Simple DIY Induction Heater
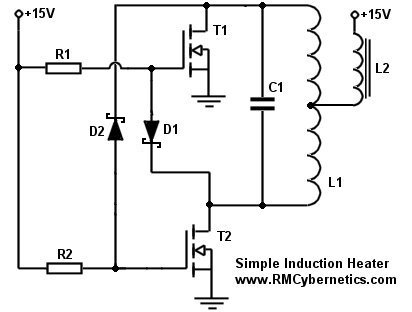
This project outlines the process of creating a simple induction heater. It is straightforward and notably efficient at heating metals through the use of high-frequency magnetic fields.
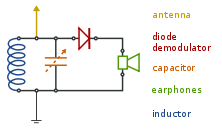
An induction heater operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where an alternating current (AC) generates a magnetic field that induces eddy currents in conductive materials, leading to rapid heating. The essential components of a simple induction heater circuit include a power supply, a high-frequency oscillator, a coil, and a workpiece (the metal to be heated).
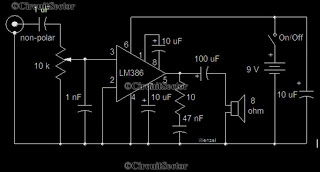
The power supply typically consists of a transformer that steps down the voltage to a suitable level for the oscillator. The oscillator can be built using a combination of transistors or integrated circuits that generate a high-frequency signal, usually in the range of 20 kHz to 100 kHz. This frequency is chosen to optimize the heating effect in the metal.
The coil, often made of copper wire, is designed to create a strong magnetic field when current flows through it. The design of the coil can vary depending on the intended application, with factors such as the number of turns, diameter, and spacing influencing the efficiency and effectiveness of the heating process.
The workpiece is placed within the coil, where it experiences the induced eddy currents generated by the magnetic field. The heat produced in the workpiece can be controlled by adjusting the frequency of the oscillator and the power supplied to the coil.
Safety precautions must be taken when working with induction heaters due to the high temperatures involved and the potential for electrical hazards. Proper insulation, heat-resistant materials, and protective equipment should be utilized to ensure safe operation.
This induction heater design can be used for various applications, including metal melting, soldering, and heat treatment, making it a versatile tool in both hobbyist and industrial settings.How to make a simple induction heater. This project is really simple, and surprisingly effective at heating metals using high frequency magnetic fields.. 🔗 External reference
An induction heater operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where an alternating current (AC) generates a magnetic field that induces eddy currents in conductive materials, leading to rapid heating. The essential components of a simple induction heater circuit include a power supply, a high-frequency oscillator, a coil, and a workpiece (the metal to be heated).
The power supply typically consists of a transformer that steps down the voltage to a suitable level for the oscillator. The oscillator can be built using a combination of transistors or integrated circuits that generate a high-frequency signal, usually in the range of 20 kHz to 100 kHz. This frequency is chosen to optimize the heating effect in the metal.
The coil, often made of copper wire, is designed to create a strong magnetic field when current flows through it. The design of the coil can vary depending on the intended application, with factors such as the number of turns, diameter, and spacing influencing the efficiency and effectiveness of the heating process.
The workpiece is placed within the coil, where it experiences the induced eddy currents generated by the magnetic field. The heat produced in the workpiece can be controlled by adjusting the frequency of the oscillator and the power supplied to the coil.
Safety precautions must be taken when working with induction heaters due to the high temperatures involved and the potential for electrical hazards. Proper insulation, heat-resistant materials, and protective equipment should be utilized to ensure safe operation.
This induction heater design can be used for various applications, including metal melting, soldering, and heat treatment, making it a versatile tool in both hobbyist and industrial settings.How to make a simple induction heater. This project is really simple, and surprisingly effective at heating metals using high frequency magnetic fields.. 🔗 External reference