TV RF Amplifier 5W Circuit With BLW98
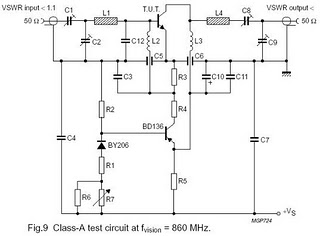
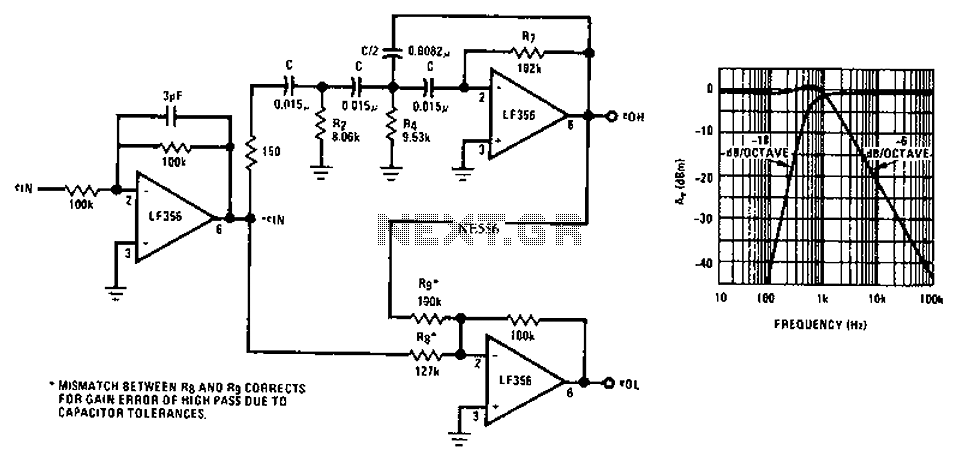
The circuit is designed for driving small UHF TV transmitters, providing a gain of 7 dB and capable of amplifying signals within the frequency range of 470-860 MHz. Key components include resistors, capacitors, and transistors.
This circuit serves as a critical amplifier stage in UHF TV transmitter applications, enhancing the strength of received signals to ensure optimal transmission quality. The gain of 7 dB indicates that the circuit effectively increases the power level of the input signal, making it suitable for broadcasting within the specified frequency range of 470-860 MHz.
The design typically incorporates a combination of resistors, capacitors, and transistors. Resistors are employed to set the biasing conditions for the transistors, ensuring they operate efficiently in the active region. Capacitors may be used for coupling and decoupling purposes, allowing AC signals to pass while blocking DC components, thus maintaining signal integrity.
Transistors, which are the primary active components in this circuit, function as the amplifying devices. Depending on the specific design, different transistor types (such as BJTs or FETs) can be utilized to achieve the desired performance characteristics. The choice of transistors will influence the overall efficiency, linearity, and thermal stability of the amplifier.
Additional considerations in the design include impedance matching to ensure maximum power transfer from the source to the load, as well as filtering components to minimize unwanted harmonics and noise. The overall layout of the circuit is crucial in minimizing parasitic capacitances and inductances, which can adversely affect performance at UHF frequencies.
In summary, this circuit is an essential component in enhancing UHF TV transmission, utilizing a well-thought-out arrangement of resistors, capacitors, and transistors to achieve a reliable gain and effective signal amplification.Function: for driving small UHF TV transmitters, with gain is 7dB and can amplify a signal between 470-860 MHz. Component: Resistor, Capacitor, Transistor, .. 🔗 External reference
This circuit serves as a critical amplifier stage in UHF TV transmitter applications, enhancing the strength of received signals to ensure optimal transmission quality. The gain of 7 dB indicates that the circuit effectively increases the power level of the input signal, making it suitable for broadcasting within the specified frequency range of 470-860 MHz.
The design typically incorporates a combination of resistors, capacitors, and transistors. Resistors are employed to set the biasing conditions for the transistors, ensuring they operate efficiently in the active region. Capacitors may be used for coupling and decoupling purposes, allowing AC signals to pass while blocking DC components, thus maintaining signal integrity.
Transistors, which are the primary active components in this circuit, function as the amplifying devices. Depending on the specific design, different transistor types (such as BJTs or FETs) can be utilized to achieve the desired performance characteristics. The choice of transistors will influence the overall efficiency, linearity, and thermal stability of the amplifier.
Additional considerations in the design include impedance matching to ensure maximum power transfer from the source to the load, as well as filtering components to minimize unwanted harmonics and noise. The overall layout of the circuit is crucial in minimizing parasitic capacitances and inductances, which can adversely affect performance at UHF frequencies.
In summary, this circuit is an essential component in enhancing UHF TV transmission, utilizing a well-thought-out arrangement of resistors, capacitors, and transistors to achieve a reliable gain and effective signal amplification.Function: for driving small UHF TV transmitters, with gain is 7dB and can amplify a signal between 470-860 MHz. Component: Resistor, Capacitor, Transistor, .. 🔗 External reference