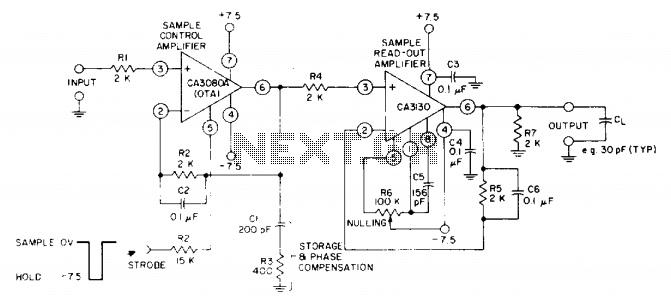
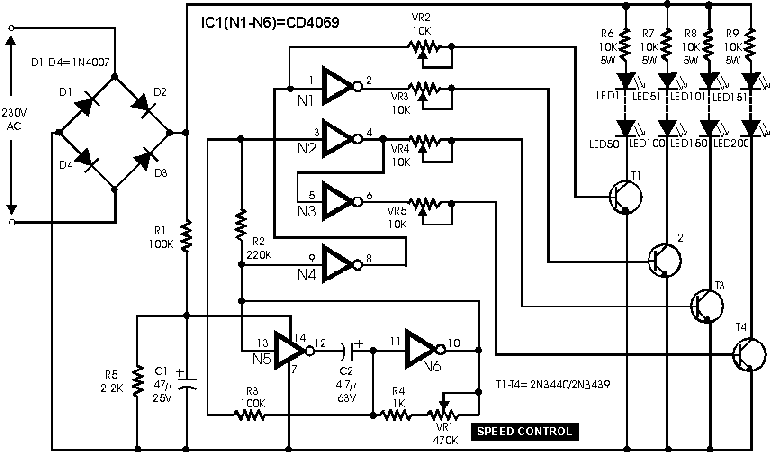
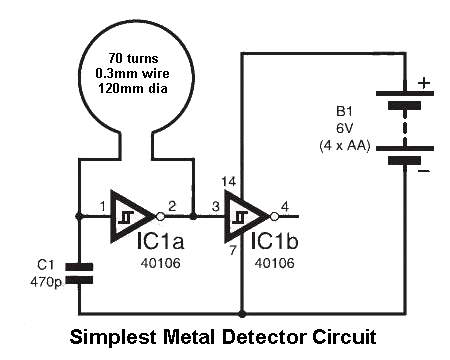
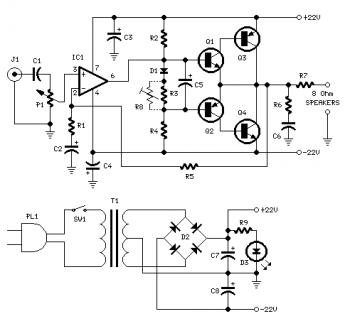
Single cell (1.5 Volt) LED flasher circuit
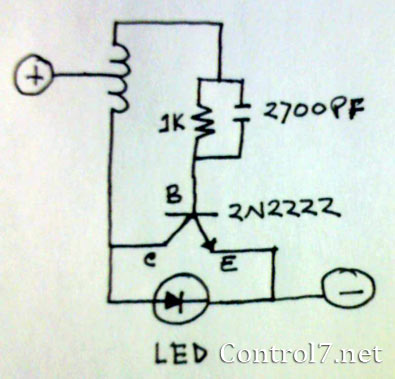
The LED is a fascinating component for amateur electronics hobbyists. The primary characteristic of an LED is that it requires a minimum of 3 volts to illuminate. Various circuits have been discovered to drive an LED using a single alkaline or manganese cell.
LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. They are widely used in various applications due to their efficiency, longevity, and versatility. The requirement of a minimum forward voltage, typically around 3 volts for standard LEDs, can present challenges when interfacing with lower voltage power sources, such as a single-cell alkaline (1.5V) or manganese (1.2V) battery.
To effectively illuminate an LED from a single-cell battery, a circuit can be designed that boosts the voltage to meet the LED's forward voltage requirement. One common approach is to use a boost converter circuit, which steps up the voltage from the battery to the necessary level for the LED.
A simple boost converter circuit may include an inductor, a switch (typically a transistor), a diode, and a capacitor. When the switch is closed, current flows through the inductor, storing energy in its magnetic field. When the switch opens, the inductor releases its stored energy, causing the voltage to increase. This boosted voltage can then be directed to the LED, allowing it to illuminate effectively.
Additionally, a resistor may be included in series with the LED to limit the current flowing through it, preventing damage. The value of this resistor can be calculated using Ohm's law, taking into account the forward voltage of the LED and the desired current rating.
In summary, while LEDs require a minimum of 3 volts to operate, various circuit designs, such as boost converters, can enable their use with lower voltage power sources, enhancing their accessibility and application in amateur electronics projects.LED is the most interesting part of amateur electronics hobbyist. The main barer of LED is, it needs minimum 3 vlots to illuminate. I`ve found many circuits to drive LED by a single cell alkaline or manganese cell. 🔗 External reference
LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. They are widely used in various applications due to their efficiency, longevity, and versatility. The requirement of a minimum forward voltage, typically around 3 volts for standard LEDs, can present challenges when interfacing with lower voltage power sources, such as a single-cell alkaline (1.5V) or manganese (1.2V) battery.
To effectively illuminate an LED from a single-cell battery, a circuit can be designed that boosts the voltage to meet the LED's forward voltage requirement. One common approach is to use a boost converter circuit, which steps up the voltage from the battery to the necessary level for the LED.
A simple boost converter circuit may include an inductor, a switch (typically a transistor), a diode, and a capacitor. When the switch is closed, current flows through the inductor, storing energy in its magnetic field. When the switch opens, the inductor releases its stored energy, causing the voltage to increase. This boosted voltage can then be directed to the LED, allowing it to illuminate effectively.
Additionally, a resistor may be included in series with the LED to limit the current flowing through it, preventing damage. The value of this resistor can be calculated using Ohm's law, taking into account the forward voltage of the LED and the desired current rating.
In summary, while LEDs require a minimum of 3 volts to operate, various circuit designs, such as boost converters, can enable their use with lower voltage power sources, enhancing their accessibility and application in amateur electronics projects.LED is the most interesting part of amateur electronics hobbyist. The main barer of LED is, it needs minimum 3 vlots to illuminate. I`ve found many circuits to drive LED by a single cell alkaline or manganese cell. 🔗 External reference