Simple JFET Preamp
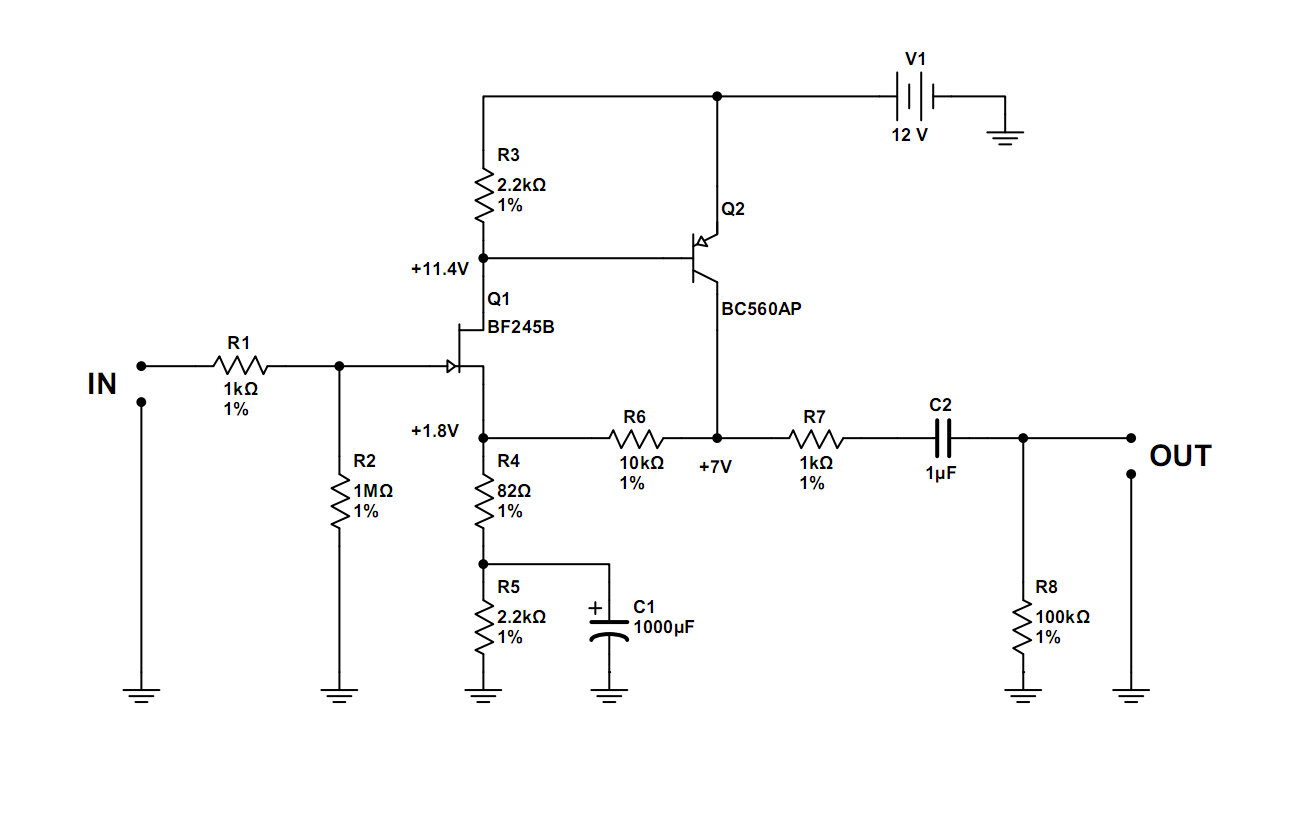
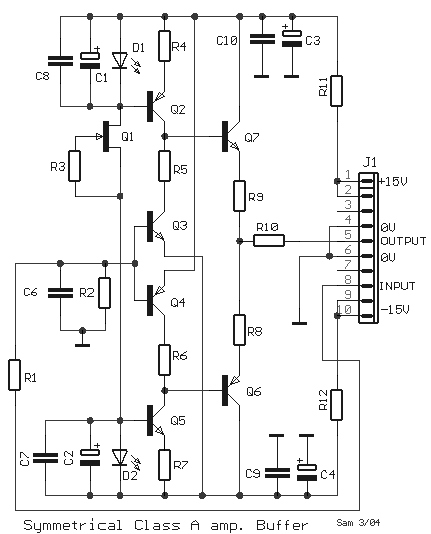
The following is an example of a simple and high-quality JFET preamplifier. This circuit can be used to amplify very low signal sources. FET transistors are typically not utilized independently in preamplifiers; they are often paired with bipolar transistors. Resistor R2 automatically sets the bias for Q1 in a manner similar to a tube circuit. This resistor ties the gate of Q1 to ground, establishing its potential. The source's potential is elevated above ground by the voltage across resistors R4 and R5. In other words, the gate is more negative than the source. The gate-source transition functions as a standard PN junction. Typically, this junction is connected in the opposite direction, which accounts for the relatively high input impedance (greater than 10^9 ohms). Essentially, the input impedance of the circuit is determined by R2, which is approximately 1M ohm in this case. Resistors R4 and R6 create an AC negative feedback loop. Resistors R1 and R7 act as over-voltage and over-current limiters to protect against short circuits at the input or output. In addition to their high input impedance, FET transistor preamps offer the advantage of very low noise, enabling the design of stages with a high signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio. Significant deviations from these specified values may result in suboptimal performance. A voltage of 0V at the collector of Q2 indicates a break in the collector-emitter junction, while a voltage of 12V suggests a short circuit between these two outputs. The voltage at the base of Q2 corresponds to one voltage drop of a standard junction, which is approximately 0.7V.
