Sine wave oscillator
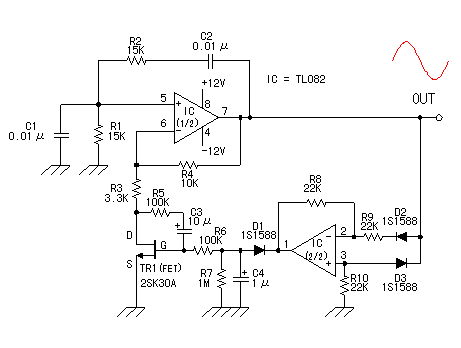
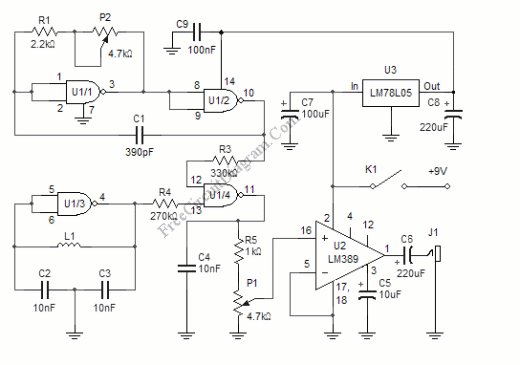
The Wien bridge sine wave oscillator is an oscillator that operates by utilizing positive feedback to return the oscillation output to the input. The key aspect of this circuit is the negative feedback mechanism, which ensures stable oscillation operation. In this design, the resistance value of the Field Effect Transistor (FET) is adjusted based on the direct current (DC) voltage derived from rectifying the oscillation output in a full-wave configuration, contributing to the stability of the oscillation. The sine wave oscillator is inherently more challenging to design than square wave or triangular wave oscillators due to the potential for distortion in the oscillation signal.
The Wien bridge oscillator circuit is a classic configuration used to generate sine waves with high stability and low distortion. It typically consists of an operational amplifier (op-amp) and a combination of resistors and capacitors arranged in a bridge configuration. The circuit operates by balancing the impedances in the bridge to achieve oscillation at a specific frequency determined by the resistor and capacitor values.
In this particular implementation, the use of a Field Effect Transistor (FET) allows for dynamic adjustment of the resistance in response to the amplitude of the output signal. This feedback mechanism helps maintain a constant amplitude of oscillation, which is crucial for minimizing distortion. The FET acts as a variable resistor, enabling fine-tuning of the circuit's gain, which is essential for sustaining oscillation without leading to amplitude fluctuations that could result in signal distortion.
The frequency of oscillation is determined by the equation f = 1 / (2πRC), where R represents the resistance and C represents the capacitance in the circuit. By selecting appropriate values for R and C, the desired frequency can be achieved. Additionally, the full-wave rectification of the output signal is implemented to provide a stable DC voltage that is used to control the FET, ensuring that the oscillation remains consistent over time.
Overall, the Wien bridge sine wave oscillator is a sophisticated circuit that effectively balances the need for stable oscillation with minimal distortion, making it suitable for various applications in signal generation and waveform synthesis.The Wien bridge sine wave oscillator to introduce is the oscillator which works in the oscillation by returning(positive feedback) the oscillation output to the input. The point of this circuit is the negative feedback circuit to make the oscillation operation be stable.
The circuit to be using this time changes the resistance value of the Field E ffect-type Transistor(FET) at the d. c. voltage which rectified the oscillation output in the full wave and is making the oscillation operation be stable. The sine wave oscillator is the oscillator which is difficult to make because the distortion of the oscillation signal occurs compared with the square wave oscillator, the triangular wave oscillator.
🔗 External reference
The Wien bridge oscillator circuit is a classic configuration used to generate sine waves with high stability and low distortion. It typically consists of an operational amplifier (op-amp) and a combination of resistors and capacitors arranged in a bridge configuration. The circuit operates by balancing the impedances in the bridge to achieve oscillation at a specific frequency determined by the resistor and capacitor values.
In this particular implementation, the use of a Field Effect Transistor (FET) allows for dynamic adjustment of the resistance in response to the amplitude of the output signal. This feedback mechanism helps maintain a constant amplitude of oscillation, which is crucial for minimizing distortion. The FET acts as a variable resistor, enabling fine-tuning of the circuit's gain, which is essential for sustaining oscillation without leading to amplitude fluctuations that could result in signal distortion.
The frequency of oscillation is determined by the equation f = 1 / (2πRC), where R represents the resistance and C represents the capacitance in the circuit. By selecting appropriate values for R and C, the desired frequency can be achieved. Additionally, the full-wave rectification of the output signal is implemented to provide a stable DC voltage that is used to control the FET, ensuring that the oscillation remains consistent over time.
Overall, the Wien bridge sine wave oscillator is a sophisticated circuit that effectively balances the need for stable oscillation with minimal distortion, making it suitable for various applications in signal generation and waveform synthesis.The Wien bridge sine wave oscillator to introduce is the oscillator which works in the oscillation by returning(positive feedback) the oscillation output to the input. The point of this circuit is the negative feedback circuit to make the oscillation operation be stable.
The circuit to be using this time changes the resistance value of the Field E ffect-type Transistor(FET) at the d. c. voltage which rectified the oscillation output in the full wave and is making the oscillation operation be stable. The sine wave oscillator is the oscillator which is difficult to make because the distortion of the oscillation signal occurs compared with the square wave oscillator, the triangular wave oscillator.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713