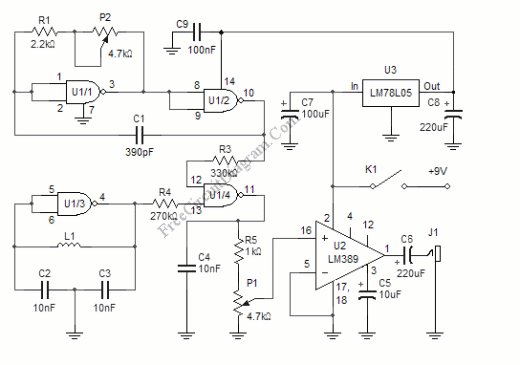
Simple Rumble Filter
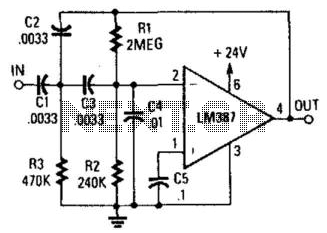
This circuit is a two-section active high-pass filter using an LM387, with a cutoff frequency below 50 Hz at a slope of 12 dB per octave. It will help reduce rumble caused by turntable defects in record systems.
The two-section active high-pass filter designed using the LM387 operational amplifier is intended to eliminate low-frequency noise, particularly rumble, which can arise from mechanical imperfections in turntables. The cutoff frequency is set below 50 Hz, ensuring that frequencies below this threshold are attenuated effectively, while allowing higher frequencies to pass through with minimal loss.
The circuit employs two cascaded stages of active filtering, which enhances the overall performance by achieving a steeper roll-off of 12 dB per octave. In practical terms, this means that for every doubling of frequency beyond the cutoff, the output signal level decreases by 12 dB. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in audio applications, where maintaining the integrity of the desired audio signal while suppressing unwanted low-frequency noise is crucial.
The LM387, a versatile operational amplifier, provides the necessary gain and bandwidth for the filter stages. It is configured in a non-inverting setup to ensure stability and low distortion in the output signal. The design incorporates feedback resistors and capacitors that define the filter's frequency response. Careful selection of these components is essential to achieve the desired cutoff frequency and filter characteristics.
Additionally, the circuit may include power supply bypass capacitors to enhance stability and reduce noise from the power supply, which can otherwise affect the performance of the filter. The layout of the circuit should minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which could alter the filter's response and degrade audio quality.
Overall, this active high-pass filter design is a valuable tool in audio systems, particularly for vinyl playback, where it addresses common issues related to low-frequency rumble, thereby improving the overall listening experience. This circuit is a two-section active HP filter using an LM387, with a cutoff below 50 Hz at 12-dB per octave. It will help reduce rumble as a result of turntable defects in record systems. 🔗 External reference
The two-section active high-pass filter designed using the LM387 operational amplifier is intended to eliminate low-frequency noise, particularly rumble, which can arise from mechanical imperfections in turntables. The cutoff frequency is set below 50 Hz, ensuring that frequencies below this threshold are attenuated effectively, while allowing higher frequencies to pass through with minimal loss.
The circuit employs two cascaded stages of active filtering, which enhances the overall performance by achieving a steeper roll-off of 12 dB per octave. In practical terms, this means that for every doubling of frequency beyond the cutoff, the output signal level decreases by 12 dB. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in audio applications, where maintaining the integrity of the desired audio signal while suppressing unwanted low-frequency noise is crucial.
The LM387, a versatile operational amplifier, provides the necessary gain and bandwidth for the filter stages. It is configured in a non-inverting setup to ensure stability and low distortion in the output signal. The design incorporates feedback resistors and capacitors that define the filter's frequency response. Careful selection of these components is essential to achieve the desired cutoff frequency and filter characteristics.
Additionally, the circuit may include power supply bypass capacitors to enhance stability and reduce noise from the power supply, which can otherwise affect the performance of the filter. The layout of the circuit should minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which could alter the filter's response and degrade audio quality.
Overall, this active high-pass filter design is a valuable tool in audio systems, particularly for vinyl playback, where it addresses common issues related to low-frequency rumble, thereby improving the overall listening experience. This circuit is a two-section active HP filter using an LM387, with a cutoff below 50 Hz at 12-dB per octave. It will help reduce rumble as a result of turntable defects in record systems. 🔗 External reference