Simplified Long-Distance Call LockCircuit
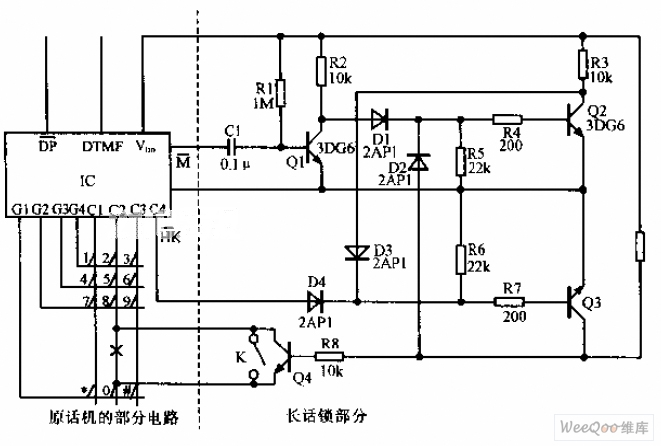
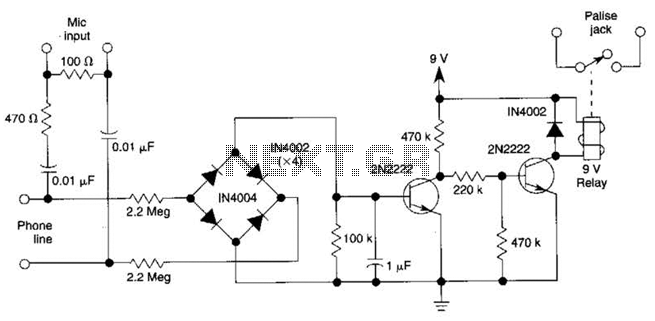
A simplified long-distance call lock is illustrated in the accompanying image. This device is designed to prevent long-distance calls while maintaining the original functionality of the phone. Although it consumes power, it exhibits excellent compatibility. When switch K is configured as depicted, dialing the number 0 will be unsuccessful, thereby blocking long-distance calls.
The long-distance call lock circuit is an essential tool for managing telecommunication expenses, particularly in environments where unauthorized long-distance calls may occur. The circuit typically incorporates a relay or a transistor switch that is controlled by the position of switch K.
When switch K is in the designated position, it engages a blocking mechanism that interrupts the dialing process for long-distance calls. The circuit is designed to detect the dialing of the number '0', which is often the prefix for long-distance calls in many telecommunication systems. The blocking mechanism can be implemented using a combination of resistors, capacitors, and diodes that work together to create a control signal to the relay or transistor.
The power consumption of the circuit is a critical consideration, as it must be low enough to avoid excessive energy costs while still providing reliable operation. The compatibility of the device with various telephone systems is facilitated through the use of standard components that can be easily integrated into existing phone lines without requiring significant modifications.
In summary, this long-distance call lock circuit effectively prevents unauthorized long-distance dialing while preserving the basic functionality of the telephone system, making it a valuable addition to any telecommunication setup.Simplified long-distance call lock is shown in the above picture. The lock can lock out the long-distance call without affecting the original function. It ispower-consuming, but it has very good compatibility. If switch K is placed as the picture shows, first dial the number 0,, and you ll find the 0 can not be dialed and the long-distance call can not.. 🔗 External reference
The long-distance call lock circuit is an essential tool for managing telecommunication expenses, particularly in environments where unauthorized long-distance calls may occur. The circuit typically incorporates a relay or a transistor switch that is controlled by the position of switch K.
When switch K is in the designated position, it engages a blocking mechanism that interrupts the dialing process for long-distance calls. The circuit is designed to detect the dialing of the number '0', which is often the prefix for long-distance calls in many telecommunication systems. The blocking mechanism can be implemented using a combination of resistors, capacitors, and diodes that work together to create a control signal to the relay or transistor.
The power consumption of the circuit is a critical consideration, as it must be low enough to avoid excessive energy costs while still providing reliable operation. The compatibility of the device with various telephone systems is facilitated through the use of standard components that can be easily integrated into existing phone lines without requiring significant modifications.
In summary, this long-distance call lock circuit effectively prevents unauthorized long-distance dialing while preserving the basic functionality of the telephone system, making it a valuable addition to any telecommunication setup.Simplified long-distance call lock is shown in the above picture. The lock can lock out the long-distance call without affecting the original function. It ispower-consuming, but it has very good compatibility. If switch K is placed as the picture shows, first dial the number 0,, and you ll find the 0 can not be dialed and the long-distance call can not.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713