Silent audio switching-mixing
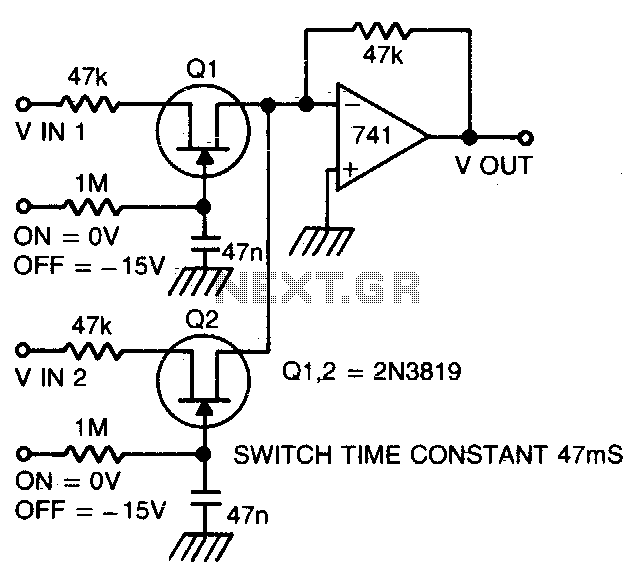
Two or more signals can be switched and/or mixed without annoying clicks by using FETs and a low input-impedance op amp circuit.
The circuit design utilizes Field Effect Transistors (FETs) to facilitate the switching and mixing of multiple signals while ensuring a smooth transition without audible clicks. FETs are favored in this application due to their high input impedance and low output capacitance, which significantly reduce the risk of signal distortion during switching events.
In this configuration, a low input-impedance operational amplifier (op amp) is employed to buffer the signals. The op amp serves to prevent loading effects that could arise from connecting multiple sources directly to the FETs. By maintaining a low input impedance, the op amp allows for effective signal processing without altering the characteristics of the original signals.
The switching mechanism can be implemented using a combination of n-channel and p-channel FETs arranged in a complementary configuration. This arrangement allows for bidirectional signal flow and enhances the circuit's versatility. Control signals applied to the gates of the FETs determine which signals are routed to the output, enabling seamless transitions between inputs.
To further minimize clicking artifacts, the circuit may incorporate additional features such as soft switching techniques or signal ramping. These methods gradually change the gate voltage of the FETs, allowing for smoother transitions and reducing the likelihood of abrupt changes in signal levels.
Overall, this circuit design presents an effective solution for mixing and switching multiple audio or signal sources in applications where signal integrity and sound quality are paramount. The careful selection of components and circuit topology ensures reliable performance while maintaining the desired signal characteristics.Two or more signals can be switched and/or mixed without annoyingclicks by using FETs and a low input-impedance op amp circuit.
The circuit design utilizes Field Effect Transistors (FETs) to facilitate the switching and mixing of multiple signals while ensuring a smooth transition without audible clicks. FETs are favored in this application due to their high input impedance and low output capacitance, which significantly reduce the risk of signal distortion during switching events.
In this configuration, a low input-impedance operational amplifier (op amp) is employed to buffer the signals. The op amp serves to prevent loading effects that could arise from connecting multiple sources directly to the FETs. By maintaining a low input impedance, the op amp allows for effective signal processing without altering the characteristics of the original signals.
The switching mechanism can be implemented using a combination of n-channel and p-channel FETs arranged in a complementary configuration. This arrangement allows for bidirectional signal flow and enhances the circuit's versatility. Control signals applied to the gates of the FETs determine which signals are routed to the output, enabling seamless transitions between inputs.
To further minimize clicking artifacts, the circuit may incorporate additional features such as soft switching techniques or signal ramping. These methods gradually change the gate voltage of the FETs, allowing for smoother transitions and reducing the likelihood of abrupt changes in signal levels.
Overall, this circuit design presents an effective solution for mixing and switching multiple audio or signal sources in applications where signal integrity and sound quality are paramount. The careful selection of components and circuit topology ensures reliable performance while maintaining the desired signal characteristics.Two or more signals can be switched and/or mixed without annoyingclicks by using FETs and a low input-impedance op amp circuit.