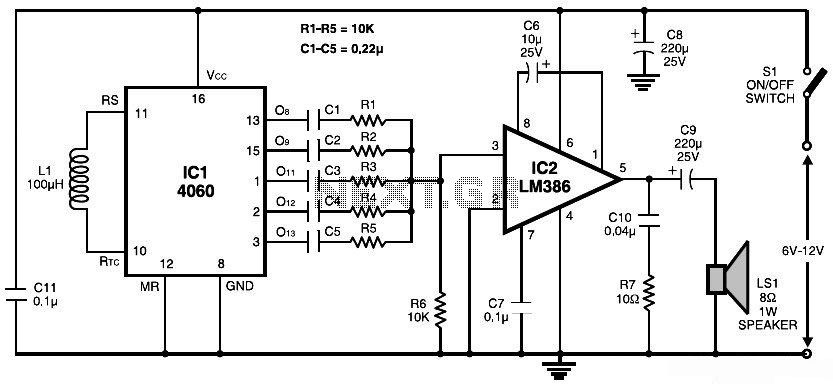
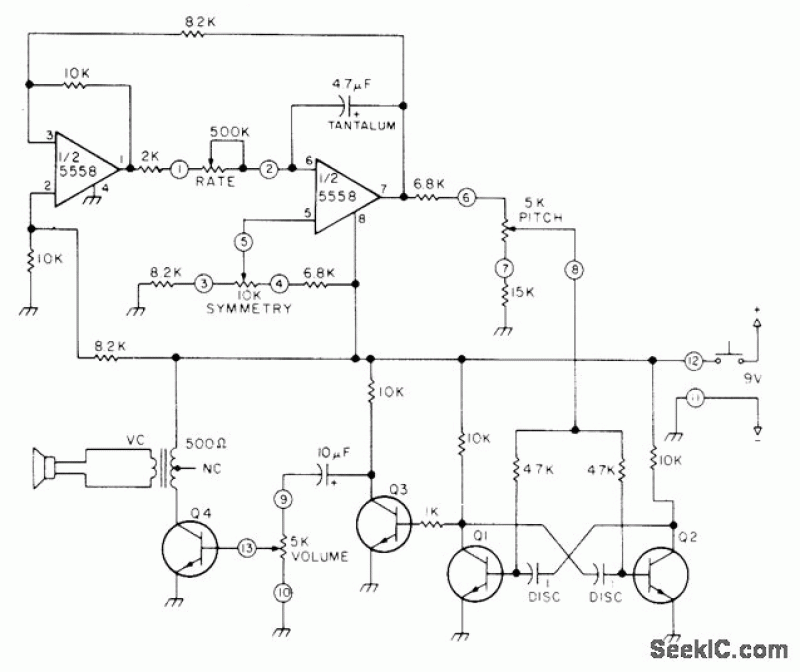
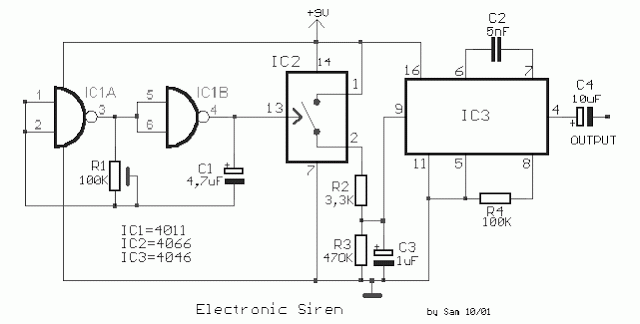
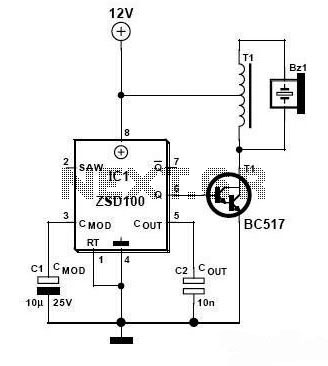
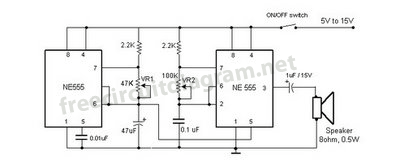
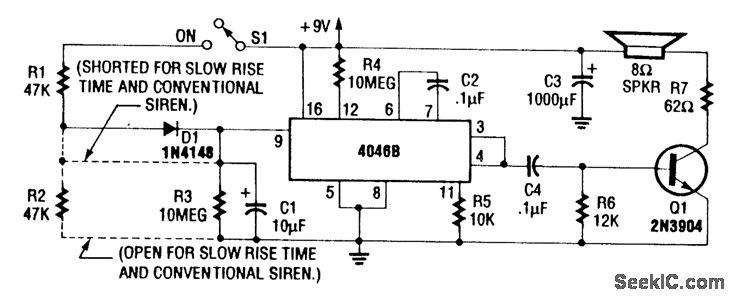
Siren
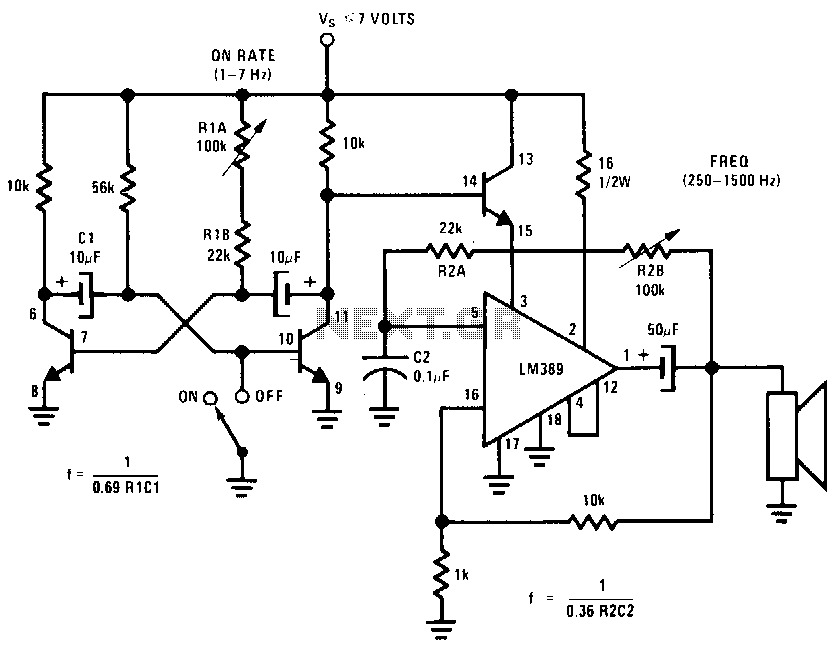
This circuit utilizes one of the LM389 transistors to control the power amplifier's operation by implementing a muting technique. The remaining transistors create a cross-coupled multivibrator circuit that regulates the frequency of the square-wave oscillator. The power amplifier functions as the square-wave oscillator, with frequency adjustment facilitated by the potentiometer R2B.
The circuit design incorporates an LM389 transistor, which serves as a critical component for switching the power amplifier on and off. This is achieved through a muting technique that effectively silences the amplifier when necessary, preventing unwanted noise or signal interference during idle periods.
The cross-coupled multivibrator circuit is constructed with complementary transistors that provide a stable oscillation. This configuration allows for the generation of a square wave, an essential waveform for various applications, including signal modulation and clock generation. The oscillation frequency can be finely tuned using potentiometer R2B, which is connected in such a way that it adjusts the timing components of the multivibrator, thereby altering the frequency of the output square wave.
The output from the power amplifier, acting as a square-wave oscillator, can be utilized in various applications, including driving speakers or other components that require a pulsed signal. The ability to adjust the frequency with R2B offers flexibility in the circuit's performance, accommodating different operational needs or specific requirements for the application at hand.
Overall, this circuit represents a versatile design that combines muting capabilities with precise frequency control, making it suitable for use in audio applications, signal processing, and other electronic systems where modulation and control of signals are critical.This circuit uses one of the LM389 transistors.to gate the power amplifier on and off by applying the muting technique. The other transistors form a cross-coupled multivibrator circuit that controls the rate of the square-wave oscillator.
