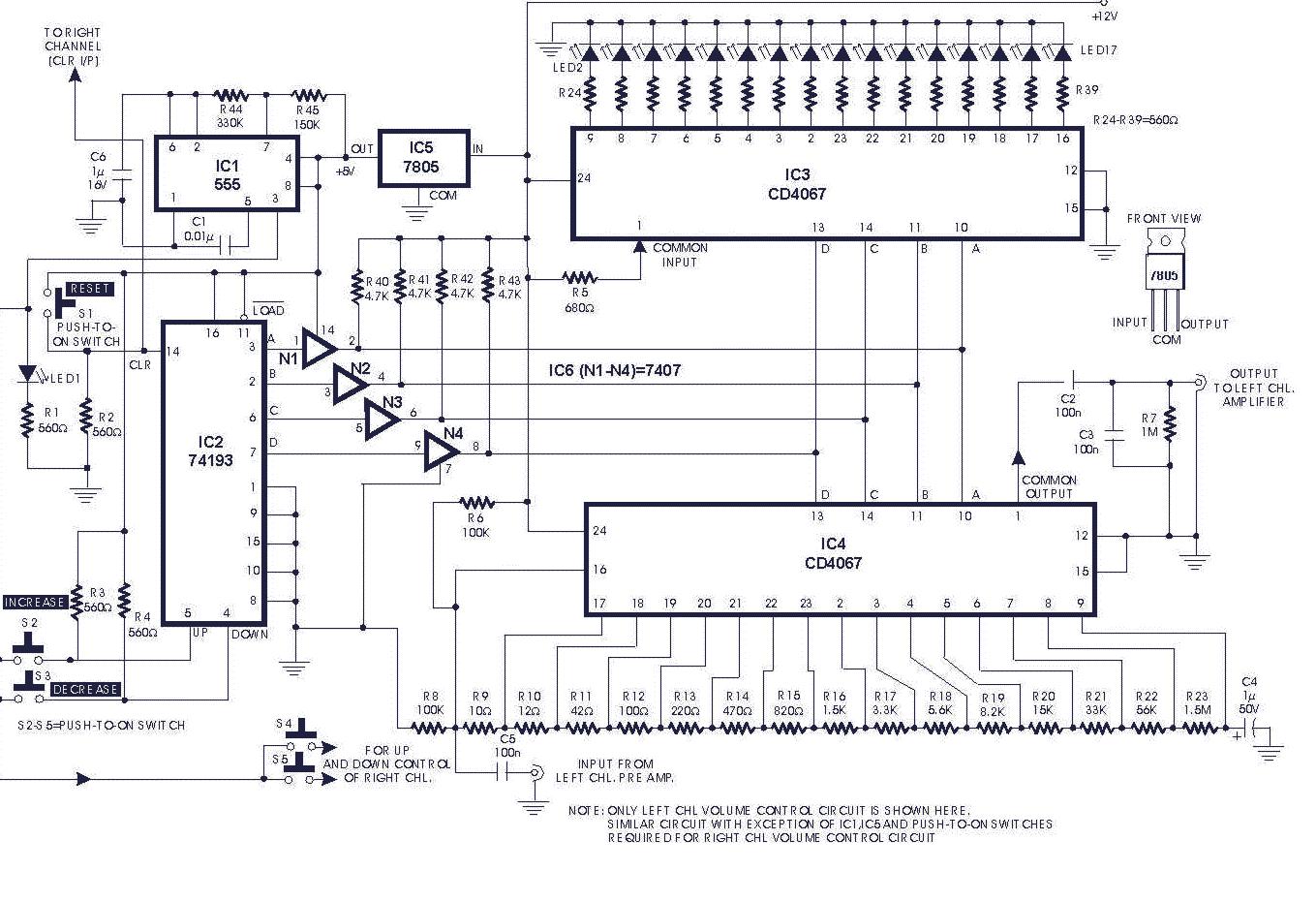
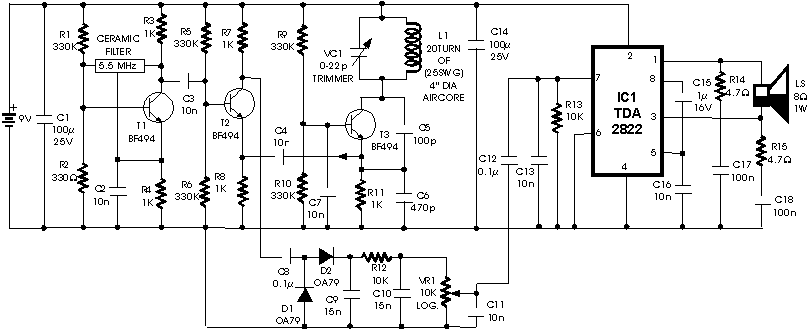
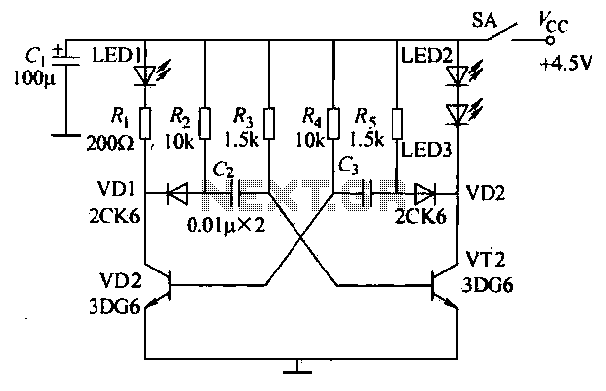
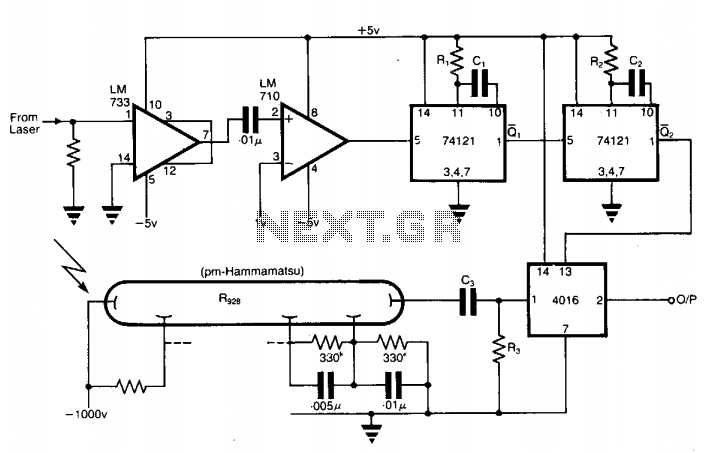
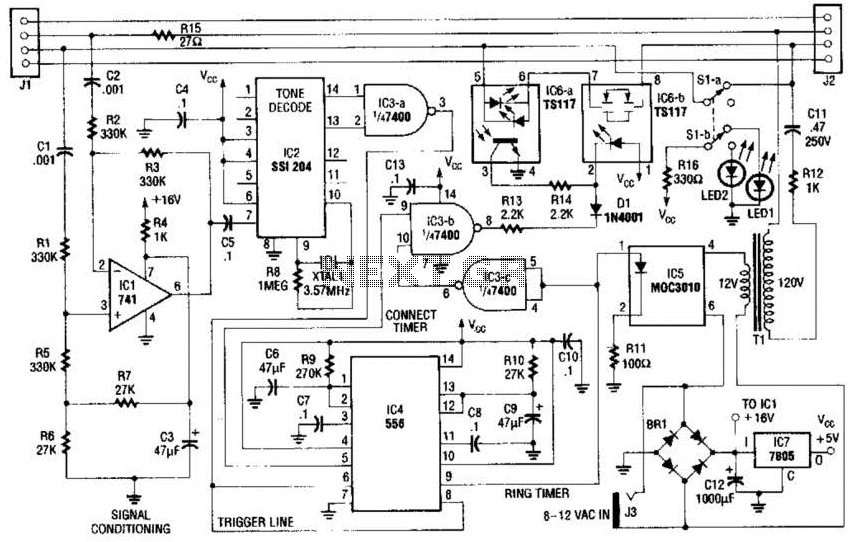
Signal Generator Circuit
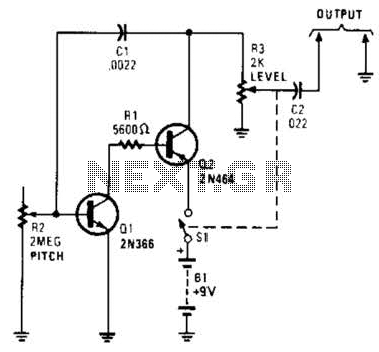
Useful for troubleshooting audio, video, and lower frequency RF amplifiers. This circuit generates a signal that is rich in harmonics.
