speed control of dc motor
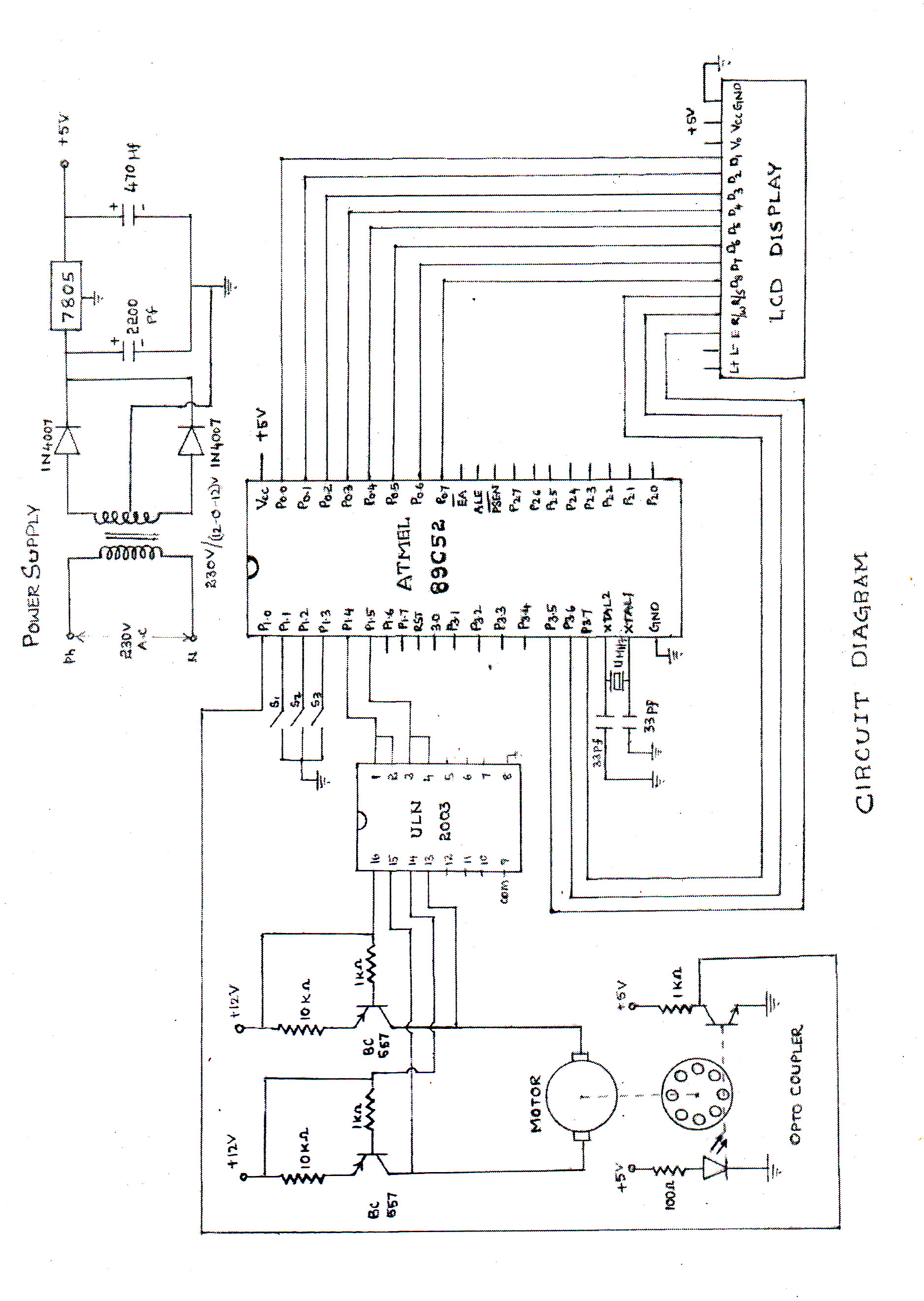
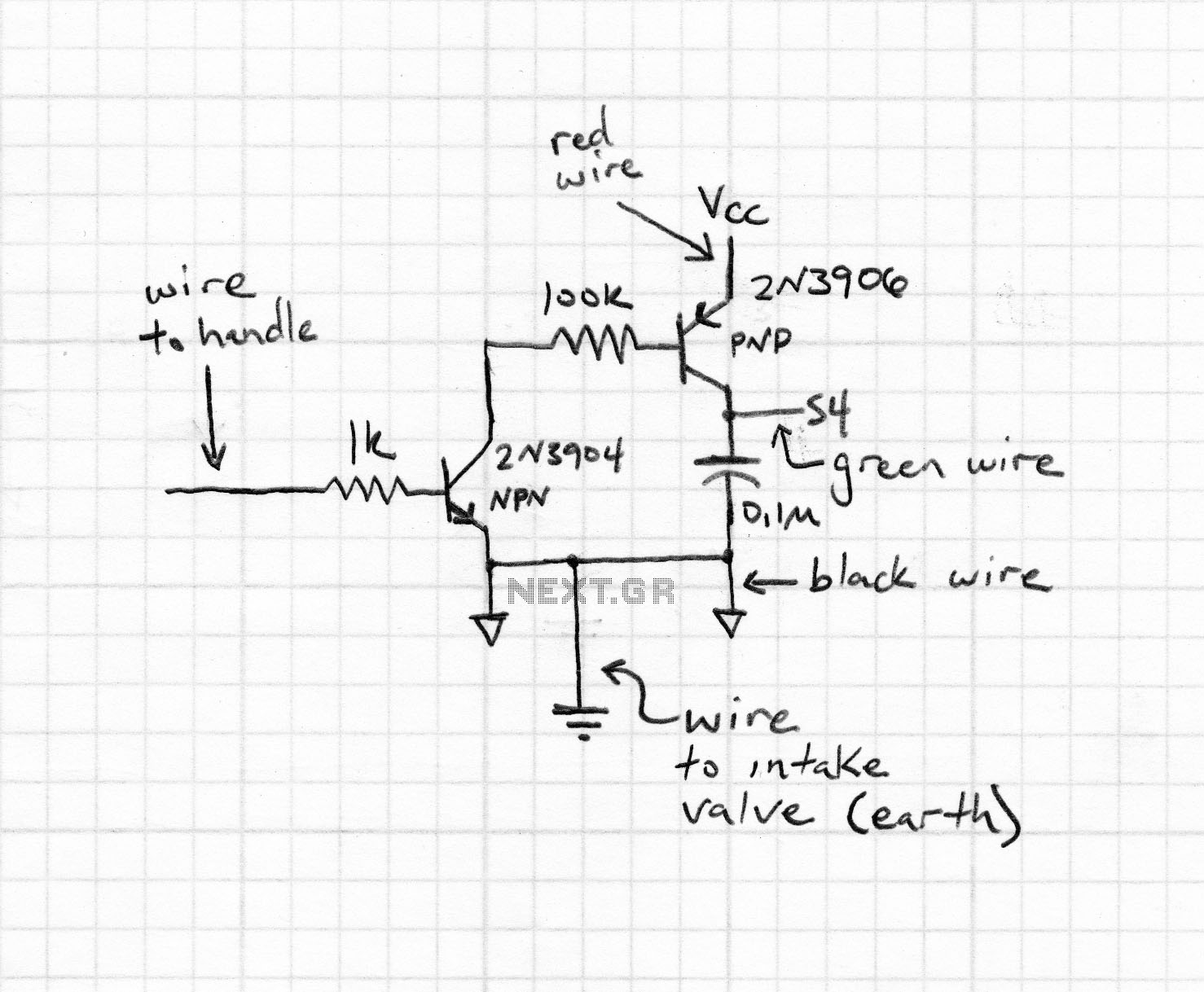
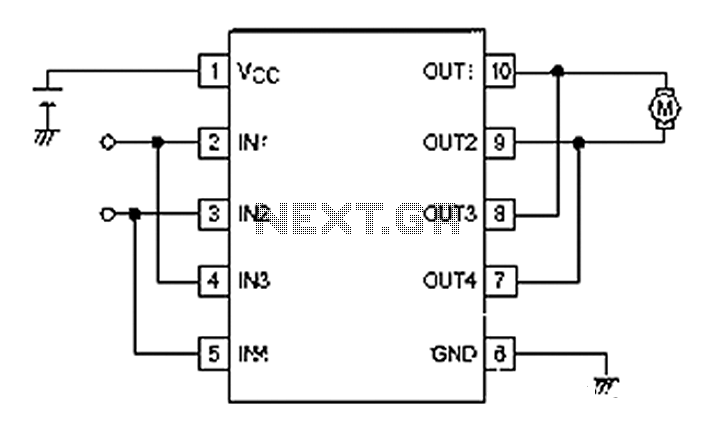
The speed of the DC motor is controlled using an ATMEL89C52 microcontroller, with feedback provided by an optocoupler. The circuit diagram can be viewed above (click on the diagram for a larger view). The motor speed is regulated by employing a transistor as a control switch, where varying the duty cycle of the switching signal to the transistor adjusts the power supplied to the motor.
The circuit described utilizes an ATMEL89C52 microcontroller to manage the speed of a DC motor through pulse width modulation (PWM). This method allows for efficient control of the motor's speed by adjusting the average voltage supplied to the motor. The microcontroller generates a PWM signal, which is fed into a transistor acting as a switch. The transistor is configured to operate in saturation and cutoff regions, enabling it to turn on and off rapidly.
An optocoupler is employed in this circuit to provide feedback from the motor. The optocoupler isolates the microcontroller from the motor circuit, ensuring that any voltage spikes or noise generated by the motor do not affect the microcontroller's operation. The feedback signal from the optocoupler allows the microcontroller to monitor the actual speed of the motor, facilitating closed-loop control.
By varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the average voltage applied to the motor can be adjusted, thereby controlling its speed. A higher duty cycle results in more power delivered to the motor, increasing its speed, while a lower duty cycle decreases the power and slows the motor down. This method is efficient and allows for precise control of motor speed.
