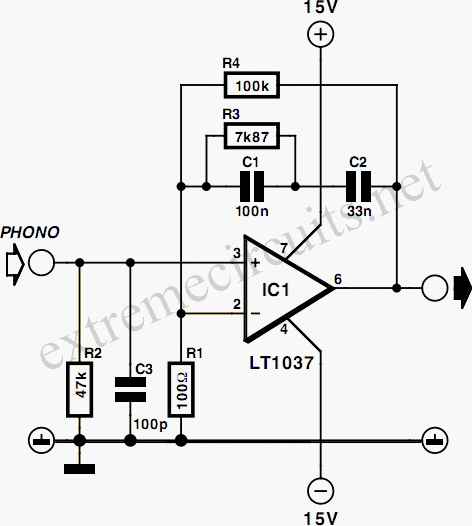
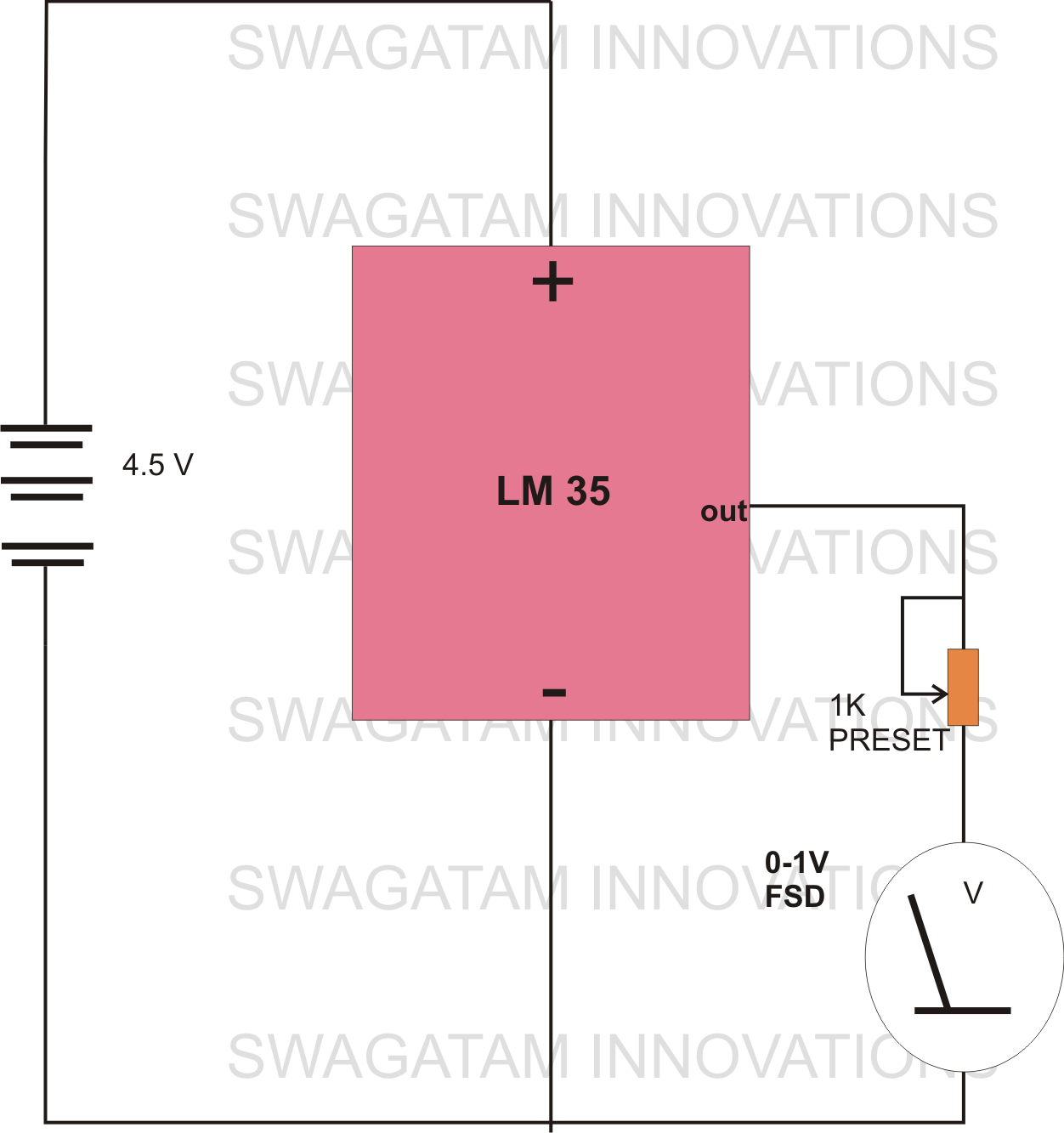
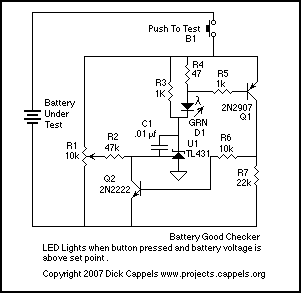
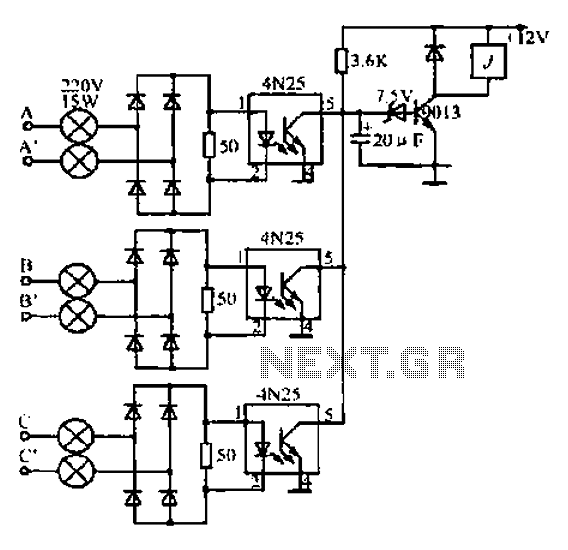
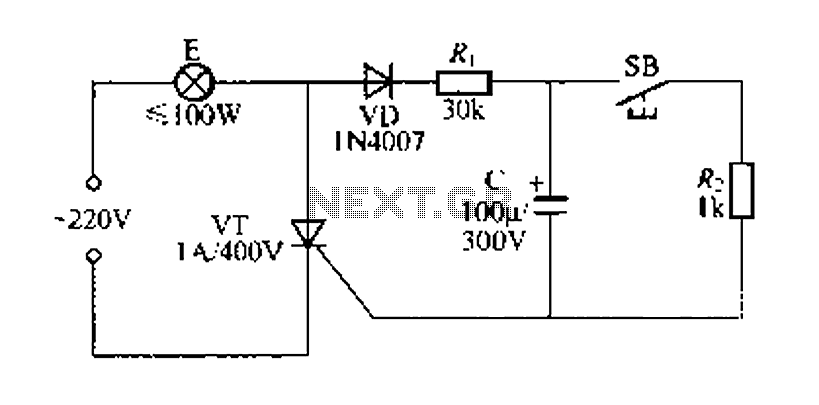
Simple Battery State Indicator
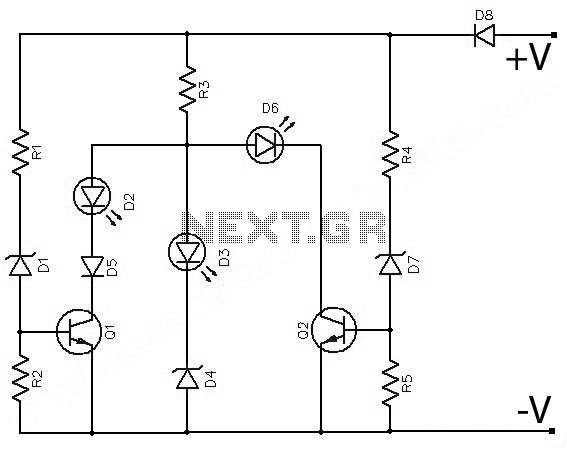
Often, outdoor audio or video recordings suffer from poor quality when the battery is low. If the battery voltage drops below 9V for a 12V recorder, the playback output will be compromised due to variations in the power supply.
To address the issue of battery voltage affecting the quality of audio and video recordings, a voltage monitoring and regulation circuit can be implemented. This circuit would continuously monitor the battery voltage and provide a stable output voltage to the recording device, ensuring that it operates within the optimal voltage range.
The schematic would typically include a voltage divider to step down the battery voltage for monitoring, an operational amplifier configured as a comparator, and a microcontroller or a simple transistor switch. The voltage divider consists of two resistors connected in series across the battery terminals, with the output taken from the junction of the resistors. This output is fed into the non-inverting input of the operational amplifier.
The inverting input of the operational amplifier is connected to a reference voltage, which is set to correspond to the minimum acceptable voltage for the recorder (in this case, 9V). When the battery voltage falls below this threshold, the operational amplifier's output will change state, triggering a response from the microcontroller or transistor switch.
The microcontroller can be programmed to activate an alarm or indicator light when the battery voltage is low, alerting the user to replace or recharge the battery. In addition, the circuit can include a buck converter to step down the voltage from the battery to a stable 12V output for the recorder, ensuring consistent performance even as the battery discharges.
