Audio 6 Band Graphic Equaliser Using 741 Op-Amp
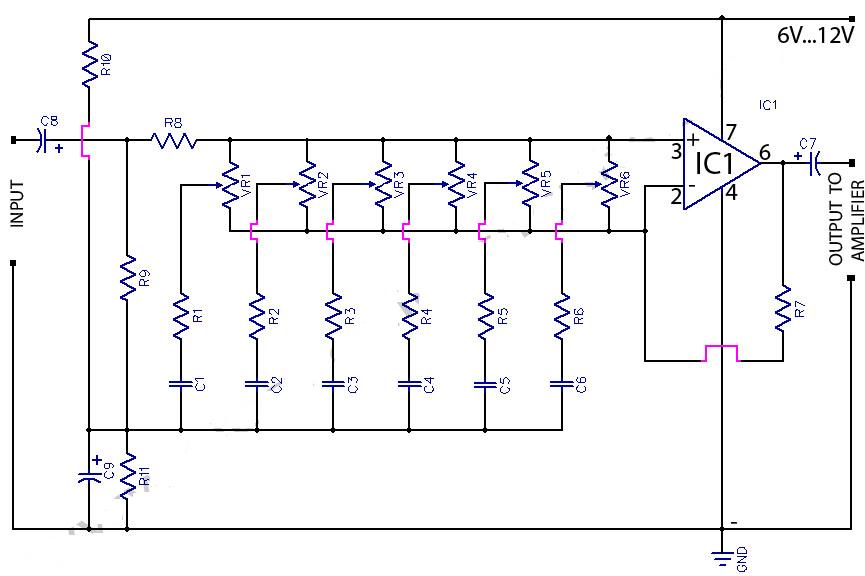
This circuit is a 6-band graphic equalizer that allows for the adjustment of low, medium, and high frequencies using the operational amplifier circuit 741. It enables control and mixing of frequencies and tones according to user preferences. The audible frequency spectrum is divided into six bands: 50Hz, 160Hz, 500Hz, 1.6kHz, 5kHz, and 16kHz. All potentiometers used in the circuit are linear 100kΩ. The circuit provides sufficient boost and cut for standard applications. The power supply for the circuit can be sourced from the amplifier or preamplifier itself, with a voltage range of 6V to 20V, enhancing the circuit's versatility. Power consumption is minimal.
The 6-band graphic equalizer circuit utilizes a series of bandpass filters, each designed to target a specific frequency range. The operational amplifier (op-amp) model 741 serves as the core component for signal amplification and processing. Each of the six frequency bands is controlled by a linear potentiometer, allowing for precise adjustments to boost or attenuate the sound levels within the specified frequency ranges.
The frequency bands are typically centered around the following frequencies: 50Hz for low bass, 160Hz for mid-bass, 500Hz for lower midrange, 1.6kHz for upper midrange, 5kHz for presence, and 16kHz for brilliance. The choice of a linear potentiometer with a resistance of 100kΩ ensures smooth and predictable changes in the audio output, facilitating a user-friendly experience when fine-tuning sound.
The circuit's power supply can be conveniently derived from an associated amplifier or preamplifier, making integration into existing audio systems straightforward. The specified supply voltage range of 6V to 20V provides flexibility, allowing the equalizer to be used in a variety of applications without the need for a dedicated power supply. This adaptability, combined with negligible power consumption, makes the circuit suitable for both portable and stationary audio setups.
In practical applications, the graphic equalizer enhances audio playback by allowing users to tailor the sound to their preferences or to compensate for acoustic deficiencies in a given environment. The overall design promotes ease of use while maintaining high fidelity in audio reproduction, making it an essential tool for audio engineers, musicians, and audiophiles alike.This circuit is 6-band graphic equalizer, you can adjust the sound of low, medium and higher than the IC op amp circuit used 741. With this circuit you can control and mix of frequencies and tones to your liking. Audiblefrequency spectrum is covered in six steps: 50Hz, 160Hz, 500Hz, 1. 6kHz, 5kHz 16kHz, . All potentiometers are linear 100k ©. The ci rcuit provides adequate boost / cut for normal use. power supply for the circuit can be derived from the amp / preamp itself. The supply voltage range of rangeof (6V-20V) makes the circuit very versatile. Power consumption is negligible. 🔗 External reference
The 6-band graphic equalizer circuit utilizes a series of bandpass filters, each designed to target a specific frequency range. The operational amplifier (op-amp) model 741 serves as the core component for signal amplification and processing. Each of the six frequency bands is controlled by a linear potentiometer, allowing for precise adjustments to boost or attenuate the sound levels within the specified frequency ranges.
The frequency bands are typically centered around the following frequencies: 50Hz for low bass, 160Hz for mid-bass, 500Hz for lower midrange, 1.6kHz for upper midrange, 5kHz for presence, and 16kHz for brilliance. The choice of a linear potentiometer with a resistance of 100kΩ ensures smooth and predictable changes in the audio output, facilitating a user-friendly experience when fine-tuning sound.
The circuit's power supply can be conveniently derived from an associated amplifier or preamplifier, making integration into existing audio systems straightforward. The specified supply voltage range of 6V to 20V provides flexibility, allowing the equalizer to be used in a variety of applications without the need for a dedicated power supply. This adaptability, combined with negligible power consumption, makes the circuit suitable for both portable and stationary audio setups.
In practical applications, the graphic equalizer enhances audio playback by allowing users to tailor the sound to their preferences or to compensate for acoustic deficiencies in a given environment. The overall design promotes ease of use while maintaining high fidelity in audio reproduction, making it an essential tool for audio engineers, musicians, and audiophiles alike.This circuit is 6-band graphic equalizer, you can adjust the sound of low, medium and higher than the IC op amp circuit used 741. With this circuit you can control and mix of frequencies and tones to your liking. Audiblefrequency spectrum is covered in six steps: 50Hz, 160Hz, 500Hz, 1. 6kHz, 5kHz 16kHz, . All potentiometers are linear 100k ©. The ci rcuit provides adequate boost / cut for normal use. power supply for the circuit can be derived from the amp / preamp itself. The supply voltage range of rangeof (6V-20V) makes the circuit very versatile. Power consumption is negligible. 🔗 External reference