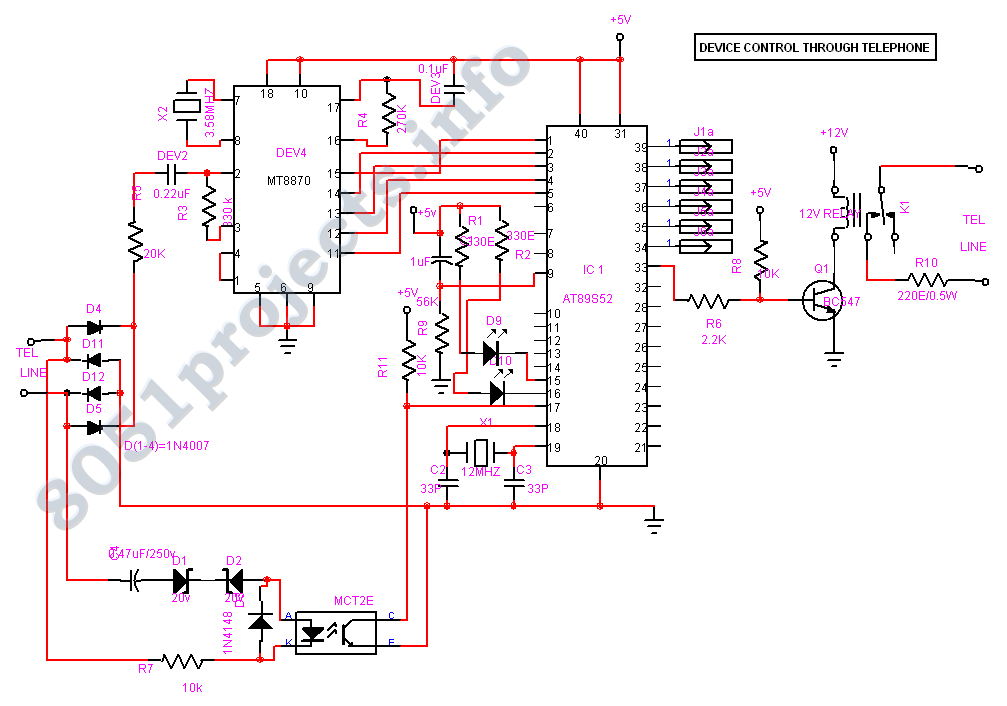
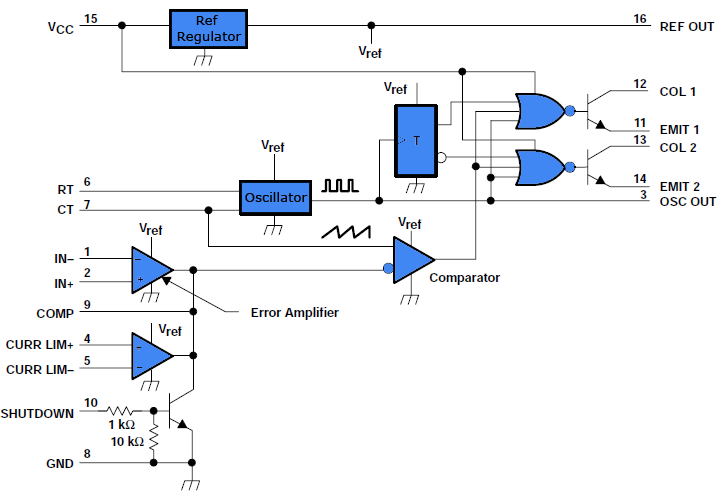
Simple Telephone Transmiter
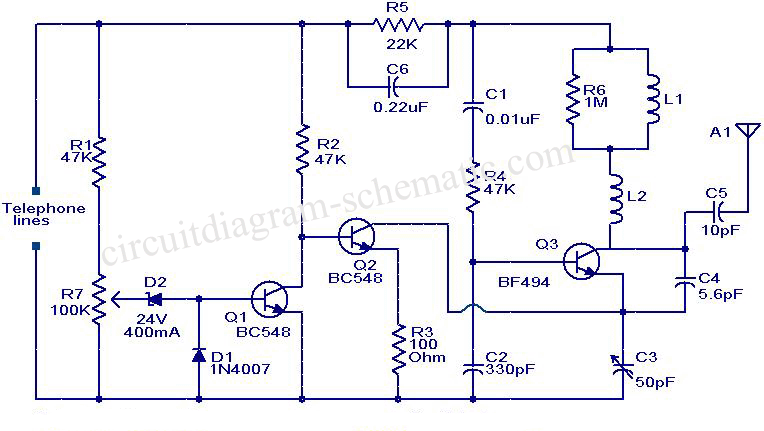
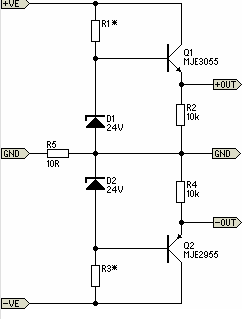
This circuit diagram represents a simple yet effective transmitter circuit, capable of transmitting telephone conversations. When the telephone receiver is on the hook, the line voltage is approximately 48 volts. The R7 preset resistor is adjusted to achieve a voltage of 24.7 V between the cathode of Zener diode D2 and ground. Under these conditions, Zener diode D2 enters breakdown mode, causing transistor T1 to conduct, which in turn switches transistor T2 OFF. When the receiver is taken off the hook, the line voltage decreases to about 11 volts, resulting in a change in the circuit's operation.
