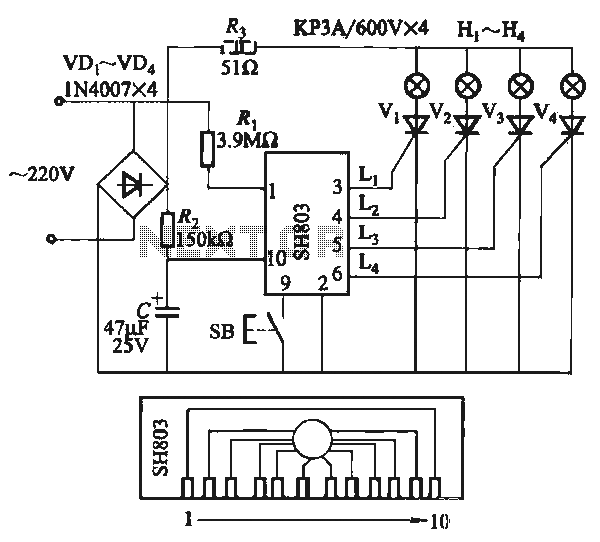
servo circuit
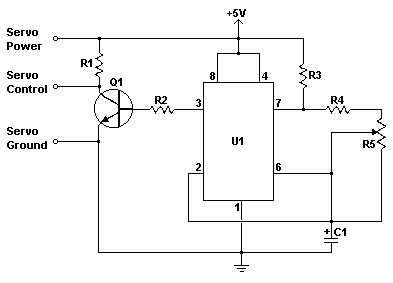
Servo motors are utilized in various applications, including robotics, puppetry, photography, and more. These compact motors can adjust their output shaft to a specified position on command and maintain that position. Most servos offer a range of motion of approximately 210 degrees and can be easily controlled using a simple circuit, as demonstrated here. By employing a 555 timer and a few supporting components, this circuit can manage a servo's full rotation based on the position of a potentiometer. This circuit was initially featured in the Think Tank column of the October 1995 issue of Popular Electronics.
This circuit utilizes a 555 timer in astable mode to generate a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal that controls the servo motor's position. The 555 timer is configured to produce a square wave output, which can be adjusted by varying the resistance of the potentiometer. The duty cycle of the PWM signal determines the angle of the servo motor's shaft, allowing for precise control over its position.
The circuit typically consists of the following components: a 555 timer IC, resistors, a potentiometer, a capacitor, and the servo motor itself. The potentiometer serves as an adjustable input, allowing the user to set the desired position of the servo. The output from the 555 timer is fed into the control wire of the servo, which interprets the PWM signal to position its shaft accordingly.
In practice, when the potentiometer is turned, it alters the resistance in the circuit, which in turn changes the timing of the 555 timer's output. This results in a variation of the pulse width, thus controlling the angle of the servo motor. The capacitor in the circuit helps to stabilize the signal and filter out any noise, ensuring smooth operation.
This type of circuit is advantageous due to its simplicity and low component count, making it accessible for hobbyists and educators. It serves as an excellent introduction to the principles of PWM control and the operation of servo motors, showcasing their versatility in various applications. The original publication in Popular Electronics highlights its relevance and utility in electronics education and practical applications.Servo motors have many uses in everything from robotics to puppetry to photography and beyond. These little motors can position their output shaft to any position on command and hold that position. Most servos have a range of motion to about 210 degrees and thankfully are very easy to control with a simple circuit such as the one presented here.
U sing just a 555 timer and a few support components this circuit can control a servo through it`s full rotation based on the position of a pot. This circuit was originally published in the Think Tank column of the October 1995 issue of Popular Electronics.
🔗 External reference
This circuit utilizes a 555 timer in astable mode to generate a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal that controls the servo motor's position. The 555 timer is configured to produce a square wave output, which can be adjusted by varying the resistance of the potentiometer. The duty cycle of the PWM signal determines the angle of the servo motor's shaft, allowing for precise control over its position.
The circuit typically consists of the following components: a 555 timer IC, resistors, a potentiometer, a capacitor, and the servo motor itself. The potentiometer serves as an adjustable input, allowing the user to set the desired position of the servo. The output from the 555 timer is fed into the control wire of the servo, which interprets the PWM signal to position its shaft accordingly.
In practice, when the potentiometer is turned, it alters the resistance in the circuit, which in turn changes the timing of the 555 timer's output. This results in a variation of the pulse width, thus controlling the angle of the servo motor. The capacitor in the circuit helps to stabilize the signal and filter out any noise, ensuring smooth operation.
This type of circuit is advantageous due to its simplicity and low component count, making it accessible for hobbyists and educators. It serves as an excellent introduction to the principles of PWM control and the operation of servo motors, showcasing their versatility in various applications. The original publication in Popular Electronics highlights its relevance and utility in electronics education and practical applications.Servo motors have many uses in everything from robotics to puppetry to photography and beyond. These little motors can position their output shaft to any position on command and hold that position. Most servos have a range of motion to about 210 degrees and thankfully are very easy to control with a simple circuit such as the one presented here.
U sing just a 555 timer and a few support components this circuit can control a servo through it`s full rotation based on the position of a pot. This circuit was originally published in the Think Tank column of the October 1995 issue of Popular Electronics.
🔗 External reference