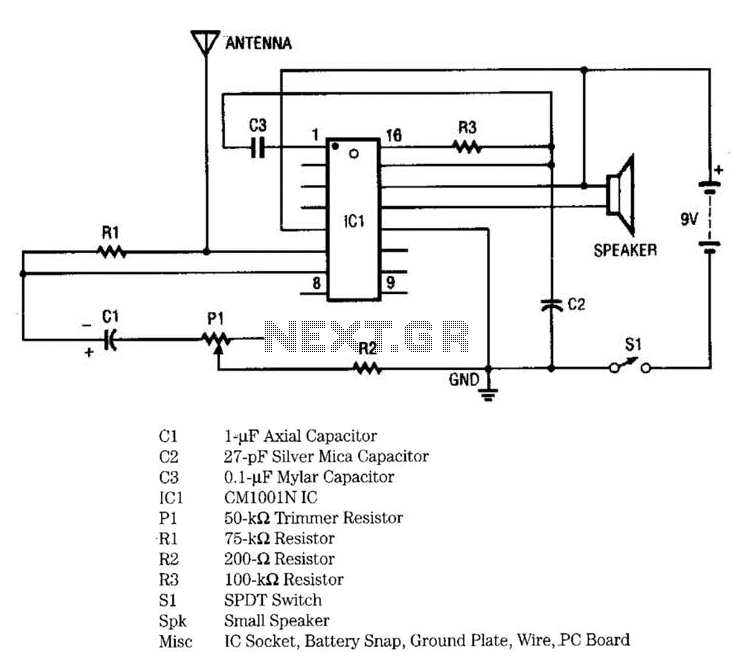
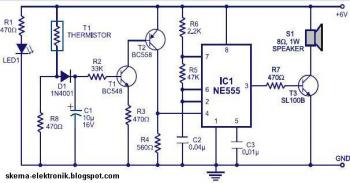
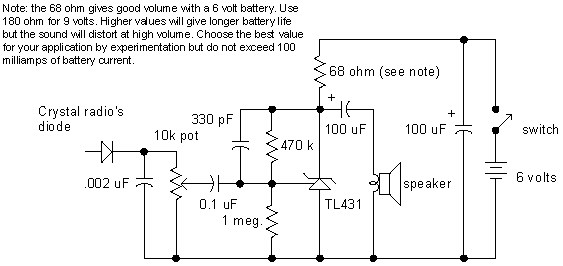
Single-tube constant current charger circuit
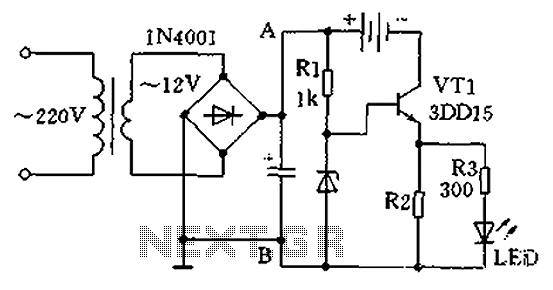
A practical single-tube constant current charger is illustrated, utilizing a transistor (VT1) that plays a crucial role in maintaining a constant current. The current value is determined by the voltage regulator and resistor R2. The general output voltage is approximately 3.3V, with resistor R2 rated between 30 to 60 ohms and 1W to 2W, resulting in a charging current of about 50mA to 80mA. Resistor R3, ranging from 200 to 500 ohms, along with an LED indicator, forms a circuit that illuminates when rechargeable batteries are connected. If the LED does not light up, it indicates a faulty battery. The circuit is designed to charge 1 to 4 nickel-cadmium batteries, with a charging duration of 12 to 14 hours. The transistor VT1 can be a 3DD15 or DS11 (plastic) type for power management, and it is recommended that a heat sink be added to the VT1 transistor. The charger does not include a charge control circuit, so users must monitor the charging time to ensure safe operation.
