Sensor
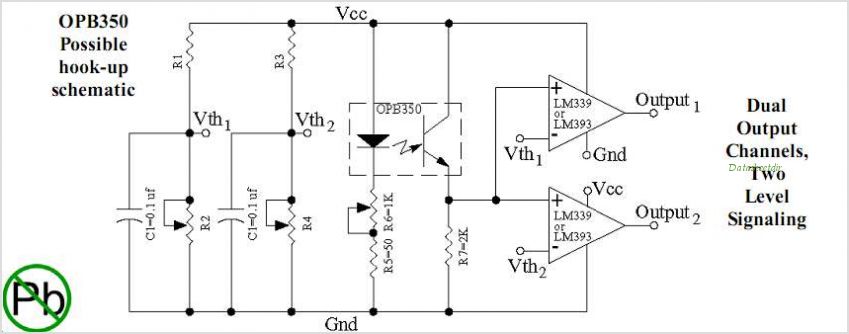
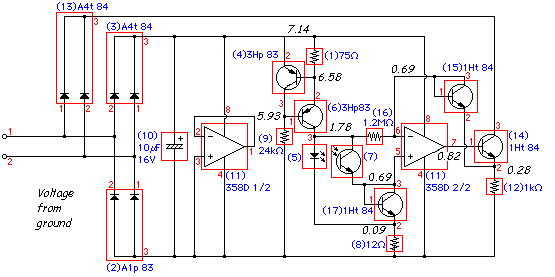
The article "Creating a Line Follower Robot with AVR" is a continuation of a previous article on Line Follower Robots, introducing a new AVR ATMega8535 and providing a block diagram of the Line Follower Robot. The earlier article, "Creating a Line Follower Robot with AVR Part 1," reviews the sensors and components utilized in the Line Follower Robot. Sensors function as the robot's "eyes," enabling it to detect the black line on its path or the absence of it. This capability allows the robot to determine when to turn right, left, or stop. Common sensors include photo reflectors, LDRs (Light Dependent Resistors), photo diodes, and photo transistors, typically mounted on the front of the robot, with two or more positioned beneath it. Additionally, a camera or image sensor may be employed for higher resolution line detection, enhancing the accuracy of the robot's movements. The operational principle of these sensors is straightforward: when the infrared transmitter emits light onto a white surface, the light reflects back to the receiver from the white areas, and the reverse occurs for darker surfaces. This interaction results in a change in the voltage level at the receiver output, which may not align with TTL logic levels. To ensure compatibility with the microcontroller, the sensor voltage must be adjusted to TTL levels, specifically 0-1 volts for logic 0 and 3-5 volts for logic 1. This adjustment can be achieved by incorporating an operational amplifier configured as a comparator. The LM324 IC is suitable for this purpose, as it operates within a VCC range of 5 volts and contains four operational amplifiers, corresponding to the number of sensors used. The sensitivity of the sensor can be adjusted using R9, which sets the reference point for the comparator. The configuration of the line follower robot sensors can be optimized by combining LEDs and photo diodes, ensuring the robot can effectively read the track at high speeds. To enhance the sensor's performance, a voltage comparator using an operational amplifier can be integrated. The line follower robot sensor circuit is equipped with a voltage comparator, ready to be connected to a microcontroller or PIC.
The design of the line follower robot circuit involves several key components that work together to facilitate efficient line tracking. The sensors, positioned strategically on the robot, detect the contrast between the line and the background. The output from these sensors is fed into the operational amplifier, which functions as a comparator to convert the analog signals into digital signals suitable for processing by the microcontroller. This step is crucial, as microcontrollers typically require inputs to be within specific voltage ranges to interpret them correctly.
The choice of the LM324 operational amplifier is beneficial due to its four-channel configuration, allowing multiple sensors to be connected without the need for additional components, thus reducing complexity and potential points of failure. The sensitivity adjustment via R9 is particularly important, as it allows for fine-tuning of the sensor's responsiveness to varying light conditions, which can significantly affect the robot's performance.
In addition to the basic sensor configuration, integrating a camera can further enhance the robot's tracking capabilities, providing a higher-resolution view of the line and enabling more precise navigation. This advanced setup may involve additional processing power and software algorithms to interpret the camera data effectively.
Overall, the line follower robot circuit is a sophisticated integration of hardware and software, where each component plays a vital role in achieving accurate and reliable line tracking. The careful selection of sensors, operational amplifiers, and microcontrollers ensures that the robot can navigate complex paths with agility and precision.The article "Creating a Line Follower Robot with AVR [Censorship]" is a continuation of Line Follower Robot article with a new AVR ATMega8535 samapai phase Line Follower Robot block diagram. In the article "Creating a Line Follower Robot with AVR Part 1 [Sensor]" This is a review of the sensor used on Line Follower Robot, and the components used.
