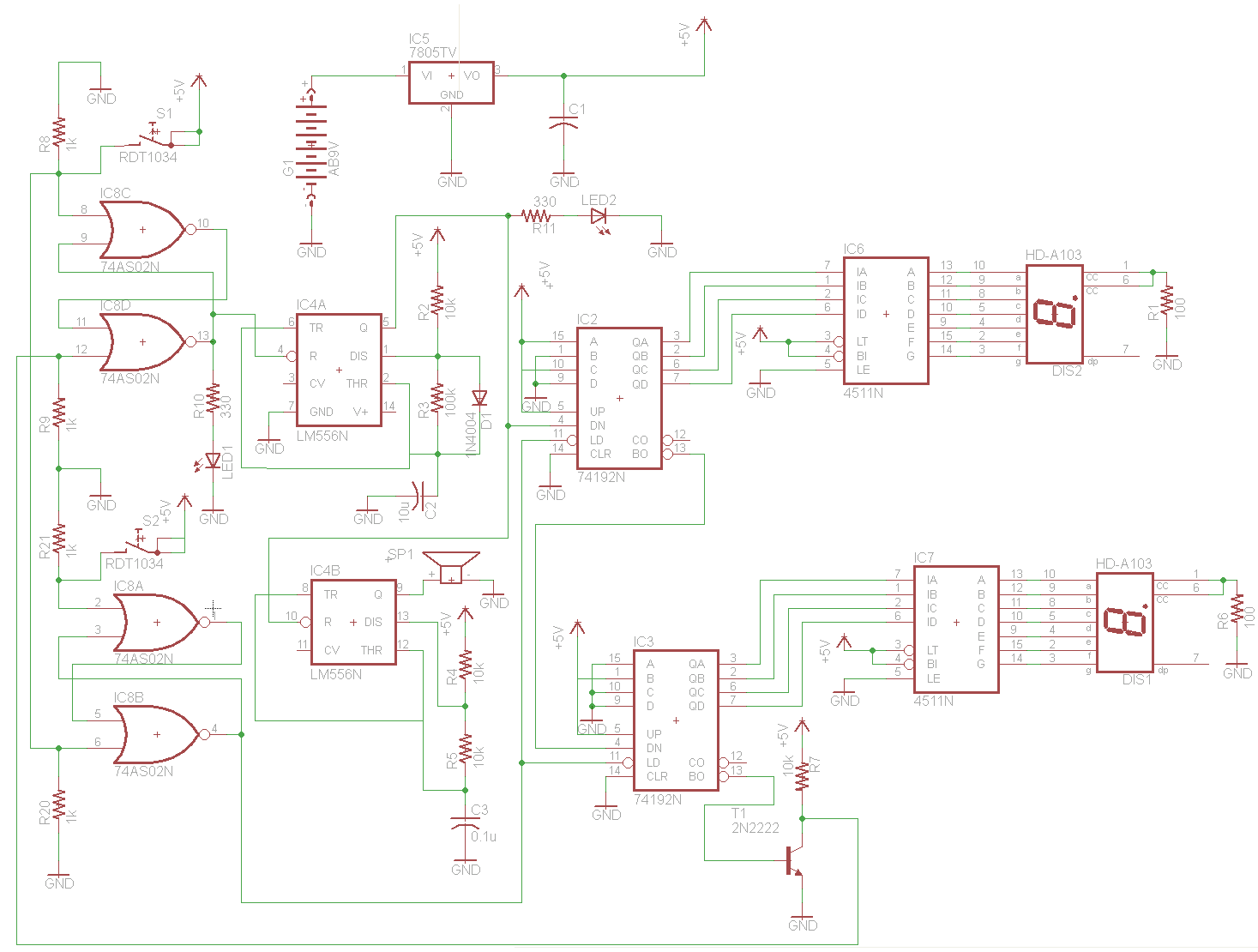
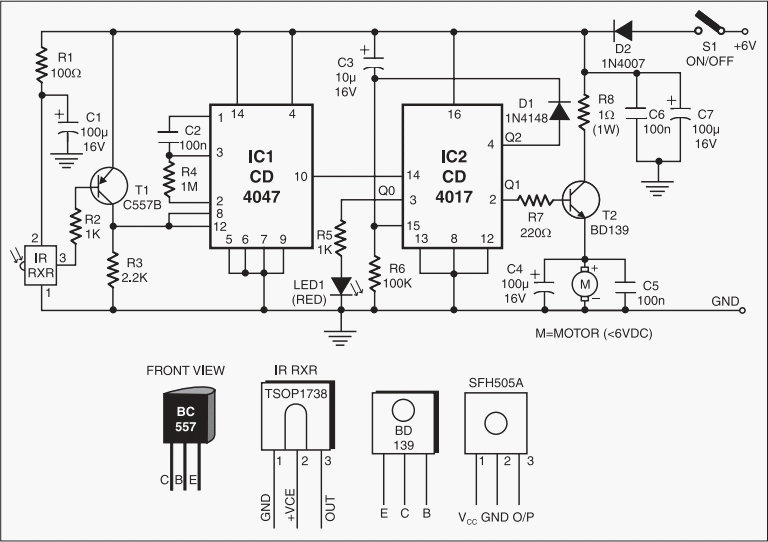
Small 3-wheel ROBOT with PIC16F84 brain & InfraRed eyes
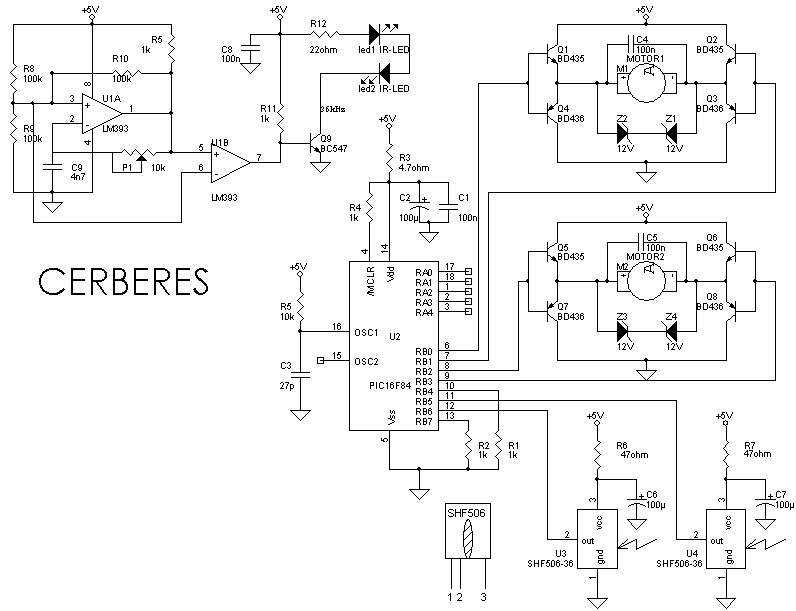
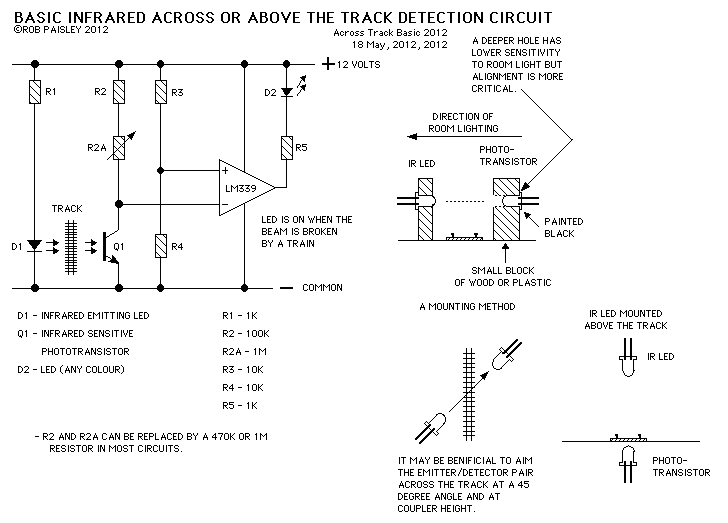
When the 36 kHz infrared light emitted by the LEDs is reflected off an object, one of the receiver modules is activated. The PIC16F84 microcontroller then directs the robot to avoid the object by reversing one of the motors.
The circuit involves an infrared LED that emits light at a frequency of 36 kHz. This light travels until it encounters an object, where it is reflected back towards a photodetector or infrared receiver module. The photodetector is designed to be sensitive to the 36 kHz frequency, ensuring that it only activates in response to the reflected infrared light.
Upon receiving the reflected signal, the receiver module sends a signal to the PIC16F84 microcontroller. This microcontroller is programmed to interpret the input from the receiver module. In response to the signal, the microcontroller executes a control algorithm that determines the appropriate action for the robot. Specifically, it will reverse one of the motors to steer the robot away from the detected obstacle.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors for current limiting, capacitors for signal smoothing, and possibly a transistor or relay to control the motor's operation. The motor driver circuit is crucial as it interfaces between the microcontroller and the motors, allowing the low-power signals from the PIC16F84 to control the higher power requirements of the motors.
