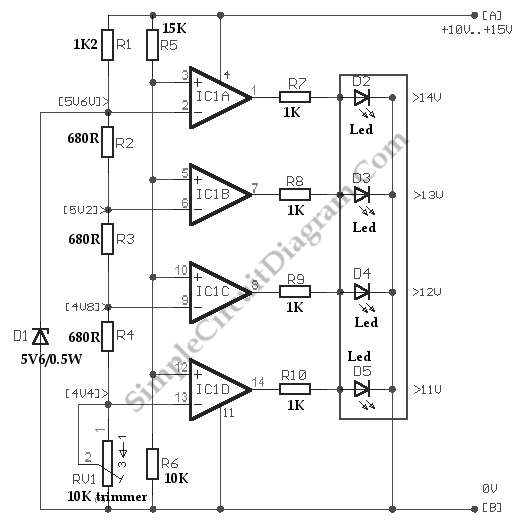
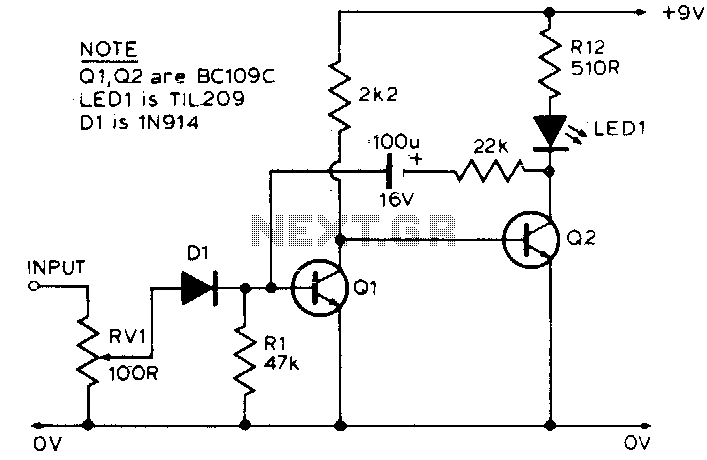
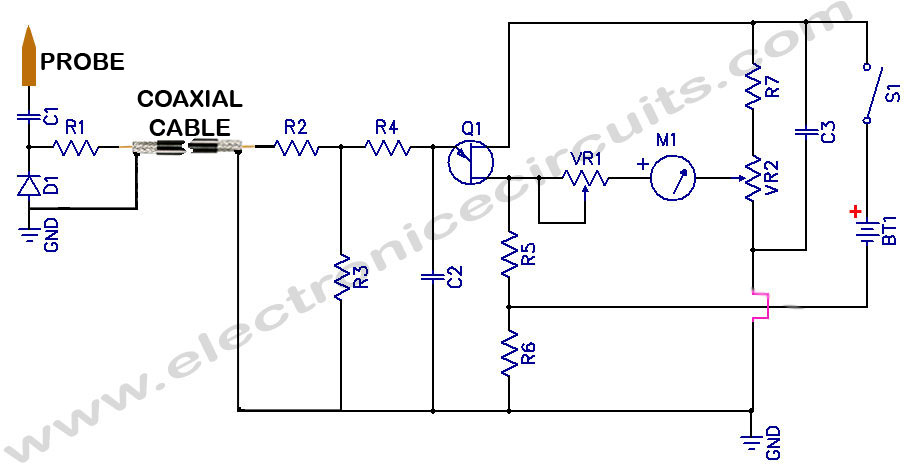
Peak (Pulse) Voltmeter
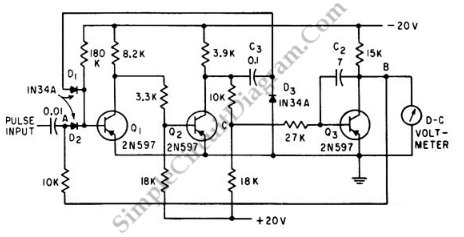
This is a Peak Voltmeter circuit. This circuit can be viewed as a pulse stretcher, which captures fast pulse signals to be measured by a slow response voltmeter.
The Peak Voltmeter circuit is designed to accurately measure the peak voltage of fast pulse signals that would typically exceed the response time of standard voltmeters. The core functionality of this circuit is to stretch the duration of the pulse, allowing a slower voltmeter to register the peak value effectively.
The circuit typically consists of a diode, a capacitor, and a resistor. The diode is oriented to allow current flow only during the positive half-cycle of the pulse signal, effectively capturing the peak voltage. When the pulse arrives, the diode conducts, charging the capacitor to the peak voltage level. The resistor is used to discharge the capacitor slowly, providing a time constant that allows the voltmeter to display the peak value accurately.
In practical applications, the choice of the capacitor and resistor values is crucial. The time constant, determined by the product of the resistor (R) and capacitor (C) values (τ = R × C), must be sufficiently large to ensure that the capacitor retains the peak voltage long enough for the voltmeter to take a reading. This ensures that even if the input signal is a rapid series of pulses, the voltmeter can still provide an accurate peak measurement.
Additionally, the circuit may include an operational amplifier to buffer the voltage across the capacitor, improving the accuracy and stability of the measurement. The output can be connected to an analog or digital voltmeter, depending on the specific application requirements.
Overall, the Peak Voltmeter circuit is a vital tool in electronics, particularly in environments where quick voltage spikes are common, such as in power electronics, communication systems, and signal processing.This is a Peak Voltmeter circuit. This circuit can be viewed as a pulse stretcher, which catch fast pulse signal to be measured by a slow response voltmeter.. 🔗 External reference
The Peak Voltmeter circuit is designed to accurately measure the peak voltage of fast pulse signals that would typically exceed the response time of standard voltmeters. The core functionality of this circuit is to stretch the duration of the pulse, allowing a slower voltmeter to register the peak value effectively.
The circuit typically consists of a diode, a capacitor, and a resistor. The diode is oriented to allow current flow only during the positive half-cycle of the pulse signal, effectively capturing the peak voltage. When the pulse arrives, the diode conducts, charging the capacitor to the peak voltage level. The resistor is used to discharge the capacitor slowly, providing a time constant that allows the voltmeter to display the peak value accurately.
In practical applications, the choice of the capacitor and resistor values is crucial. The time constant, determined by the product of the resistor (R) and capacitor (C) values (τ = R × C), must be sufficiently large to ensure that the capacitor retains the peak voltage long enough for the voltmeter to take a reading. This ensures that even if the input signal is a rapid series of pulses, the voltmeter can still provide an accurate peak measurement.
Additionally, the circuit may include an operational amplifier to buffer the voltage across the capacitor, improving the accuracy and stability of the measurement. The output can be connected to an analog or digital voltmeter, depending on the specific application requirements.
Overall, the Peak Voltmeter circuit is a vital tool in electronics, particularly in environments where quick voltage spikes are common, such as in power electronics, communication systems, and signal processing.This is a Peak Voltmeter circuit. This circuit can be viewed as a pulse stretcher, which catch fast pulse signal to be measured by a slow response voltmeter.. 🔗 External reference