Sensors, can be analogous to the `eye` of a robot that serves to `read` the black line of the track robot or vice versa. So that the robot is able to know when he will turn right, when he turned left and when he stopped. Sensors used are usually photo reflector, LDR (Light Dependent Resistor), Photo Diodes and Photo Transistor - mounted on the front two or more below the line follower robot.
There also are using the camera as a sensor (or image sensor) to a higher-resolution readout line, making more accurate robot motion. The working principle of the sensor is simple, when the transmitter (infrared) emitting light onto a white field, the light will be reflected back to the receiver by the white areas and vice versa.
This gives the change in the voltage level at the receiver output, but it usually changes the voltage can not be accepted as a TTL logic level. To be able to read by the microcontroller, the sensor voltage should be adjusted to TTL voltage level that is 0-1 volts for logic 0 and 3-5 volts for logic 1.
This can be done by installing the operational amplifier is used as a comparator as shown in the picture above. Op Amp is used as a comparator LM324 IC, because IC is able to work at VCC 5 volt range and there are 4 in 1 Op Amp IC corresponding to the number of sensors are used.
The sensitivity of this sensor can be set through R9 which controls the comparator reference point. Line follower robot sensors can be made with a combination between LED and photo diode. Line follower robot sensor configuration is good to be able to read the track with a hard and fast. To make the robot sensor is firm and fast can not merely rely on the ability of photo diodes and LED configurations only. As an alternative to maximize the performance of line follower robot sensors can be added to the voltage comparator with Op-Amp.
sensor circuit line follower robot equipped with a voltage comparator that is ready to be connected to a microcontroller or PIC can use the following series of robot sensor. 🔗 External reference
The design of the line follower robot circuit involves several key components that work together to facilitate efficient line tracking. The sensors, positioned strategically on the robot, detect the contrast between the line and the background. The output from these sensors is fed into the operational amplifier, which functions as a comparator to convert the analog signals into digital signals suitable for processing by the microcontroller. This step is crucial, as microcontrollers typically require inputs to be within specific voltage ranges to interpret them correctly.
The choice of the LM324 operational amplifier is beneficial due to its four-channel configuration, allowing multiple sensors to be connected without the need for additional components, thus reducing complexity and potential points of failure. The sensitivity adjustment via R9 is particularly important, as it allows for fine-tuning of the sensor's responsiveness to varying light conditions, which can significantly affect the robot's performance.
In addition to the basic sensor configuration, integrating a camera can further enhance the robot's tracking capabilities, providing a higher-resolution view of the line and enabling more precise navigation. This advanced setup may involve additional processing power and software algorithms to interpret the camera data effectively.
Overall, the line follower robot circuit is a sophisticated integration of hardware and software, where each component plays a vital role in achieving accurate and reliable line tracking. The careful selection of sensors, operational amplifiers, and microcontrollers ensures that the robot can navigate complex paths with agility and precision.The article "Creating a Line Follower Robot with AVR [Censorship]" is a continuation of Line Follower Robot article with a new AVR ATMega8535 samapai phase Line Follower Robot block diagram. In the article "Creating a Line Follower Robot with AVR Part 1 [Sensor]" This is a review of the sensor used on Line Follower Robot, and the components used.
Sensors, can be analogous to the `eye` of a robot that serves to `read` the black line of the track robot or vice versa. So that the robot is able to know when he will turn right, when he turned left and when he stopped. Sensors used are usually photo reflector, LDR (Light Dependent Resistor), Photo Diodes and Photo Transistor - mounted on the front two or more below the line follower robot.
There also are using the camera as a sensor (or image sensor) to a higher-resolution readout line, making more accurate robot motion. The working principle of the sensor is simple, when the transmitter (infrared) emitting light onto a white field, the light will be reflected back to the receiver by the white areas and vice versa.
This gives the change in the voltage level at the receiver output, but it usually changes the voltage can not be accepted as a TTL logic level. To be able to read by the microcontroller, the sensor voltage should be adjusted to TTL voltage level that is 0-1 volts for logic 0 and 3-5 volts for logic 1.
This can be done by installing the operational amplifier is used as a comparator as shown in the picture above. Op Amp is used as a comparator LM324 IC, because IC is able to work at VCC 5 volt range and there are 4 in 1 Op Amp IC corresponding to the number of sensors are used.
The sensitivity of this sensor can be set through R9 which controls the comparator reference point. Line follower robot sensors can be made with a combination between LED and photo diode. Line follower robot sensor configuration is good to be able to read the track with a hard and fast. To make the robot sensor is firm and fast can not merely rely on the ability of photo diodes and LED configurations only. As an alternative to maximize the performance of line follower robot sensors can be added to the voltage comparator with Op-Amp.
sensor circuit line follower robot equipped with a voltage comparator that is ready to be connected to a microcontroller or PIC can use the following series of robot sensor. 🔗 External reference