Overall, implementing such a circuit will enhance the reliability of outdoor audio and video recordings by maintaining the necessary power levels for optimal operation.Many a time the outdoor audio or video recording becomes imperfect due to a ˜dying battery. If the battery voltage is less than 9V for a 12V recorder, the output during playback will not be of a good quality due to variations in the mo.. 🔗 External reference
To address the issue of battery voltage affecting the quality of audio and video recordings, a voltage monitoring and regulation circuit can be implemented. This circuit would continuously monitor the battery voltage and provide a stable output voltage to the recording device, ensuring that it operates within the optimal voltage range.
The schematic would typically include a voltage divider to step down the battery voltage for monitoring, an operational amplifier configured as a comparator, and a microcontroller or a simple transistor switch. The voltage divider consists of two resistors connected in series across the battery terminals, with the output taken from the junction of the resistors. This output is fed into the non-inverting input of the operational amplifier.
The inverting input of the operational amplifier is connected to a reference voltage, which is set to correspond to the minimum acceptable voltage for the recorder (in this case, 9V). When the battery voltage falls below this threshold, the operational amplifier's output will change state, triggering a response from the microcontroller or transistor switch.
The microcontroller can be programmed to activate an alarm or indicator light when the battery voltage is low, alerting the user to replace or recharge the battery. In addition, the circuit can include a buck converter to step down the voltage from the battery to a stable 12V output for the recorder, ensuring consistent performance even as the battery discharges.
Overall, implementing such a circuit will enhance the reliability of outdoor audio and video recordings by maintaining the necessary power levels for optimal operation.Many a time the outdoor audio or video recording becomes imperfect due to a ˜dying battery. If the battery voltage is less than 9V for a 12V recorder, the output during playback will not be of a good quality due to variations in the mo.. 🔗 External reference