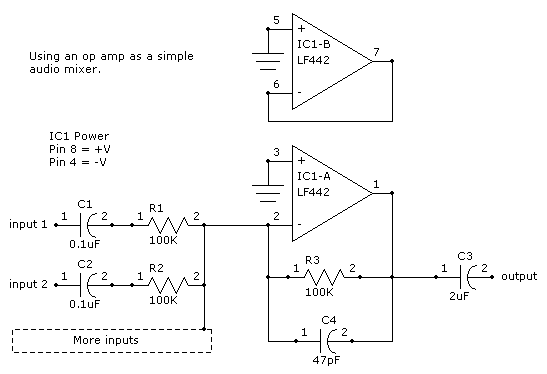
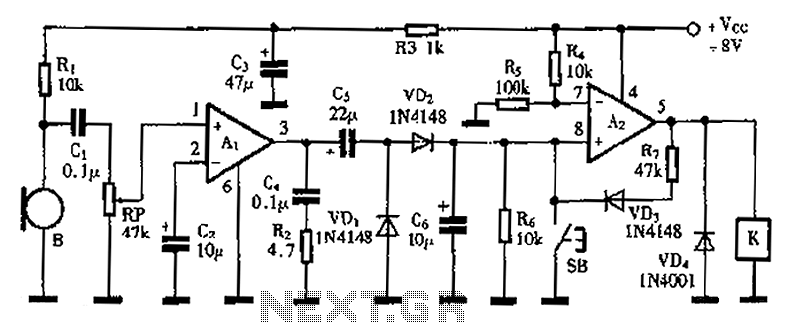
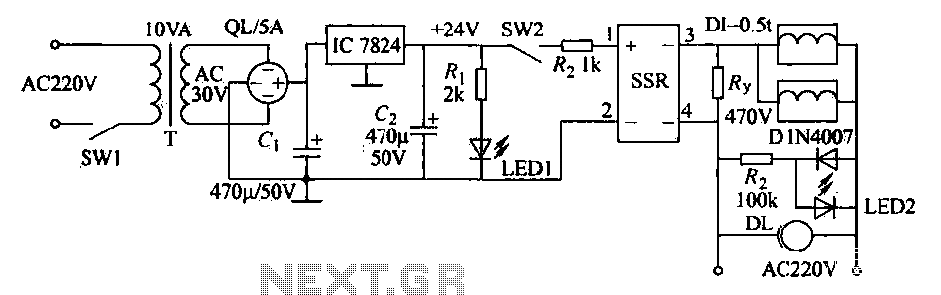
Sound mixer circuit

The sound mixer circuit is designed for service applications. This mixer is straightforward to implement and cost-effective, as it consists of two transistors along with a few simple resistors and capacitors.
The sound mixer circuit typically utilizes two transistors configured in a way that allows for the mixing of audio signals from multiple sources. The transistors serve as amplifiers, boosting the audio signals to a suitable level for output. The circuit can be designed using common NPN or PNP transistors, depending on the desired characteristics of the mixer.
Resistors are employed to set the biasing conditions for the transistors, ensuring they operate within their active regions. The values of these resistors are crucial for controlling gain and impedance matching, which directly affects the quality and clarity of the mixed audio output. Capacitors are used for coupling and decoupling purposes, allowing AC signals to pass while blocking DC components, thereby preventing unwanted shifts in the signal level.
The overall layout of the circuit can be arranged on a printed circuit board (PCB) or a breadboard for prototyping. Attention should be given to the placement of components to minimize noise and interference, which can significantly impact audio quality. Proper grounding techniques and the use of shielded cables may also be considered to enhance performance.
This sound mixer circuit is suitable for various applications, including small audio mixing tasks in home studios, educational projects, or as a component in larger audio systems. Its simplicity and cost-effectiveness make it an ideal choice for beginners and hobbyists looking to explore audio electronics.Sound mixer circuit of Service This mixer is easy to implement and Expensive as it consists of 2 transistors And some simple resistors and capacito. 🔗 External reference
The sound mixer circuit typically utilizes two transistors configured in a way that allows for the mixing of audio signals from multiple sources. The transistors serve as amplifiers, boosting the audio signals to a suitable level for output. The circuit can be designed using common NPN or PNP transistors, depending on the desired characteristics of the mixer.
Resistors are employed to set the biasing conditions for the transistors, ensuring they operate within their active regions. The values of these resistors are crucial for controlling gain and impedance matching, which directly affects the quality and clarity of the mixed audio output. Capacitors are used for coupling and decoupling purposes, allowing AC signals to pass while blocking DC components, thereby preventing unwanted shifts in the signal level.
The overall layout of the circuit can be arranged on a printed circuit board (PCB) or a breadboard for prototyping. Attention should be given to the placement of components to minimize noise and interference, which can significantly impact audio quality. Proper grounding techniques and the use of shielded cables may also be considered to enhance performance.
This sound mixer circuit is suitable for various applications, including small audio mixing tasks in home studios, educational projects, or as a component in larger audio systems. Its simplicity and cost-effectiveness make it an ideal choice for beginners and hobbyists looking to explore audio electronics.Sound mixer circuit of Service This mixer is easy to implement and Expensive as it consists of 2 transistors And some simple resistors and capacito. 🔗 External reference