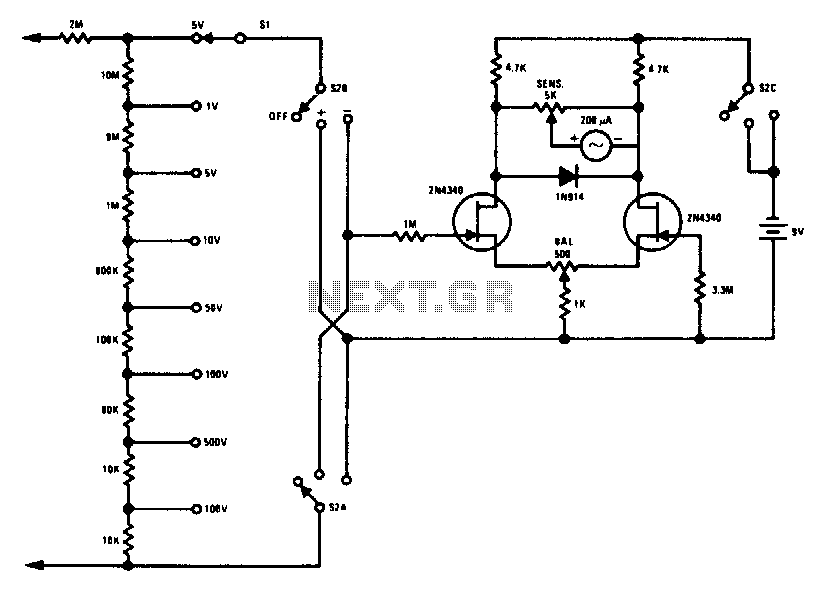
Sensitive rf voltmeter
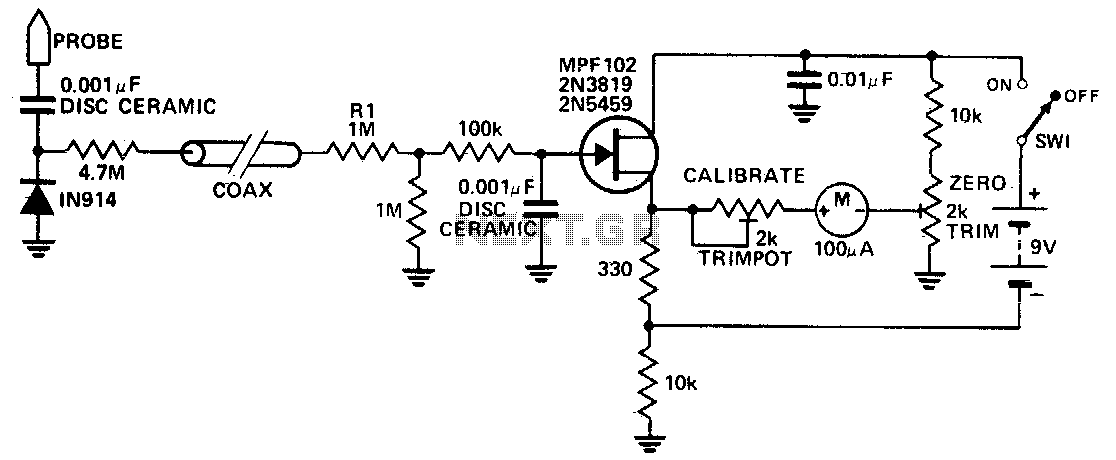
This circuit measures RF voltages exceeding 200 MHz and reaching up to approximately 5 V. The diode must be installed in a remote probe, positioned near the probe tip. The sensitivity is exceptional, allowing for the measurement of voltages below 1 V peak with ease. The unit can be calibrated by connecting the input to a known RF voltage level, such as from a calibrated signal generator, and adjusting the calibration control.
The RF voltage measurement circuit is designed to operate efficiently in high-frequency applications, specifically in the range beyond 200 MHz. The core component of this circuit is a diode, which is strategically placed in a remote probe. This configuration enhances the accuracy and responsiveness of the circuit, as the diode's proximity to the probe tip allows for minimal signal loss and distortion during measurement.
The circuit is capable of detecting very low voltage levels, with a sensitivity threshold that permits the measurement of RF voltages as low as 1 V peak. This makes it particularly useful in environments where signal strength may be weak, such as in certain RF communication applications or in the testing of RF components.
Calibration of the unit is straightforward, involving the connection of the probe input to a known RF voltage source, typically a calibrated signal generator. This allows for precise adjustments to be made using the calibration control, ensuring that the readings from the circuit are accurate and reliable. Proper calibration is essential for maintaining the integrity of measurements, especially in critical applications where precise voltage levels are necessary for effective performance.
Overall, this circuit design provides a robust solution for measuring high-frequency RF voltages, combining sensitivity, ease of calibration, and effective placement of components to achieve high performance in a variety of electronic testing scenarios.This circuit measures RF voltages beyond 200 MHz and up to about 5 V. The diode should be mounted in a remote probe, close to the probe tip. Sensitivity is excellent and voltages less than 1 V peak can be easily measured The unit can be calibrated by connecting the input to a known level of RF voltage, such as a calibrated signal generator, and setting the calibrate control. 🔗 External reference
The RF voltage measurement circuit is designed to operate efficiently in high-frequency applications, specifically in the range beyond 200 MHz. The core component of this circuit is a diode, which is strategically placed in a remote probe. This configuration enhances the accuracy and responsiveness of the circuit, as the diode's proximity to the probe tip allows for minimal signal loss and distortion during measurement.
The circuit is capable of detecting very low voltage levels, with a sensitivity threshold that permits the measurement of RF voltages as low as 1 V peak. This makes it particularly useful in environments where signal strength may be weak, such as in certain RF communication applications or in the testing of RF components.
Calibration of the unit is straightforward, involving the connection of the probe input to a known RF voltage source, typically a calibrated signal generator. This allows for precise adjustments to be made using the calibration control, ensuring that the readings from the circuit are accurate and reliable. Proper calibration is essential for maintaining the integrity of measurements, especially in critical applications where precise voltage levels are necessary for effective performance.
Overall, this circuit design provides a robust solution for measuring high-frequency RF voltages, combining sensitivity, ease of calibration, and effective placement of components to achieve high performance in a variety of electronic testing scenarios.This circuit measures RF voltages beyond 200 MHz and up to about 5 V. The diode should be mounted in a remote probe, close to the probe tip. Sensitivity is excellent and voltages less than 1 V peak can be easily measured The unit can be calibrated by connecting the input to a known level of RF voltage, such as a calibrated signal generator, and setting the calibrate control. 🔗 External reference