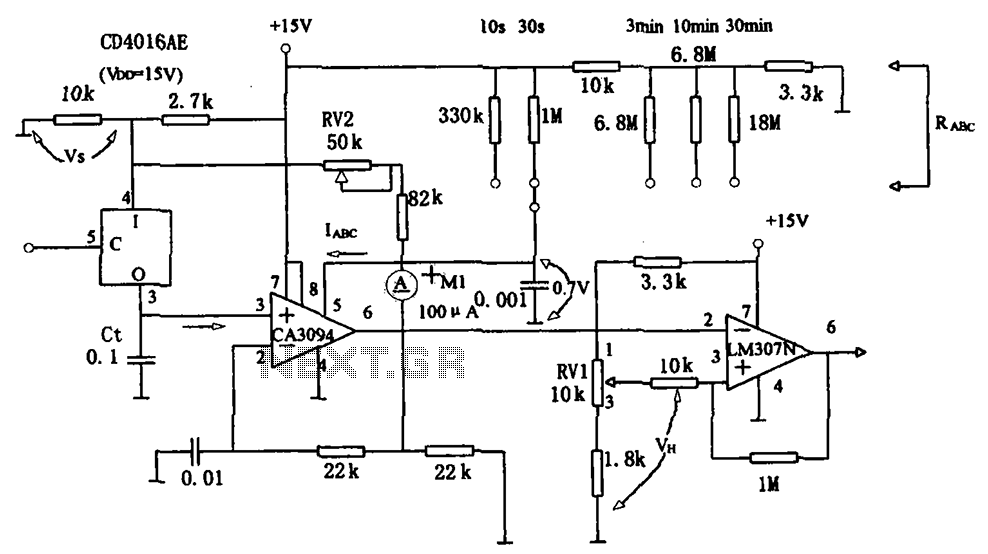
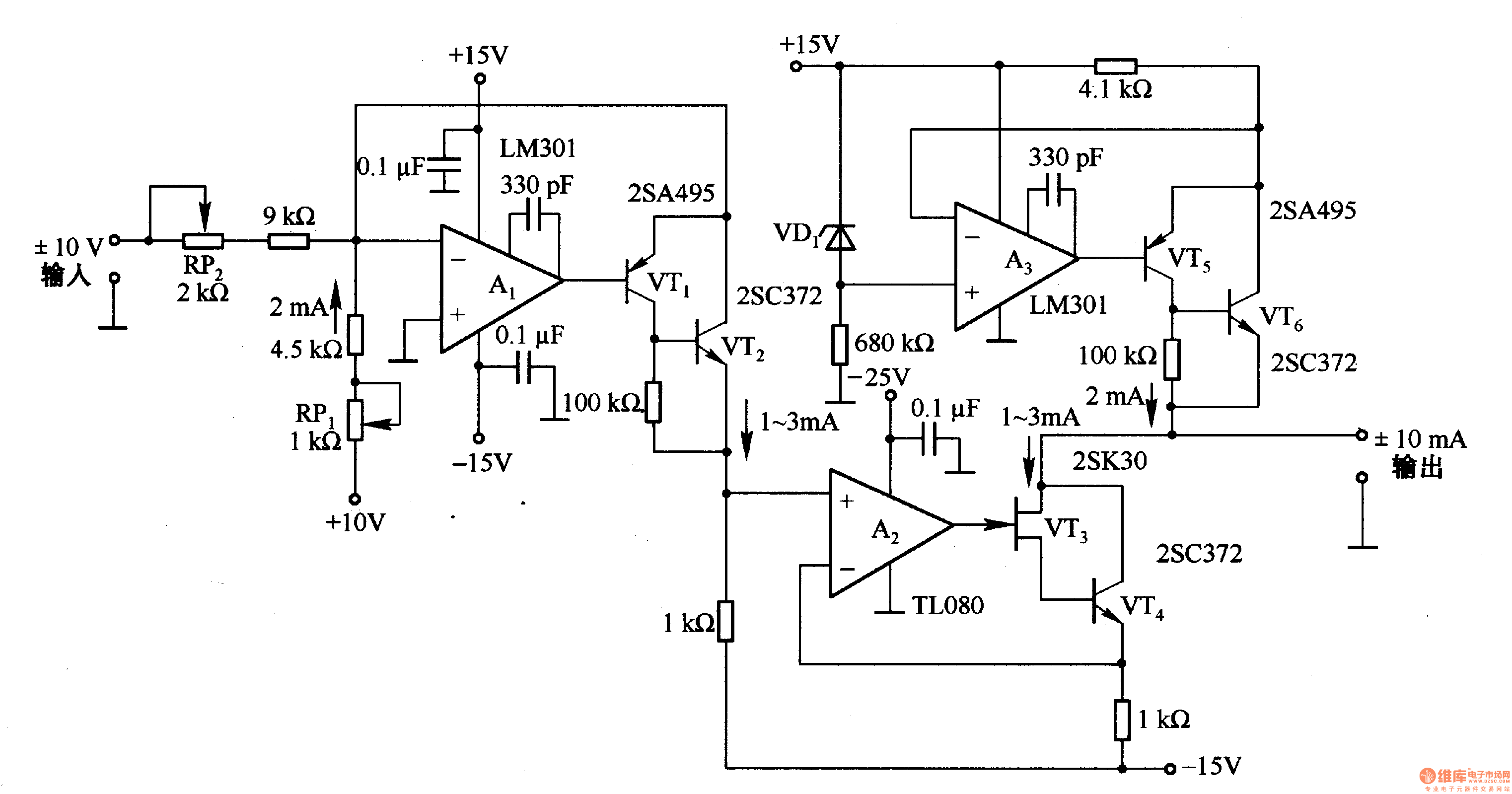
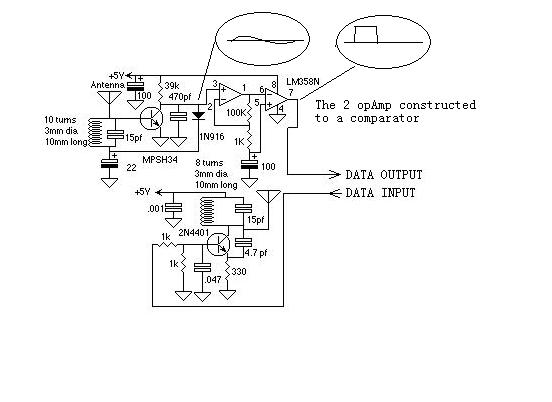
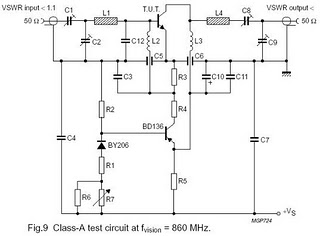
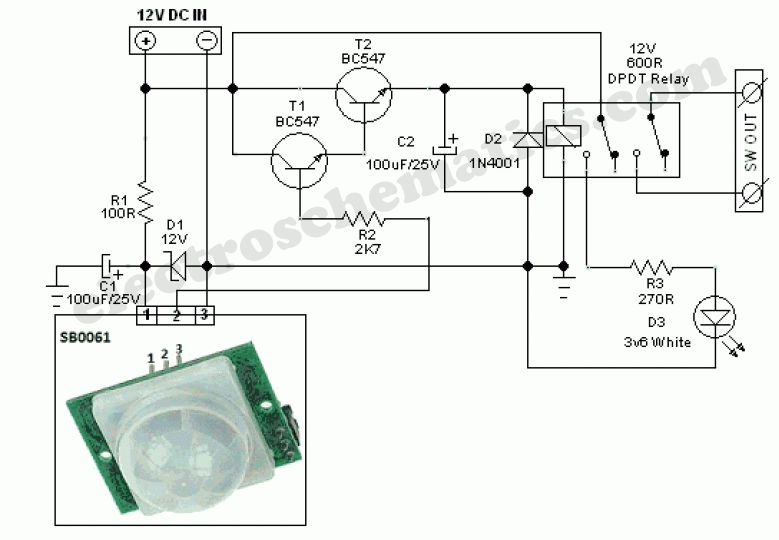
Single Transistor Half-Wave Peak Detector Circuit
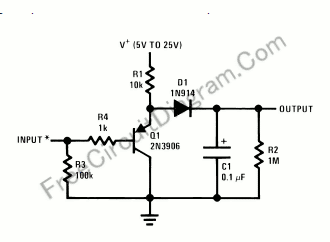
Using only a single transistor and a few passive components, a fairly sensitive peak detector circuit can be built. This peak detector circuit is suitable for various applications.
The peak detector circuit utilizes a single transistor, typically configured in a common-emitter arrangement, to achieve its functionality. The primary role of the transistor is to amplify the input signal, allowing for the detection of peak values. The circuit also incorporates passive components such as resistors and capacitors, which are essential for setting the time constant and determining the sensitivity of the detector.
In a standard configuration, the input signal is applied to the base of the transistor, which responds by conducting and allowing current to flow through the collector. A diode is often included in the circuit to ensure that the capacitor, which stores the peak voltage, only charges when the input signal exceeds the previously detected peak. This prevents the capacitor from discharging back through the input.
The output of the circuit is taken from the junction of the capacitor and the diode, providing a voltage that corresponds to the peak value of the input signal. By adjusting the values of the passive components, such as the resistor connected to the base, the sensitivity and response time of the peak detector can be tailored to suit specific application needs.
This type of peak detector circuit is particularly useful in audio processing, signal conditioning, and various measurement applications where it is necessary to capture and hold the maximum voltage level of an incoming signal. Overall, the simplicity of the design, combined with the effectiveness of the peak detection, makes this circuit an attractive option for engineers and hobbyists alike.Using only a single transistor and few passive components, you can build a fairly sensitive peak detector. circuit This peak detector circuit is suitable for. 🔗 External reference
