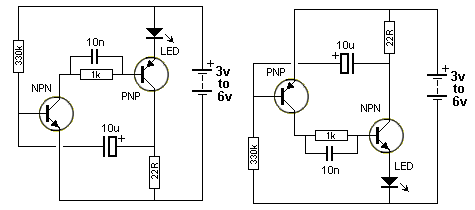
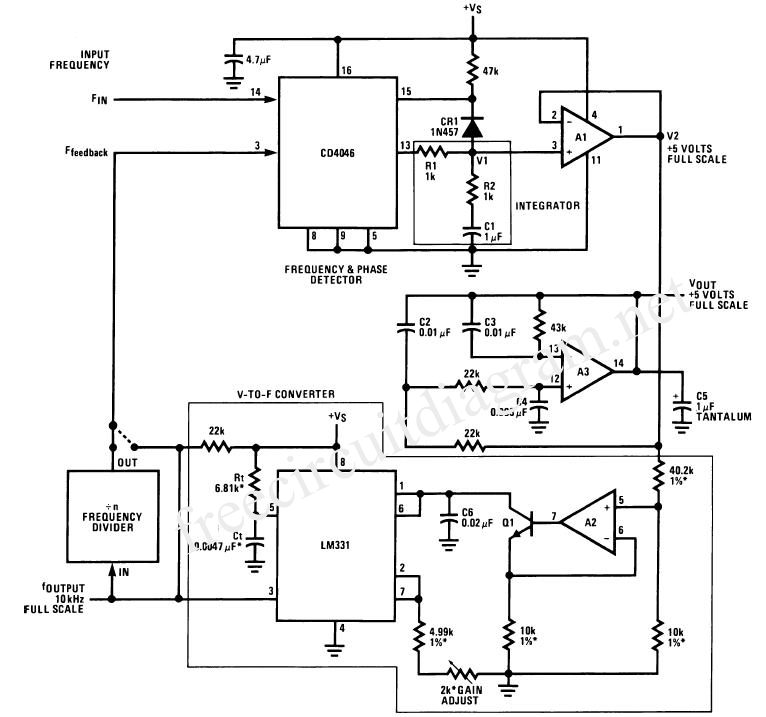
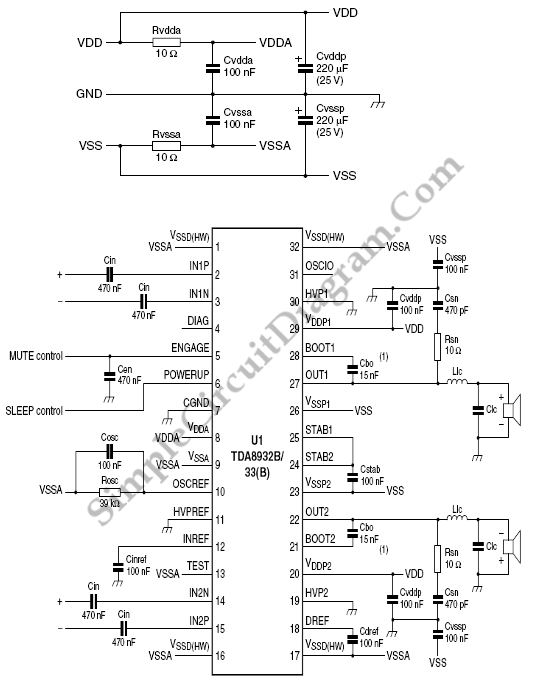
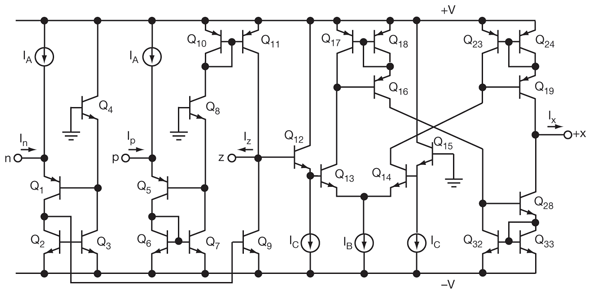
Single injector-tracer
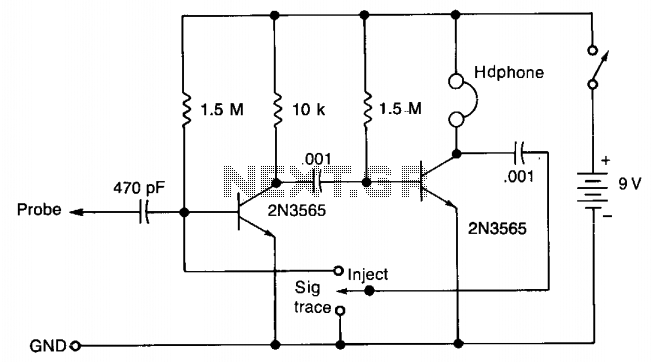
In the "Trace" mode, the non-linear operation of the amplifier will detect modulated RF signals, which will be filtered by the 0.001 µF capacitor and heard in the headphones. In the "Inject" mode, this circuit will provide a nominal square wave output in the audio range, with harmonics that should be audible at several MHz.
The described circuit features two operational modes: "Trace" and "Inject." In "Trace" mode, the circuit utilizes a non-linear amplifier configuration to effectively detect modulated radio frequency (RF) signals. The amplifier's non-linear characteristics enable it to respond to variations in the RF signal, allowing for the extraction of modulation information. The output from the amplifier is then filtered through a capacitor with a value of 0.001 µF, which serves to block unwanted frequencies while allowing the desired audio frequencies to pass through. This filtered audio signal is then routed to headphones, enabling the user to listen to the detected modulated RF signals.
In "Inject" mode, the circuit generates a nominal square wave output within the audio frequency range. The square wave is characterized by its sharp transitions between high and low states, producing a rich harmonic content. The harmonics generated by the square wave can extend into the megahertz (MHz) range, making them audible when monitored through appropriate audio equipment. This mode is particularly useful for testing and calibration purposes, as it allows for the examination of the circuit's response to different frequency components.
