Sound Controlled Lights Circuit
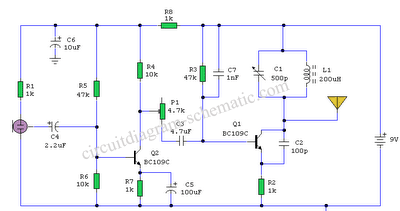
This sound-controlled lighting circuit design is utilized to adjust the brightness of connected lights in synchronization with captured sound.
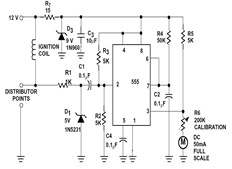
The sound-controlled lighting circuit operates by detecting audio signals through a microphone or sound sensor. The circuit typically consists of several key components: a microphone for sound detection, an operational amplifier (op-amp) to amplify the audio signals, a rectifier to convert the AC signal into a DC signal, and a microcontroller or a transistor-based control mechanism to modulate the light intensity.
The microphone captures ambient sound waves, converting them into an electrical signal. This signal is then fed into an op-amp, which amplifies the weak audio signal to a suitable level for further processing. The output from the op-amp is usually an alternating current (AC) signal, which is then rectified using a diode bridge or a single diode to produce a direct current (DC) signal that can be used to control the brightness of the lights.
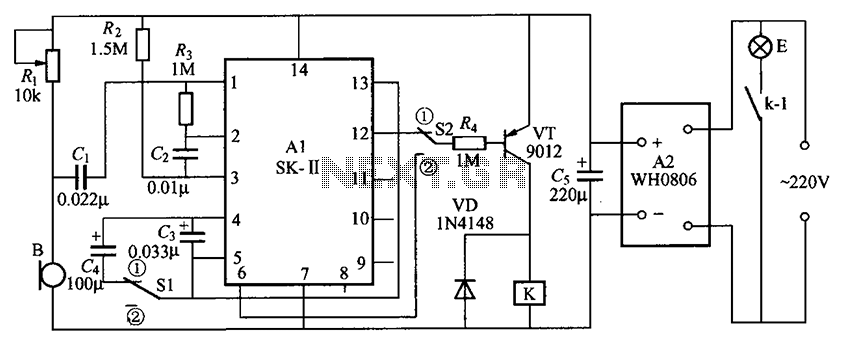
The rectified signal is then processed by a microcontroller or a transistor circuit. If a microcontroller is employed, it can be programmed to analyze the amplitude of the incoming signal and adjust the output to the lights accordingly, creating a dynamic lighting effect that responds to the sound. Alternatively, a transistor-based circuit can be used, where the DC signal controls the base of the transistor, allowing it to regulate the current flowing to the lights, thereby adjusting their brightness.
This circuit can be enhanced by incorporating additional features such as adjustable sensitivity, different lighting modes, or integration with other control systems. Overall, the sound-controlled lighting circuit provides an innovative way to create visually engaging environments that respond to auditory stimuli.This sound controlled lights circuit design is used to control the brightness of the lights attached to it in sync with the sound that is being capturated.. 🔗 External reference
The sound-controlled lighting circuit operates by detecting audio signals through a microphone or sound sensor. The circuit typically consists of several key components: a microphone for sound detection, an operational amplifier (op-amp) to amplify the audio signals, a rectifier to convert the AC signal into a DC signal, and a microcontroller or a transistor-based control mechanism to modulate the light intensity.
The microphone captures ambient sound waves, converting them into an electrical signal. This signal is then fed into an op-amp, which amplifies the weak audio signal to a suitable level for further processing. The output from the op-amp is usually an alternating current (AC) signal, which is then rectified using a diode bridge or a single diode to produce a direct current (DC) signal that can be used to control the brightness of the lights.
The rectified signal is then processed by a microcontroller or a transistor circuit. If a microcontroller is employed, it can be programmed to analyze the amplitude of the incoming signal and adjust the output to the lights accordingly, creating a dynamic lighting effect that responds to the sound. Alternatively, a transistor-based circuit can be used, where the DC signal controls the base of the transistor, allowing it to regulate the current flowing to the lights, thereby adjusting their brightness.
This circuit can be enhanced by incorporating additional features such as adjustable sensitivity, different lighting modes, or integration with other control systems. Overall, the sound-controlled lighting circuit provides an innovative way to create visually engaging environments that respond to auditory stimuli.This sound controlled lights circuit design is used to control the brightness of the lights attached to it in sync with the sound that is being capturated.. 🔗 External reference