Simple Mixer with 4 Input
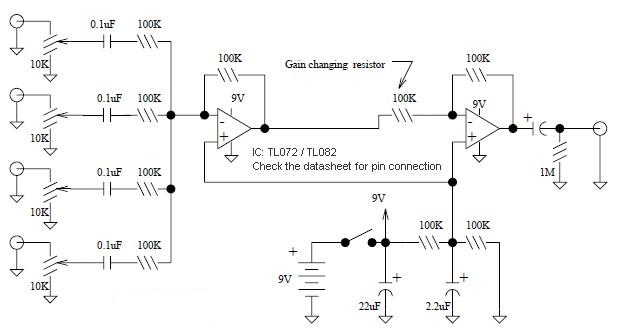
A basic mixer suitable for mixing microphones or effects outputs. The overall gain from input to output is unity if the potentiometer related to the input is fully turned up. This gain can be increased to ten (or any other reasonable value) by reducing the input resistor connected to the second operational amplifier. A 10K resistor in this position provides a gain of ten, equivalent to 20 dB. When mixing effects outputs that feature an output level control, it is possible to adjust the input level controls accordingly, allowing some to have level controls while others do not. Audio taper potentiometers are generally preferable, although linear ones will suffice.
This circuit describes a basic audio mixer designed to accommodate multiple input sources, such as microphones and effects outputs. The primary function of this mixer is to combine audio signals while maintaining control over the overall gain. The circuit employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) to achieve desired signal mixing and amplification.
The input stage consists of a potentiometer that allows for the adjustment of the input signal level. When the potentiometer is fully turned up, the circuit achieves a gain of unity, meaning that the output signal level equals the input signal level. To increase the gain, a resistor is placed in series with the input of the second op-amp. By selecting a 10K resistor in this position, the circuit can achieve a gain of ten, providing a significant boost of 20 dB to the audio signal.
This mixer is particularly versatile when dealing with effects outputs that may already have built-in level controls. The design allows for flexibility in managing input levels, enabling the user to choose whether to utilize level controls on each input. This feature is beneficial for mixing various audio sources with differing output levels, ensuring a balanced mix.
In terms of component selection, audio taper potentiometers are recommended for controlling levels due to their logarithmic response, which is more suitable for audio applications. However, linear potentiometers can also be used effectively, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
Overall, this basic mixer circuit provides a simple yet effective solution for mixing audio signals from multiple sources, offering adjustable gain and flexibility in input level management.A basic mixer suitable for mixing microphones or even effects outputs. The overall gain from input to output is one if the pot related towards the input is full up. You can make this a net gain of ten (or any other reasonable gain) by reducing the input resistor towards the second op amp. 10K in this position gives a gain of ten, or 20db. In case you are mixing effects outputs that have an output level control constructed into them, you are able to dispense using the input level controls, or make some have level controls, some not. Audio taper pots are possibly much better, but linear will do the job. 🔗 External reference
This circuit describes a basic audio mixer designed to accommodate multiple input sources, such as microphones and effects outputs. The primary function of this mixer is to combine audio signals while maintaining control over the overall gain. The circuit employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) to achieve desired signal mixing and amplification.
The input stage consists of a potentiometer that allows for the adjustment of the input signal level. When the potentiometer is fully turned up, the circuit achieves a gain of unity, meaning that the output signal level equals the input signal level. To increase the gain, a resistor is placed in series with the input of the second op-amp. By selecting a 10K resistor in this position, the circuit can achieve a gain of ten, providing a significant boost of 20 dB to the audio signal.
This mixer is particularly versatile when dealing with effects outputs that may already have built-in level controls. The design allows for flexibility in managing input levels, enabling the user to choose whether to utilize level controls on each input. This feature is beneficial for mixing various audio sources with differing output levels, ensuring a balanced mix.
In terms of component selection, audio taper potentiometers are recommended for controlling levels due to their logarithmic response, which is more suitable for audio applications. However, linear potentiometers can also be used effectively, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
Overall, this basic mixer circuit provides a simple yet effective solution for mixing audio signals from multiple sources, offering adjustable gain and flexibility in input level management.A basic mixer suitable for mixing microphones or even effects outputs. The overall gain from input to output is one if the pot related towards the input is full up. You can make this a net gain of ten (or any other reasonable gain) by reducing the input resistor towards the second op amp. 10K in this position gives a gain of ten, or 20db. In case you are mixing effects outputs that have an output level control constructed into them, you are able to dispense using the input level controls, or make some have level controls, some not. Audio taper pots are possibly much better, but linear will do the job. 🔗 External reference