The peak detector circuit utilizes a single transistor, typically configured in a common-emitter arrangement, to achieve its functionality. The primary role of the transistor is to amplify the input signal, allowing for the detection of peak values. The circuit also incorporates passive components such as resistors and capacitors, which are essential for setting the time constant and determining the sensitivity of the detector.
In a standard configuration, the input signal is applied to the base of the transistor, which responds by conducting and allowing current to flow through the collector. A diode is often included in the circuit to ensure that the capacitor, which stores the peak voltage, only charges when the input signal exceeds the previously detected peak. This prevents the capacitor from discharging back through the input.
The output of the circuit is taken from the junction of the capacitor and the diode, providing a voltage that corresponds to the peak value of the input signal. By adjusting the values of the passive components, such as the resistor connected to the base, the sensitivity and response time of the peak detector can be tailored to suit specific application needs.
This type of peak detector circuit is particularly useful in audio processing, signal conditioning, and various measurement applications where it is necessary to capture and hold the maximum voltage level of an incoming signal. Overall, the simplicity of the design, combined with the effectiveness of the peak detection, makes this circuit an attractive option for engineers and hobbyists alike.Using only a single transistor and few passive components, you can build a fairly sensitive peak detector. circuit This peak detector circuit is suitable for. 🔗 External reference