Simple Audio Peak Detector
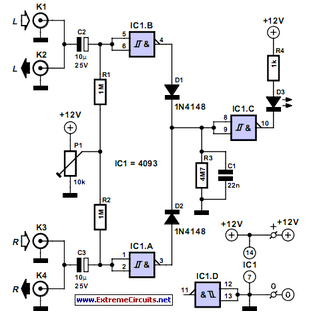
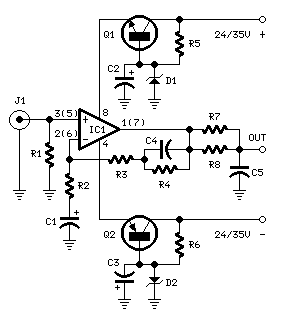
This audio peak detector enables the monitoring of a pair of stereo channels using a single LED. The circuitry employed for both the left and right channels is identical.
The audio peak detector circuit is designed to provide a visual indication of the peak levels in audio signals, making it particularly useful in audio processing and mixing applications. The circuit typically consists of two main sections: the signal input stage and the peak detection stage.
In the signal input stage, the audio signals from the left and right channels are fed into the circuit. Each channel's signal is first buffered and then processed to ensure that it is at the appropriate level for detection. This may involve the use of operational amplifiers configured as voltage followers or gain stages to maintain signal integrity.
The peak detection stage employs a diode and capacitor arrangement to capture the peak voltage of the incoming audio signal. The diode allows current to flow only in one direction, charging the capacitor to the peak voltage level. A resistor may be placed in parallel with the capacitor to provide a discharge path, allowing the capacitor to reset after the peak has been indicated.
To combine the output of both channels for monitoring with a single LED, the circuit may utilize a summing amplifier or a simple resistor network. This ensures that the highest peak from either channel is represented by the LED. The LED will illuminate when the voltage across it exceeds a certain threshold, indicating that a peak has been detected.
The design can be further enhanced by incorporating additional features such as adjustable sensitivity, which can be achieved through variable resistors in the circuit, or by adding a filter to limit the response to specific frequency ranges. This flexibility allows the audio peak detector to adapt to various audio environments and requirements.
Overall, the audio peak detector circuit is a valuable tool for audio engineers and musicians, providing essential feedback on audio levels and ensuring optimal performance during mixing and live sound applications.This audio peak detector allows a pair of stereo channels to be monitored on a single LED. Identical circuitry is used in the left and right channels. Use.. 🔗 External reference
The audio peak detector circuit is designed to provide a visual indication of the peak levels in audio signals, making it particularly useful in audio processing and mixing applications. The circuit typically consists of two main sections: the signal input stage and the peak detection stage.
In the signal input stage, the audio signals from the left and right channels are fed into the circuit. Each channel's signal is first buffered and then processed to ensure that it is at the appropriate level for detection. This may involve the use of operational amplifiers configured as voltage followers or gain stages to maintain signal integrity.
The peak detection stage employs a diode and capacitor arrangement to capture the peak voltage of the incoming audio signal. The diode allows current to flow only in one direction, charging the capacitor to the peak voltage level. A resistor may be placed in parallel with the capacitor to provide a discharge path, allowing the capacitor to reset after the peak has been indicated.
To combine the output of both channels for monitoring with a single LED, the circuit may utilize a summing amplifier or a simple resistor network. This ensures that the highest peak from either channel is represented by the LED. The LED will illuminate when the voltage across it exceeds a certain threshold, indicating that a peak has been detected.
The design can be further enhanced by incorporating additional features such as adjustable sensitivity, which can be achieved through variable resistors in the circuit, or by adding a filter to limit the response to specific frequency ranges. This flexibility allows the audio peak detector to adapt to various audio environments and requirements.
Overall, the audio peak detector circuit is a valuable tool for audio engineers and musicians, providing essential feedback on audio levels and ensuring optimal performance during mixing and live sound applications.This audio peak detector allows a pair of stereo channels to be monitored on a single LED. Identical circuitry is used in the left and right channels. Use.. 🔗 External reference