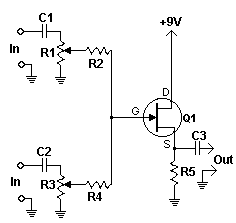
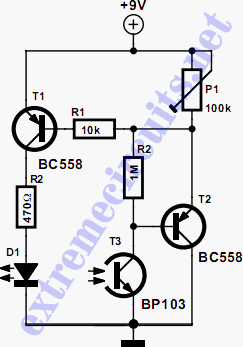
Simple Audio Clipper/Limiter
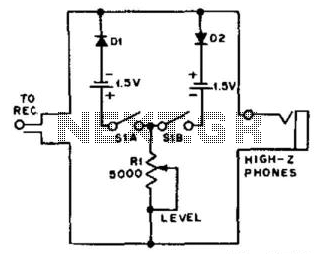
For use with headphones, this circuit sets the audio clipping level via a 5-kOhm potentiometer. This type of noise clipper is most effective for pulse-type noise with a low duty cycle, such as ignition noise. The resistor Rl establishes the bias on the diodes to achieve the desired limiting level.
The circuit is designed to enhance audio quality by preventing distortion caused by excessive signal levels. It utilizes a 5-kOhm potentiometer to adjust the clipping threshold, allowing users to tailor the audio output according to their preferences and the characteristics of the input signal. The potentiometer functions as a variable resistor, enabling fine-tuning of the clipping level, which is crucial for protecting headphones from damage due to high audio levels.
The noise clipper operates effectively on low duty cycle pulse-type noise, which is common in various electronic environments, particularly those influenced by ignition systems in vehicles. By targeting this specific type of noise, the circuit ensures that audio clarity is maintained while unwanted spikes are mitigated.
In this configuration, the resistor Rl plays a vital role in setting the bias for the diodes used in the clipping stage. The diodes are arranged to conduct when the audio signal exceeds a certain threshold, thus limiting the output to a safe level. The value of Rl is critical, as it influences the forward voltage drop across the diodes, determining the point at which clipping occurs.
The overall design of the circuit ensures that it is compact and suitable for integration into headphone amplifiers or other audio devices, providing an effective solution for managing noise and enhancing the listening experience. Proper implementation of this circuit can significantly improve the performance of audio systems in environments with high electromagnetic interference. For use with headphones, this circuit sets the audio clipping level via a 5-KOhmhm pot. This type of noise cli pper works best for pulse-type noise of low duty cycle, such as ignition noise. Rl sets the bias on the diodes for the desired limiting level. 🔗 External reference
The circuit is designed to enhance audio quality by preventing distortion caused by excessive signal levels. It utilizes a 5-kOhm potentiometer to adjust the clipping threshold, allowing users to tailor the audio output according to their preferences and the characteristics of the input signal. The potentiometer functions as a variable resistor, enabling fine-tuning of the clipping level, which is crucial for protecting headphones from damage due to high audio levels.
The noise clipper operates effectively on low duty cycle pulse-type noise, which is common in various electronic environments, particularly those influenced by ignition systems in vehicles. By targeting this specific type of noise, the circuit ensures that audio clarity is maintained while unwanted spikes are mitigated.
In this configuration, the resistor Rl plays a vital role in setting the bias for the diodes used in the clipping stage. The diodes are arranged to conduct when the audio signal exceeds a certain threshold, thus limiting the output to a safe level. The value of Rl is critical, as it influences the forward voltage drop across the diodes, determining the point at which clipping occurs.
The overall design of the circuit ensures that it is compact and suitable for integration into headphone amplifiers or other audio devices, providing an effective solution for managing noise and enhancing the listening experience. Proper implementation of this circuit can significantly improve the performance of audio systems in environments with high electromagnetic interference. For use with headphones, this circuit sets the audio clipping level via a 5-KOhmhm pot. This type of noise cli pper works best for pulse-type noise of low duty cycle, such as ignition noise. Rl sets the bias on the diodes for the desired limiting level. 🔗 External reference