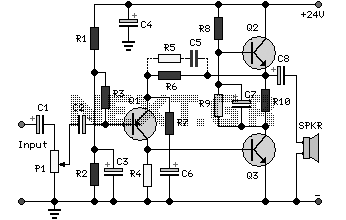
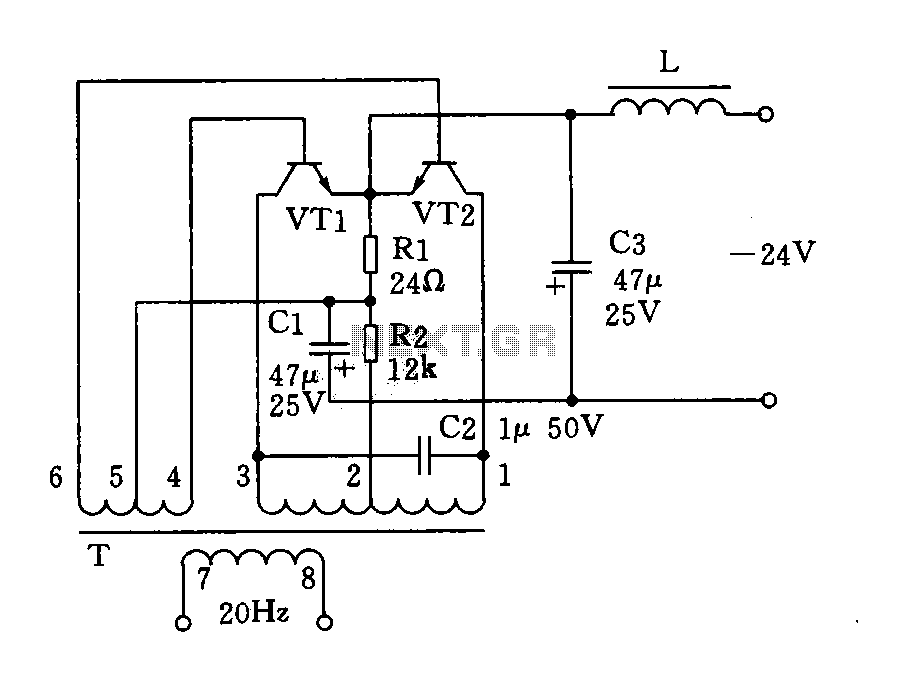
Simple Digital Logic Probe Circuit
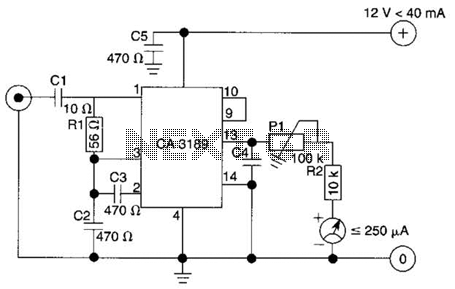
The design of the digital logic probe centers around a pair of complementary bipolar transistors, which, in this application, are used as electronic switches.
The digital logic probe is a diagnostic tool utilized for testing and analyzing digital circuits. The core of its design involves two complementary bipolar transistors, typically an NPN and a PNP type, configured to operate as electronic switches. This configuration allows for the detection of high and low logic levels in a circuit, facilitating the identification of signal states.
When a voltage is applied to the base of the NPN transistor, it turns on, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter. Conversely, when the PNP transistor is activated, it allows current to flow in the opposite direction. This complementary action ensures that the probe can effectively toggle between detecting logic high (1) and logic low (0) states.
The output of the probe can be connected to an LED indicator or a microcontroller input, providing a visual or digital representation of the logic state. Additional components, such as pull-up or pull-down resistors, may be included in the circuit to stabilize the input signals and prevent floating states.
In summary, the digital logic probe serves as an essential tool in electronic testing, leveraging the properties of complementary bipolar transistors to provide accurate readings of digital signals in various applications. The design of the digital logic probe centers around a pair of complementary bipolar transistors, which, in this application, are used as electronic switches. 🔗 External reference
The digital logic probe is a diagnostic tool utilized for testing and analyzing digital circuits. The core of its design involves two complementary bipolar transistors, typically an NPN and a PNP type, configured to operate as electronic switches. This configuration allows for the detection of high and low logic levels in a circuit, facilitating the identification of signal states.
When a voltage is applied to the base of the NPN transistor, it turns on, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter. Conversely, when the PNP transistor is activated, it allows current to flow in the opposite direction. This complementary action ensures that the probe can effectively toggle between detecting logic high (1) and logic low (0) states.
The output of the probe can be connected to an LED indicator or a microcontroller input, providing a visual or digital representation of the logic state. Additional components, such as pull-up or pull-down resistors, may be included in the circuit to stabilize the input signals and prevent floating states.
In summary, the digital logic probe serves as an essential tool in electronic testing, leveraging the properties of complementary bipolar transistors to provide accurate readings of digital signals in various applications. The design of the digital logic probe centers around a pair of complementary bipolar transistors, which, in this application, are used as electronic switches. 🔗 External reference