This transmitter circuit operates based on the principle of detecting the state of a telephone receiver. The line voltage is crucial for determining the operational state of the circuit. When the receiver is on the hook, the high line voltage allows for the Zener diode D2 to function in its breakdown region, which is essential for the activation of transistor T1. The conduction of T1 is significant because it controls the state of T2, effectively isolating the transmitter from the line to prevent unwanted signal transmission during idle periods.
The R7 preset resistor plays a vital role in fine-tuning the voltage at the cathode of D2, ensuring that the Zener diode operates correctly at its breakdown voltage. The precise adjustment of this resistor is essential for maintaining the desired functionality of the circuit.
Upon lifting the receiver off the hook, the line voltage drops to approximately 11 volts, which alters the operational state of the transistors. This voltage drop ceases the conduction of T1, thereby allowing T2 to turn ON. The activation of T2 enables the circuit to transmit audio signals, facilitating the transmission of telephone conversations.
This circuit design emphasizes the importance of voltage levels in controlling the state of transistors, which are pivotal in switching applications. The simplicity of the design, combined with the effective use of Zener diodes and transistors, makes it a practical solution for audio transmission in telecommunication systems. Proper understanding and implementation of this circuit can lead to successful applications in various telecommunication projects.This circuit is a circuit diagram of a simple transmitter, but very useful circuit which can be used to transmit telephone conversations. When the telephone receiver on the hook to the line voltage of about 48 volts. R7 preset is adjusted to 24.7 V between the cathode of D2 and ground. In voltage Zener diode D2 will be in the breakdown and the transistor T1 will conduct. This makes the transistor T2 OFF. When the receiver off the hook, the line voltage drops to about 11 volts. This makes the tra. 🔗 External reference
This transmitter circuit operates based on the principle of detecting the state of a telephone receiver. The line voltage is crucial for determining the operational state of the circuit. When the receiver is on the hook, the high line voltage allows for the Zener diode D2 to function in its breakdown region, which is essential for the activation of transistor T1. The conduction of T1 is significant because it controls the state of T2, effectively isolating the transmitter from the line to prevent unwanted signal transmission during idle periods.
The R7 preset resistor plays a vital role in fine-tuning the voltage at the cathode of D2, ensuring that the Zener diode operates correctly at its breakdown voltage. The precise adjustment of this resistor is essential for maintaining the desired functionality of the circuit.
Upon lifting the receiver off the hook, the line voltage drops to approximately 11 volts, which alters the operational state of the transistors. This voltage drop ceases the conduction of T1, thereby allowing T2 to turn ON. The activation of T2 enables the circuit to transmit audio signals, facilitating the transmission of telephone conversations.
This circuit design emphasizes the importance of voltage levels in controlling the state of transistors, which are pivotal in switching applications. The simplicity of the design, combined with the effective use of Zener diodes and transistors, makes it a practical solution for audio transmission in telecommunication systems. Proper understanding and implementation of this circuit can lead to successful applications in various telecommunication projects.This circuit is a circuit diagram of a simple transmitter, but very useful circuit which can be used to transmit telephone conversations. When the telephone receiver on the hook to the line voltage of about 48 volts. R7 preset is adjusted to 24.7 V between the cathode of D2 and ground. In voltage Zener diode D2 will be in the breakdown and the transistor T1 will conduct. This makes the transistor T2 OFF. When the receiver off the hook, the line voltage drops to about 11 volts. This makes the tra. 🔗 External reference