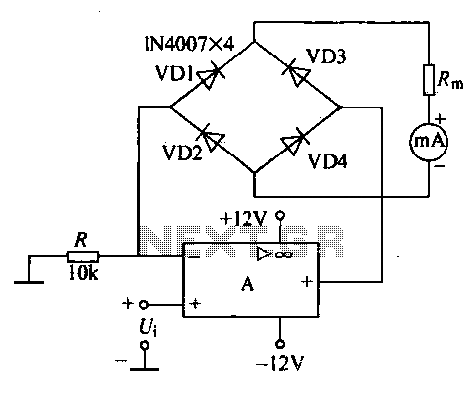
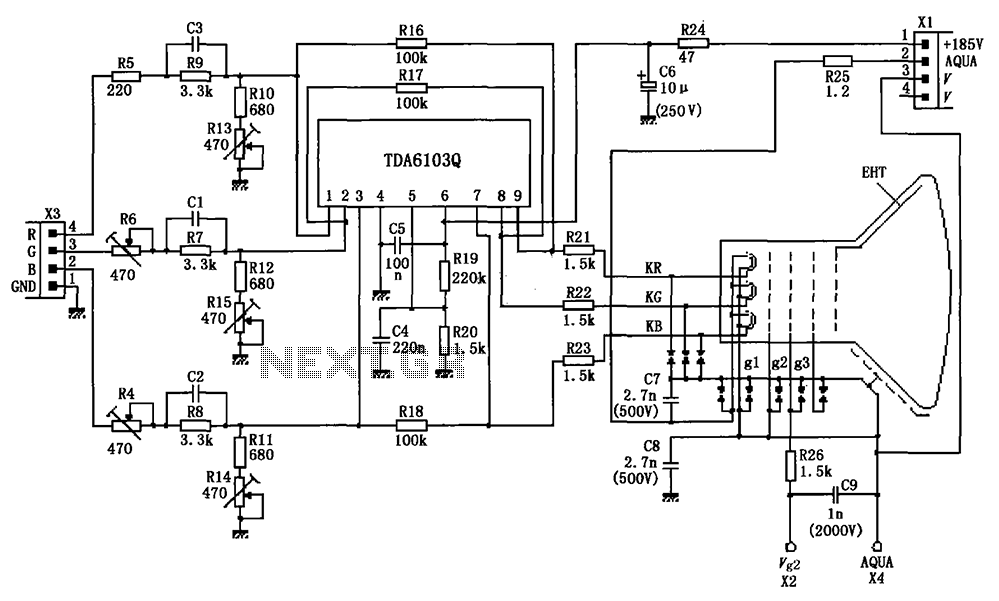
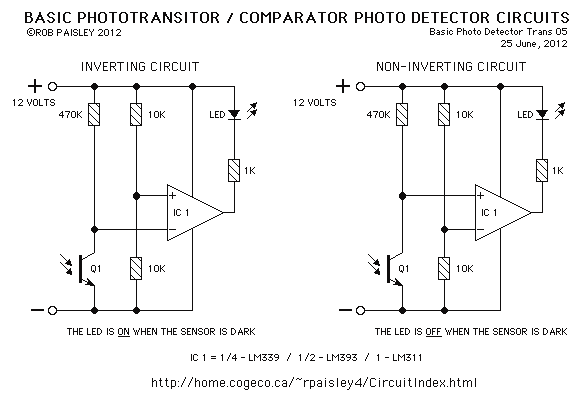
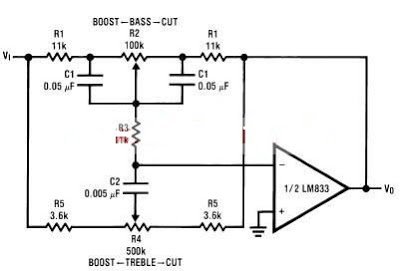
Single-Chip Dc Supply Circuit
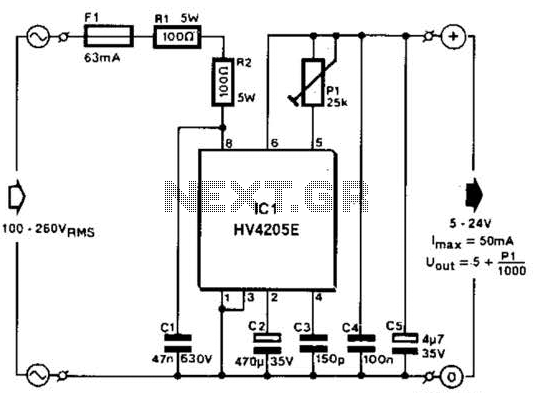
Direct derivation of 5 to 24 Vdc from AC mains without a transformer is possible with this circuit. Note that a direct mains connection to the DC output exists. Suitable safety precautions must be taken.
This circuit design allows for the conversion of AC mains voltage to a DC output voltage ranging from 5 to 24 volts without the use of a transformer. The primary advantage of this approach is its compact size and reduced weight, as transformers can add significant bulk to power supply designs. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the inherent risks associated with connecting directly to AC mains, necessitating stringent safety measures.
The circuit typically employs a rectification stage, which can be implemented using diodes arranged in a bridge configuration. This setup converts the AC voltage into pulsating DC. A filtering stage follows the rectification, often using capacitors to smooth out the pulsating DC into a more stable voltage.
To regulate the output voltage within the specified range of 5 to 24 V, a voltage regulator may be incorporated. This component ensures that variations in load do not affect the output voltage significantly. Common choices for voltage regulation include linear regulators or switching regulators, depending on the efficiency requirements and thermal considerations of the application.
Safety precautions are paramount when designing circuits that interface directly with AC mains. Isolation techniques, such as opto-isolators or protective fuses, should be implemented to safeguard both the circuit and the user. Additionally, proper enclosure and insulation are critical to prevent accidental contact with live components.
Overall, while this circuit offers a straightforward solution for deriving DC voltage from AC mains without a transformer, careful attention to design and safety standards is essential to ensure reliable and safe operation. Direct derivation of 5 to 24 Vdc from ac mains, without a transformer is possible with tiiis circuit. Note that a direct mains connection to the dc output exists. Suitable safety precautixyris must be taken. 🔗 External reference
This circuit design allows for the conversion of AC mains voltage to a DC output voltage ranging from 5 to 24 volts without the use of a transformer. The primary advantage of this approach is its compact size and reduced weight, as transformers can add significant bulk to power supply designs. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the inherent risks associated with connecting directly to AC mains, necessitating stringent safety measures.
The circuit typically employs a rectification stage, which can be implemented using diodes arranged in a bridge configuration. This setup converts the AC voltage into pulsating DC. A filtering stage follows the rectification, often using capacitors to smooth out the pulsating DC into a more stable voltage.
To regulate the output voltage within the specified range of 5 to 24 V, a voltage regulator may be incorporated. This component ensures that variations in load do not affect the output voltage significantly. Common choices for voltage regulation include linear regulators or switching regulators, depending on the efficiency requirements and thermal considerations of the application.
Safety precautions are paramount when designing circuits that interface directly with AC mains. Isolation techniques, such as opto-isolators or protective fuses, should be implemented to safeguard both the circuit and the user. Additionally, proper enclosure and insulation are critical to prevent accidental contact with live components.
Overall, while this circuit offers a straightforward solution for deriving DC voltage from AC mains without a transformer, careful attention to design and safety standards is essential to ensure reliable and safe operation. Direct derivation of 5 to 24 Vdc from ac mains, without a transformer is possible with tiiis circuit. Note that a direct mains connection to the dc output exists. Suitable safety precautixyris must be taken. 🔗 External reference