The described JFET preamplifier circuit is designed to enhance weak signals, making it an essential component in various audio and signal processing applications. The circuit utilizes a JFET (Junction Field Effect Transistor) as the primary amplification element, which is favored for its high input impedance and low noise characteristics. The connection of the gate to ground through R2 ensures that the JFET operates in its optimal biasing region, facilitating effective signal amplification.
The circuit's configuration includes feedback mechanisms through R4 and R6, which stabilize the gain and improve linearity by reducing distortion. The feedback loop allows for better control over the gain of the amplifier, ensuring that it remains consistent across varying input signal levels. The use of resistors R1 and R7 as protective elements is critical for safeguarding the circuit from potential damage due to excessive voltage or current, which could occur during fault conditions.
The high input impedance, primarily determined by R2, allows the preamp to interface effectively with high-impedance sources, such as microphones or piezoelectric sensors, without loading them down. The low noise performance of the JFET further enhances the circuit's capability to maintain a high S/N ratio, making it suitable for applications where signal integrity is paramount.
Overall, the design of this JFET preamp exemplifies the principles of low-noise amplification and high input impedance, making it a valuable tool in the field of electronic signal processing. The careful selection of component values and configurations ensures reliable performance and protection against common electrical faults.The following is an example for a very simple and high quality JFET preamp. You can use this to amplify a very low signal sources. FET transistors are usually not used independently in preamplifiers. In most of the cases they are paired with bipolar transistors. R2 automatically sets the bias for Q1 in a way similar to a tube circuit. This resisto r tides the gate of Q1 to ground and sets its potential. Source`s potential is higher than ground by the voltage across R4 and R5. In other words the gate is more negative then the source. The gate-source transition represents a normal PN junction. Usually this junction is tied in opposite direction, which explains the relatively high input impedance (more than 109 ©). Basically the input impedance of the circuit is set by R2 and in this case it`s around 1M ©. R4 and R6 form an AC negative feedback. R1 and R7 serve as over voltage limiters and over current limiters in case of short circuit at the input or output.
Besides their high input impedance, the FET transistor preamps have one more advantage. This is the very low noise. This means that we can easily design a stage with high S/N ratio. Considerable deviations from these values will cause the stage not to perform as it should be. 0V at the collector of Q2 means that there is a break into collector-emitter junction while 12V means there is a short between those two outputs. The voltage at the base of Q2 is equal to one voltage drop of a normal junction which is about 🔗 External reference
The described JFET preamplifier circuit is designed to enhance weak signals, making it an essential component in various audio and signal processing applications. The circuit utilizes a JFET (Junction Field Effect Transistor) as the primary amplification element, which is favored for its high input impedance and low noise characteristics. The connection of the gate to ground through R2 ensures that the JFET operates in its optimal biasing region, facilitating effective signal amplification.
The circuit's configuration includes feedback mechanisms through R4 and R6, which stabilize the gain and improve linearity by reducing distortion. The feedback loop allows for better control over the gain of the amplifier, ensuring that it remains consistent across varying input signal levels. The use of resistors R1 and R7 as protective elements is critical for safeguarding the circuit from potential damage due to excessive voltage or current, which could occur during fault conditions.
The high input impedance, primarily determined by R2, allows the preamp to interface effectively with high-impedance sources, such as microphones or piezoelectric sensors, without loading them down. The low noise performance of the JFET further enhances the circuit's capability to maintain a high S/N ratio, making it suitable for applications where signal integrity is paramount.
Overall, the design of this JFET preamp exemplifies the principles of low-noise amplification and high input impedance, making it a valuable tool in the field of electronic signal processing. The careful selection of component values and configurations ensures reliable performance and protection against common electrical faults.The following is an example for a very simple and high quality JFET preamp. You can use this to amplify a very low signal sources. FET transistors are usually not used independently in preamplifiers. In most of the cases they are paired with bipolar transistors. R2 automatically sets the bias for Q1 in a way similar to a tube circuit. This resisto r tides the gate of Q1 to ground and sets its potential. Source`s potential is higher than ground by the voltage across R4 and R5. In other words the gate is more negative then the source. The gate-source transition represents a normal PN junction. Usually this junction is tied in opposite direction, which explains the relatively high input impedance (more than 109 ©). Basically the input impedance of the circuit is set by R2 and in this case it`s around 1M ©. R4 and R6 form an AC negative feedback. R1 and R7 serve as over voltage limiters and over current limiters in case of short circuit at the input or output.
Besides their high input impedance, the FET transistor preamps have one more advantage. This is the very low noise. This means that we can easily design a stage with high S/N ratio. Considerable deviations from these values will cause the stage not to perform as it should be. 0V at the collector of Q2 means that there is a break into collector-emitter junction while 12V means there is a short between those two outputs. The voltage at the base of Q2 is equal to one voltage drop of a normal junction which is about 🔗 External reference