The power amplifier is used as the square-wave oscillator with individual frequency adjust provided by potentiometer R2B.
The circuit design incorporates an LM389 transistor, which serves as a critical component for switching the power amplifier on and off. This is achieved through a muting technique that effectively silences the amplifier when necessary, preventing unwanted noise or signal interference during idle periods.
The cross-coupled multivibrator circuit is constructed with complementary transistors that provide a stable oscillation. This configuration allows for the generation of a square wave, an essential waveform for various applications, including signal modulation and clock generation. The oscillation frequency can be finely tuned using potentiometer R2B, which is connected in such a way that it adjusts the timing components of the multivibrator, thereby altering the frequency of the output square wave.
The output from the power amplifier, acting as a square-wave oscillator, can be utilized in various applications, including driving speakers or other components that require a pulsed signal. The ability to adjust the frequency with R2B offers flexibility in the circuit's performance, accommodating different operational needs or specific requirements for the application at hand.
Overall, this circuit represents a versatile design that combines muting capabilities with precise frequency control, making it suitable for use in audio applications, signal processing, and other electronic systems where modulation and control of signals are critical.This circuit uses one of the LM389 transistors.to gate the power amplifier on and off by applying the muting technique. The other transistors form a cross-coupled multivibrator circuit that controls the rate of the square-wave oscillator.
The power amplifier is used as the square-wave oscillator with individual frequency adjust provided by potentiometer R2B.