Overall, the circuit effectively combines RF detection and audio signal generation, making it a versatile tool for various applications in electronics, including signal analysis and testing. In the "Trace" mode the non-linear operation of the amplifier will detect modulated rf signals which will be filtered by the .001 µ¥ capacitor and heard in the headphones. This circuit will provide a nominal square wave output in the audio range in the "Inject" mode, the harmonics of which should be heard at several MHz. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit features two operational modes: "Trace" and "Inject." In "Trace" mode, the circuit utilizes a non-linear amplifier configuration to effectively detect modulated radio frequency (RF) signals. The amplifier's non-linear characteristics enable it to respond to variations in the RF signal, allowing for the extraction of modulation information. The output from the amplifier is then filtered through a capacitor with a value of 0.001 µF, which serves to block unwanted frequencies while allowing the desired audio frequencies to pass through. This filtered audio signal is then routed to headphones, enabling the user to listen to the detected modulated RF signals.
In "Inject" mode, the circuit generates a nominal square wave output within the audio frequency range. The square wave is characterized by its sharp transitions between high and low states, producing a rich harmonic content. The harmonics generated by the square wave can extend into the megahertz (MHz) range, making them audible when monitored through appropriate audio equipment. This mode is particularly useful for testing and calibration purposes, as it allows for the examination of the circuit's response to different frequency components.
Overall, the circuit effectively combines RF detection and audio signal generation, making it a versatile tool for various applications in electronics, including signal analysis and testing. In the "Trace" mode the non-linear operation of the amplifier will detect modulated rf signals which will be filtered by the .001 µ¥ capacitor and heard in the headphones. This circuit will provide a nominal square wave output in the audio range in the "Inject" mode, the harmonics of which should be heard at several MHz. 🔗 External reference