SIMPLE DOOR ALARM CIRCUIT
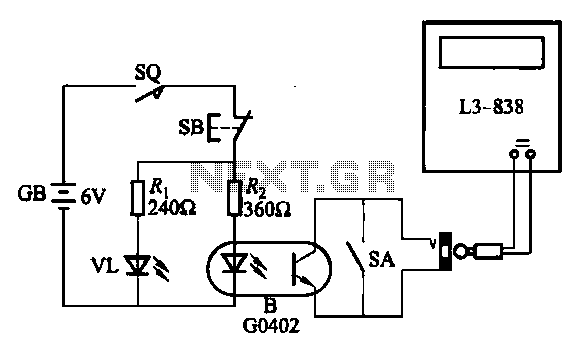
This is a circuit diagram for a simple doorbell. The circuit can be assembled indoors, while the switch should be placed outside, making it easily noticeable for visitors. The operation of this circuit is similar to a previous project.
The simple doorbell circuit typically consists of a few essential components: a power source, a switch, a bell or chime, and connecting wires. The power source can be a standard AC or DC supply, depending on the specifications of the bell used. The switch serves as the triggering mechanism, which, when pressed, completes the circuit and activates the bell.
In this design, the switch is positioned outside the home or room, allowing visitors to ring the doorbell easily. When the switch is pressed, current flows from the power source through the switch to the bell. The bell will then produce a sound, alerting the occupants of the home to the presence of a visitor.
To ensure safety and functionality, it is important to use components that can handle the voltage and current levels of the power source. Additionally, proper insulation and secure connections should be maintained throughout the assembly to prevent any short circuits or electrical hazards.
This doorbell circuit can be further enhanced by integrating features such as LED indicators to show when the doorbell is activated or by using a wireless system to eliminate the need for extensive wiring. The simplicity of this circuit allows for easy troubleshooting and modifications, making it a practical choice for basic doorbell applications.Here is the circuit diagram for simple door bell, you can assemble this circuit inside your room or home where as keep the switch outside your home or room that is easily noticable by the visitors. The working of this circuit is almost similar to my previous project. 🔗 External reference
The simple doorbell circuit typically consists of a few essential components: a power source, a switch, a bell or chime, and connecting wires. The power source can be a standard AC or DC supply, depending on the specifications of the bell used. The switch serves as the triggering mechanism, which, when pressed, completes the circuit and activates the bell.
In this design, the switch is positioned outside the home or room, allowing visitors to ring the doorbell easily. When the switch is pressed, current flows from the power source through the switch to the bell. The bell will then produce a sound, alerting the occupants of the home to the presence of a visitor.
To ensure safety and functionality, it is important to use components that can handle the voltage and current levels of the power source. Additionally, proper insulation and secure connections should be maintained throughout the assembly to prevent any short circuits or electrical hazards.
This doorbell circuit can be further enhanced by integrating features such as LED indicators to show when the doorbell is activated or by using a wireless system to eliminate the need for extensive wiring. The simplicity of this circuit allows for easy troubleshooting and modifications, making it a practical choice for basic doorbell applications.Here is the circuit diagram for simple door bell, you can assemble this circuit inside your room or home where as keep the switch outside your home or room that is easily noticable by the visitors. The working of this circuit is almost similar to my previous project. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713