A single-tube constant current charger operates by regulating the current flowing into the battery pack using a transistor (VT1). The design features a voltage regulator that outputs approximately 3.3V, which is essential for the proper charging of nickel-cadmium batteries. Resistor R2 plays a pivotal role in setting the charging current, which can be adjusted within the range of 50mA to 80mA, depending on the specific resistance value chosen. The resistive load of R2 should be selected within the range of 30 to 60 ohms and rated for 1W to 2W to handle the power dissipation effectively.
In conjunction with the LED indicator, resistor R3, with a value between 200 to 500 ohms, is used to signal the charging status. When the circuit is operational and batteries are connected, the LED will illuminate, indicating that charging is taking place. A non-illuminating LED suggests a potential issue with the batteries, warranting further investigation.
The charger is capable of charging between 1 to 4 nickel-cadmium batteries, with a recommended charging time of approximately 12 to 14 hours, depending on the battery's state of charge and capacity. The choice of transistor, such as the 3DD15 or DS11, is critical for effective power management. It is advisable to attach a heat sink to the VT1 transistor to mitigate overheating during operation, ensuring reliability and longevity.
As there is no built-in charge control circuit, users must diligently monitor the charging time to prevent overcharging, which could lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan. This aspect emphasizes the importance of user awareness and adherence to safe charging practices when utilizing this charger design. As shown in a practical single-tube constant current charger, which play a constant role transistor VT1, its current value is determined by the voltage regulator and R2. Genera l election regulator about 3.3V, resistor R2 taken (30 to 60 Euro)/(1W ~ 2W), when the charge current is about 50mA ~ 80mA. R3 (200 ~ 500 ohms) and LED charging indicator composition circuit is connected as long as rechargeable batteries, LED will glow.
If the LED does not light, the battery is bad. The circuit of 1 ~ 4 5 nickel-cadmium batteries, charging time is 12 to 14 hours. Transistor VT1 available 3DD15 or DS11 (plastic) power management, installation, VT1 tube should be added to the radiator. Two kinds of charger neither add charge control circuit should be used to grasp the charging time, in order to ensure safe charging.
A single-tube constant current charger operates by regulating the current flowing into the battery pack using a transistor (VT1). The design features a voltage regulator that outputs approximately 3.3V, which is essential for the proper charging of nickel-cadmium batteries. Resistor R2 plays a pivotal role in setting the charging current, which can be adjusted within the range of 50mA to 80mA, depending on the specific resistance value chosen. The resistive load of R2 should be selected within the range of 30 to 60 ohms and rated for 1W to 2W to handle the power dissipation effectively.
In conjunction with the LED indicator, resistor R3, with a value between 200 to 500 ohms, is used to signal the charging status. When the circuit is operational and batteries are connected, the LED will illuminate, indicating that charging is taking place. A non-illuminating LED suggests a potential issue with the batteries, warranting further investigation.
The charger is capable of charging between 1 to 4 nickel-cadmium batteries, with a recommended charging time of approximately 12 to 14 hours, depending on the battery's state of charge and capacity. The choice of transistor, such as the 3DD15 or DS11, is critical for effective power management. It is advisable to attach a heat sink to the VT1 transistor to mitigate overheating during operation, ensuring reliability and longevity.
As there is no built-in charge control circuit, users must diligently monitor the charging time to prevent overcharging, which could lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan. This aspect emphasizes the importance of user awareness and adherence to safe charging practices when utilizing this charger design. As shown in a practical single-tube constant current charger, which play a constant role transistor VT1, its current value is determined by the voltage regulator and R2. Genera l election regulator about 3.3V, resistor R2 taken (30 to 60 Euro)/(1W ~ 2W), when the charge current is about 50mA ~ 80mA. R3 (200 ~ 500 ohms) and LED charging indicator composition circuit is connected as long as rechargeable batteries, LED will glow.
If the LED does not light, the battery is bad. The circuit of 1 ~ 4 5 nickel-cadmium batteries, charging time is 12 to 14 hours. Transistor VT1 available 3DD15 or DS11 (plastic) power management, installation, VT1 tube should be added to the radiator. Two kinds of charger neither add charge control circuit should be used to grasp the charging time, in order to ensure safe charging.