Sensor-Activated Relay Pulser Circuit
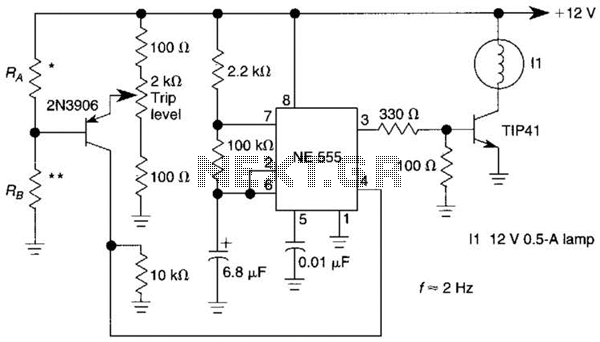
A sensor activates transistor Q1 to turn on the low-frequency 555 oscillator, which generates pulses to control LAMP II. The sensor may respond to variations in light or temperature. Either resistor RA or RB can function as the sensor, depending on the application. A reduction in RB or an increase in RA will result in the NE555 flashing.
The circuit utilizes a low-frequency NE555 timer configured in astable mode to generate a square wave output that drives LAMP II. The sensor's operation is critical, as it determines the conditions under which the NE555 timer activates. The choice of RA or RB as the sensing element allows for flexibility; either can be a thermistor for temperature sensitivity or a photoresistor for light sensitivity.
In this configuration, RA and RB should not exceed 100 kΩ to ensure proper functioning of the oscillator. The values of these resistors will influence the timing characteristics of the NE555, specifically the frequency and duty cycle of the output signal. The pulse width and frequency can be adjusted by varying the resistance values and the capacitance connected to the timing pins of the NE555.
When the sensor detects a decrease in resistance (for instance, a rise in temperature) at RB or an increase in resistance at RA (like a decrease in ambient light), the NE555 timer is triggered to output a pulse. This output pulse activates Q1, allowing current to flow through LAMP II, thereby illuminating it. The design can be further refined by incorporating additional components such as diodes for flyback protection, capacitors for noise filtering, and potentiometers for fine-tuning the sensitivity of the sensor.
Overall, this circuit provides a simple yet effective means of controlling a lamp based on environmental changes, showcasing the versatility of the NE555 timer in various applications. A sensor turns on Ql to activate the low-frequency 555 oscillator, which pulses LAMP II. Sensor may be sensitive to changes in light or temperature. Either RA or RB can be sensors, as desired. A decrease in RB or an increase in RA will cause the NE555 to flash M. fl and RB should be 100 kohm max. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a low-frequency NE555 timer configured in astable mode to generate a square wave output that drives LAMP II. The sensor's operation is critical, as it determines the conditions under which the NE555 timer activates. The choice of RA or RB as the sensing element allows for flexibility; either can be a thermistor for temperature sensitivity or a photoresistor for light sensitivity.
In this configuration, RA and RB should not exceed 100 kΩ to ensure proper functioning of the oscillator. The values of these resistors will influence the timing characteristics of the NE555, specifically the frequency and duty cycle of the output signal. The pulse width and frequency can be adjusted by varying the resistance values and the capacitance connected to the timing pins of the NE555.
When the sensor detects a decrease in resistance (for instance, a rise in temperature) at RB or an increase in resistance at RA (like a decrease in ambient light), the NE555 timer is triggered to output a pulse. This output pulse activates Q1, allowing current to flow through LAMP II, thereby illuminating it. The design can be further refined by incorporating additional components such as diodes for flyback protection, capacitors for noise filtering, and potentiometers for fine-tuning the sensitivity of the sensor.
Overall, this circuit provides a simple yet effective means of controlling a lamp based on environmental changes, showcasing the versatility of the NE555 timer in various applications. A sensor turns on Ql to activate the low-frequency 555 oscillator, which pulses LAMP II. Sensor may be sensitive to changes in light or temperature. Either RA or RB can be sensors, as desired. A decrease in RB or an increase in RA will cause the NE555 to flash M. fl and RB should be 100 kohm max. 🔗 External reference