Cmos Touch Dimmer Circuit

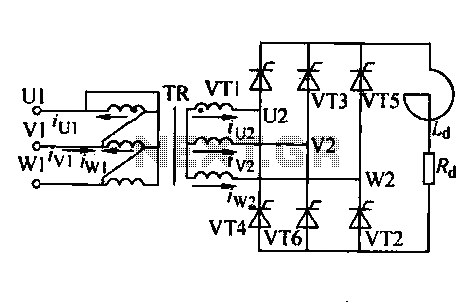
A Siemens SLB0586A IC enables the creation of a straightforward touch-controlled dimmer circuit. This circuit regulates a triac AC switch, allowing control of loads ranging from 10 to 400 W.
The Siemens SLB0586A integrated circuit is designed to facilitate the development of touch-sensitive dimmer circuits for AC loads. The primary function of this IC is to control a triac, which acts as an electronic switch capable of managing alternating current (AC) loads with a power rating between 10 W and 400 W.
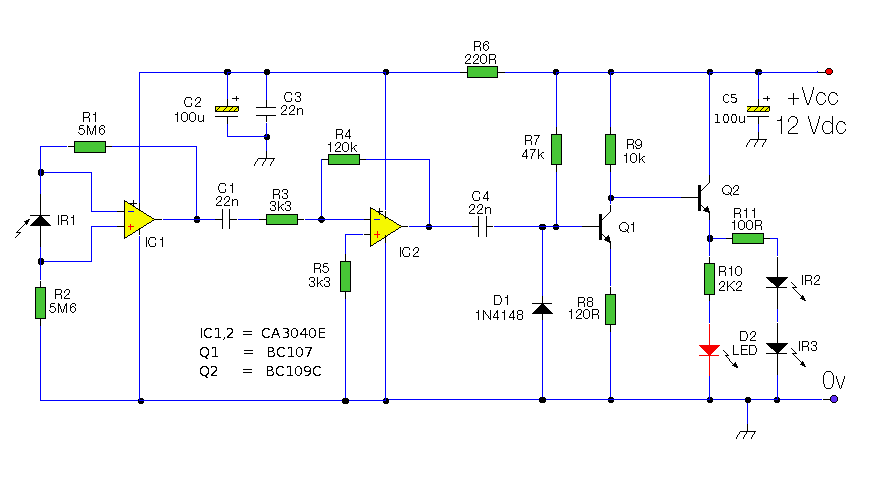
The touch control feature is achieved through a capacitive sensing mechanism integrated within the IC, which detects user input without the need for mechanical switches. This allows for a more durable and aesthetically pleasing design, as there are no moving parts that can wear out over time.
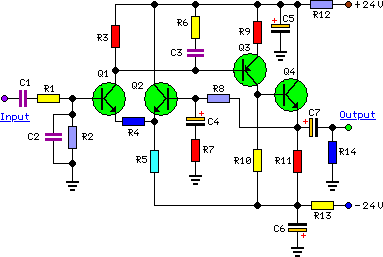
In typical applications, the circuit will consist of the SLB0586A IC, a triac, a zero-cross detection circuit, and additional passive components such as resistors and capacitors. The zero-cross detection is crucial for minimizing electrical noise and ensuring smooth dimming transitions, as it allows the triac to turn on and off at the points where the AC waveform crosses zero volts.
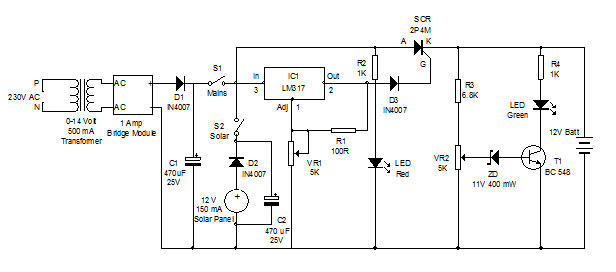
The circuit design can be further enhanced with features such as overcurrent protection, which may involve the integration of additional components like fuses or circuit breakers to safeguard against excessive load conditions. By implementing these safety measures, the reliability and longevity of the dimmer circuit can be significantly improved.
Overall, the Siemens SLB0586A IC provides an efficient solution for creating touch-controlled dimmer circuits suitable for a variety of lighting applications, enhancing user experience through modern touch technology while maintaining high performance in controlling AC loads. A Seimens SLB0586A IC allows the construction of a simple touch-controlled dirrauer circuit. The circuit controls a triac ac switch, which allows control of loads from 10 to 400 W. 🔗 External reference
The Siemens SLB0586A integrated circuit is designed to facilitate the development of touch-sensitive dimmer circuits for AC loads. The primary function of this IC is to control a triac, which acts as an electronic switch capable of managing alternating current (AC) loads with a power rating between 10 W and 400 W.
The touch control feature is achieved through a capacitive sensing mechanism integrated within the IC, which detects user input without the need for mechanical switches. This allows for a more durable and aesthetically pleasing design, as there are no moving parts that can wear out over time.
In typical applications, the circuit will consist of the SLB0586A IC, a triac, a zero-cross detection circuit, and additional passive components such as resistors and capacitors. The zero-cross detection is crucial for minimizing electrical noise and ensuring smooth dimming transitions, as it allows the triac to turn on and off at the points where the AC waveform crosses zero volts.
The circuit design can be further enhanced with features such as overcurrent protection, which may involve the integration of additional components like fuses or circuit breakers to safeguard against excessive load conditions. By implementing these safety measures, the reliability and longevity of the dimmer circuit can be significantly improved.
Overall, the Siemens SLB0586A IC provides an efficient solution for creating touch-controlled dimmer circuits suitable for a variety of lighting applications, enhancing user experience through modern touch technology while maintaining high performance in controlling AC loads. A Seimens SLB0586A IC allows the construction of a simple touch-controlled dirrauer circuit. The circuit controls a triac ac switch, which allows control of loads from 10 to 400 W. 🔗 External reference