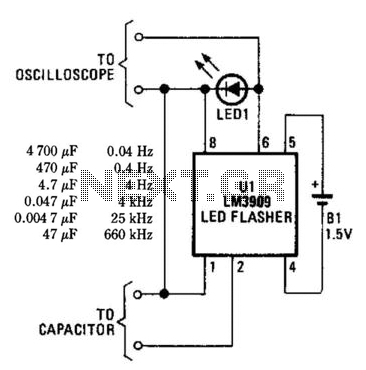
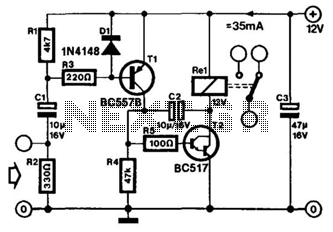
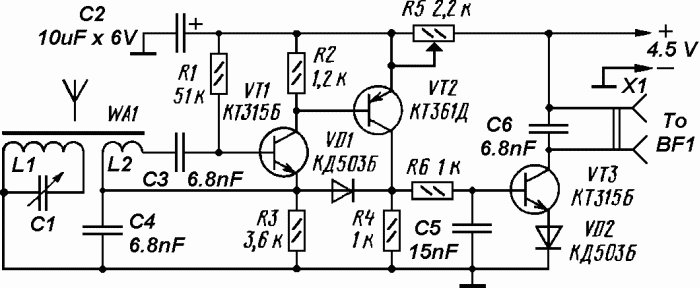
Simple Pulse Stretcher
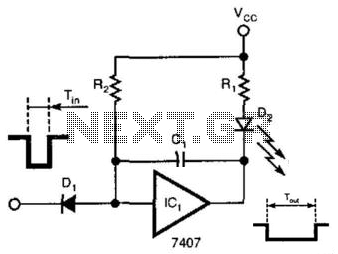
A single gate (open collector, non-inverting) generates a simple one-shot pulse that lasts for a duration equal to t, plus the RiCi time constant. R2 serves as a pull-up resistor to maintain the input of the gate high while awaiting a pulse.
The circuit described utilizes an open collector configuration, which is commonly employed in digital logic applications to create a one-shot pulse generator. The operation relies on the characteristics of the open collector output, which can effectively pull the output low while allowing an external resistor to pull it high when not actively driven low.
In this configuration, the pulse duration is determined by both a specified time interval 't' and the time constant associated with the resistor-capacitor (RC) network, denoted as RiCi. The time constant is critical as it defines how quickly the capacitor charges and discharges, directly influencing the length of the output pulse.
The resistor R2, functioning as a pull-up resistor, is connected between the supply voltage and the output of the gate. This arrangement ensures that the output remains high when there is no active pull-down from the open collector. When the gate is triggered, it drives the output low, allowing the capacitor in the RC network to charge or discharge based on the circuit's design. The combination of the resistor and capacitor values determines the pulse width, which is essential for applications requiring precise timing control.
In summary, this open collector one-shot circuit is a versatile component in digital electronics, providing reliable pulse generation with adjustable timing characteristics through the careful selection of resistor and capacitor values. A single gate (open collector, noninverting) produces a simple one-shot to produce a pulse that stretches equal to t he pulse duration, plus the RiCi time constant. R2 is a pull-up resistor to keep the gate"s input high while waiting for a pulse.
The circuit described utilizes an open collector configuration, which is commonly employed in digital logic applications to create a one-shot pulse generator. The operation relies on the characteristics of the open collector output, which can effectively pull the output low while allowing an external resistor to pull it high when not actively driven low.
In this configuration, the pulse duration is determined by both a specified time interval 't' and the time constant associated with the resistor-capacitor (RC) network, denoted as RiCi. The time constant is critical as it defines how quickly the capacitor charges and discharges, directly influencing the length of the output pulse.
The resistor R2, functioning as a pull-up resistor, is connected between the supply voltage and the output of the gate. This arrangement ensures that the output remains high when there is no active pull-down from the open collector. When the gate is triggered, it drives the output low, allowing the capacitor in the RC network to charge or discharge based on the circuit's design. The combination of the resistor and capacitor values determines the pulse width, which is essential for applications requiring precise timing control.
In summary, this open collector one-shot circuit is a versatile component in digital electronics, providing reliable pulse generation with adjustable timing characteristics through the careful selection of resistor and capacitor values. A single gate (open collector, noninverting) produces a simple one-shot to produce a pulse that stretches equal to t he pulse duration, plus the RiCi time constant. R2 is a pull-up resistor to keep the gate"s input high while waiting for a pulse.