Overall, this design exemplifies a basic obstacle avoidance mechanism in robotic applications, utilizing infrared sensing technology and microcontroller logic to achieve autonomous navigation.When the 36 kHz infrared light from the LEDs is reflected by an object, one of the receiver modules will be triggered, and the PIC16F84 µController will steer the ROBOT away from the objects by reversing one of the motors. 🔗 External reference
The circuit involves an infrared LED that emits light at a frequency of 36 kHz. This light travels until it encounters an object, where it is reflected back towards a photodetector or infrared receiver module. The photodetector is designed to be sensitive to the 36 kHz frequency, ensuring that it only activates in response to the reflected infrared light.
Upon receiving the reflected signal, the receiver module sends a signal to the PIC16F84 microcontroller. This microcontroller is programmed to interpret the input from the receiver module. In response to the signal, the microcontroller executes a control algorithm that determines the appropriate action for the robot. Specifically, it will reverse one of the motors to steer the robot away from the detected obstacle.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors for current limiting, capacitors for signal smoothing, and possibly a transistor or relay to control the motor's operation. The motor driver circuit is crucial as it interfaces between the microcontroller and the motors, allowing the low-power signals from the PIC16F84 to control the higher power requirements of the motors.
Overall, this design exemplifies a basic obstacle avoidance mechanism in robotic applications, utilizing infrared sensing technology and microcontroller logic to achieve autonomous navigation.When the 36 kHz infrared light from the LEDs is reflected by an object, one of the receiver modules will be triggered, and the PIC16F84 µController will steer the ROBOT away from the objects by reversing one of the motors. 🔗 External reference