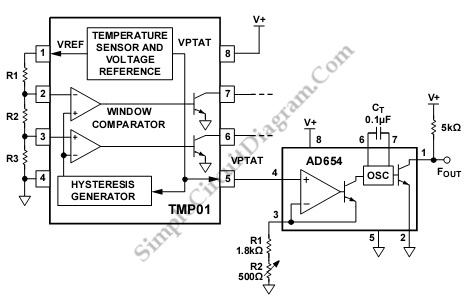
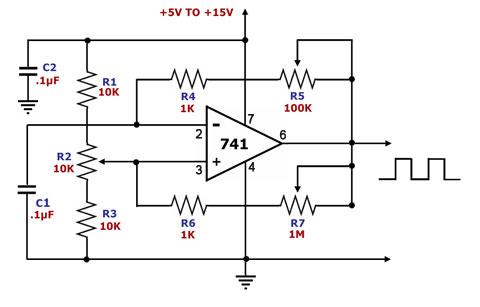
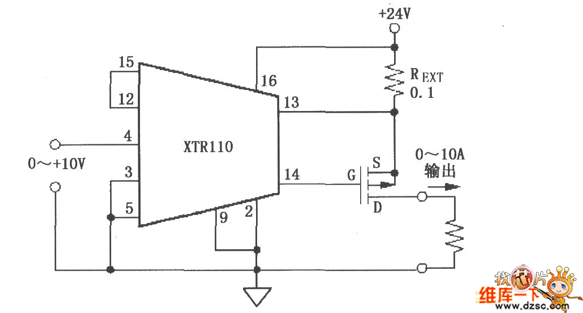
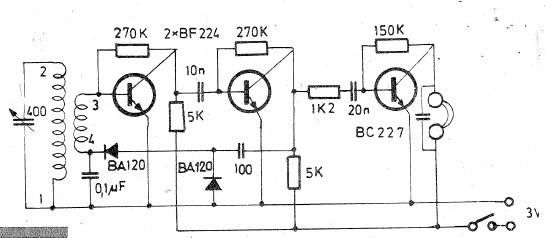
Sine Wave To TTL Converter

The circuit is designed to convert sinusoidal input signals into TTL output signals and can process input voltages exceeding 100 mV.
This circuit typically employs a comparator to achieve the conversion from sinusoidal to TTL levels. The sinusoidal input signal is fed into the non-inverting input of the comparator. The inverting input is connected to a reference voltage, which can be set at half the supply voltage for optimal performance.
When the sinusoidal signal exceeds the reference voltage, the comparator outputs a high TTL signal (typically close to the supply voltage, such as 5V for standard TTL). Conversely, when the sinusoidal signal falls below the reference voltage, the output transitions to a low TTL signal (close to 0V).
To ensure proper operation, the circuit may include hysteresis, which helps to prevent false triggering due to noise or small fluctuations in the input signal. This is often implemented by adding a feedback resistor from the output of the comparator back to the non-inverting input, thereby creating a stable operating point.
The circuit can be powered by a dual supply or a single supply, depending on the design requirements. Additionally, the input signal should be AC-coupled through a capacitor to block any DC offset that could affect the performance of the comparator.
Overall, this circuit is suitable for applications where it is necessary to convert analog sinusoidal signals into digital TTL signals for further processing or interfacing with digital logic circuits.As the title implies, the present circuit is intended to convert sinusoidal input signals to TTL output signals. It can handle inputs of more than 100 mV.. 🔗 External reference
This circuit typically employs a comparator to achieve the conversion from sinusoidal to TTL levels. The sinusoidal input signal is fed into the non-inverting input of the comparator. The inverting input is connected to a reference voltage, which can be set at half the supply voltage for optimal performance.
When the sinusoidal signal exceeds the reference voltage, the comparator outputs a high TTL signal (typically close to the supply voltage, such as 5V for standard TTL). Conversely, when the sinusoidal signal falls below the reference voltage, the output transitions to a low TTL signal (close to 0V).
To ensure proper operation, the circuit may include hysteresis, which helps to prevent false triggering due to noise or small fluctuations in the input signal. This is often implemented by adding a feedback resistor from the output of the comparator back to the non-inverting input, thereby creating a stable operating point.
The circuit can be powered by a dual supply or a single supply, depending on the design requirements. Additionally, the input signal should be AC-coupled through a capacitor to block any DC offset that could affect the performance of the comparator.
Overall, this circuit is suitable for applications where it is necessary to convert analog sinusoidal signals into digital TTL signals for further processing or interfacing with digital logic circuits.As the title implies, the present circuit is intended to convert sinusoidal input signals to TTL output signals. It can handle inputs of more than 100 mV.. 🔗 External reference