The circuit designed for troubleshooting audio, video, and lower frequency RF amplifiers is crucial for diagnosing issues in these systems. It generates a signal characterized by a rich harmonic content, which is essential for testing the frequency response and linearity of amplifiers. The harmonic-rich signal can effectively reveal distortion, frequency response anomalies, and other performance-related issues within the amplifier circuits.
The circuit typically consists of a signal generator that produces a fundamental frequency, followed by a series of nonlinear components that introduce harmonics. These nonlinear components can include diodes, transistors, or specialized harmonic generation ICs. The output of the circuit may be connected to an oscilloscope or a spectrum analyzer to visualize the harmonic content and assess the amplifier's performance.
In audio applications, the generated signal can simulate complex waveforms, allowing for thorough testing of audio amplifiers. For video systems, the harmonic content can help in identifying issues related to bandwidth and signal integrity. In lower frequency RF applications, the circuit can assist in evaluating the linearity and gain of RF amplifiers, ensuring they operate within specified parameters.
In summary, this circuit serves as a vital tool for engineers and technicians in the field of electronics, providing a means to troubleshoot and optimize amplifier performance across various applications. Its ability to generate a harmonic-rich signal makes it an invaluable asset in the testing and maintenance of audio, video, and RF amplification systems. Useful for troubleshooting audio, video, and lower frequency RF amplifiers, this circuit generates a signal that is rich in harmonics. 🔗 External reference
The circuit designed for troubleshooting audio, video, and lower frequency RF amplifiers is crucial for diagnosing issues in these systems. It generates a signal characterized by a rich harmonic content, which is essential for testing the frequency response and linearity of amplifiers. The harmonic-rich signal can effectively reveal distortion, frequency response anomalies, and other performance-related issues within the amplifier circuits.
The circuit typically consists of a signal generator that produces a fundamental frequency, followed by a series of nonlinear components that introduce harmonics. These nonlinear components can include diodes, transistors, or specialized harmonic generation ICs. The output of the circuit may be connected to an oscilloscope or a spectrum analyzer to visualize the harmonic content and assess the amplifier's performance.
In audio applications, the generated signal can simulate complex waveforms, allowing for thorough testing of audio amplifiers. For video systems, the harmonic content can help in identifying issues related to bandwidth and signal integrity. In lower frequency RF applications, the circuit can assist in evaluating the linearity and gain of RF amplifiers, ensuring they operate within specified parameters.
In summary, this circuit serves as a vital tool for engineers and technicians in the field of electronics, providing a means to troubleshoot and optimize amplifier performance across various applications. Its ability to generate a harmonic-rich signal makes it an invaluable asset in the testing and maintenance of audio, video, and RF amplification systems. Useful for troubleshooting audio, video, and lower frequency RF amplifiers, this circuit generates a signal that is rich in harmonics. 🔗 External reference