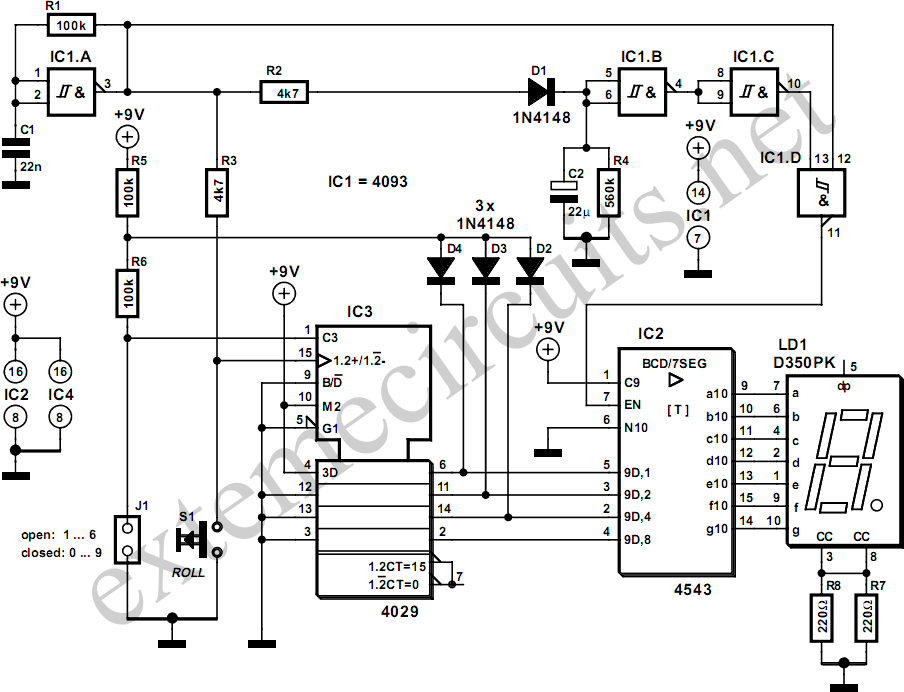
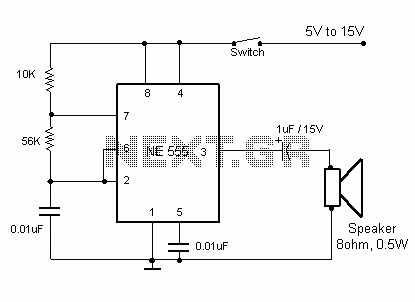
Simple Electronic Metronome
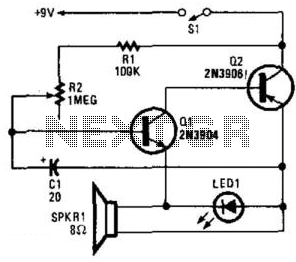
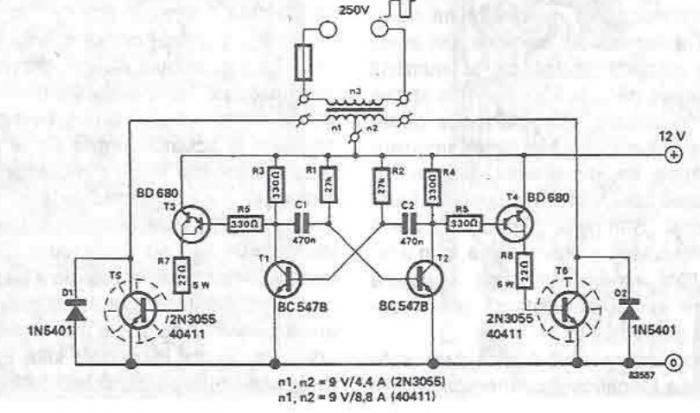
Two complementary transistors create a basic oscillator with a frequency range of approximately 0.5 to several Hz. This circuit serves as a metronome, timer, or pacer for exercise equipment.
The oscillator circuit utilizes a pair of complementary transistors, typically one NPN and one PNP, configured in a feedback loop to generate oscillations. The transistors are connected in such a way that the output of one transistor is fed back to the base of the other, establishing a regenerative feedback that sustains oscillations. The frequency of oscillation is primarily determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors in the circuit.
In terms of component selection, the transistors should be chosen based on their switching speed and current handling capabilities to ensure reliable operation within the desired frequency range. Resistors are used to set the biasing conditions for the transistors, while capacitors determine the timing characteristics of the oscillation. By adjusting the values of these passive components, the frequency can be fine-tuned to meet specific application requirements.
The output of the oscillator can be used to drive an LED, a speaker, or an electronic timer, making it versatile for various applications such as metronomes in music practice or timing devices in exercise equipment. The simplicity of the design allows for easy integration into various electronic projects, making it a valuable circuit for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics. Two complementary transistors form a simple oscillator whose frequency range is from about 0.5 to several Hz. T his circuit is useful as a metronome, timer, or pacer for exercise equipment. 🔗 External reference
The oscillator circuit utilizes a pair of complementary transistors, typically one NPN and one PNP, configured in a feedback loop to generate oscillations. The transistors are connected in such a way that the output of one transistor is fed back to the base of the other, establishing a regenerative feedback that sustains oscillations. The frequency of oscillation is primarily determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors in the circuit.
In terms of component selection, the transistors should be chosen based on their switching speed and current handling capabilities to ensure reliable operation within the desired frequency range. Resistors are used to set the biasing conditions for the transistors, while capacitors determine the timing characteristics of the oscillation. By adjusting the values of these passive components, the frequency can be fine-tuned to meet specific application requirements.
The output of the oscillator can be used to drive an LED, a speaker, or an electronic timer, making it versatile for various applications such as metronomes in music practice or timing devices in exercise equipment. The simplicity of the design allows for easy integration into various electronic projects, making it a valuable circuit for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics. Two complementary transistors form a simple oscillator whose frequency range is from about 0.5 to several Hz. T his circuit is useful as a metronome, timer, or pacer for exercise equipment. 🔗 External reference