The schematic diagram associated with this circuit illustrates the connections between the microcontroller, transistor, optocoupler, and the DC motor. It is essential to ensure that the components are rated appropriately for the motor's voltage and current requirements to prevent damage. Additionally, proper heat sinking should be considered for the transistor if high currents are involved.speed of the d.c. motor is controlled by using ATMEL89C52 lmicrocontroller ,feedback from optocoupler. the circuit diagram can be seen above(click on the diagram to get larger view) the motor speed is controlled by the use of transistor as control switch varying the dutycycle of the switching signal to the transistor varies the power of.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described utilizes an ATMEL89C52 microcontroller to manage the speed of a DC motor through pulse width modulation (PWM). This method allows for efficient control of the motor's speed by adjusting the average voltage supplied to the motor. The microcontroller generates a PWM signal, which is fed into a transistor acting as a switch. The transistor is configured to operate in saturation and cutoff regions, enabling it to turn on and off rapidly.
An optocoupler is employed in this circuit to provide feedback from the motor. The optocoupler isolates the microcontroller from the motor circuit, ensuring that any voltage spikes or noise generated by the motor do not affect the microcontroller's operation. The feedback signal from the optocoupler allows the microcontroller to monitor the actual speed of the motor, facilitating closed-loop control.
By varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the average voltage applied to the motor can be adjusted, thereby controlling its speed. A higher duty cycle results in more power delivered to the motor, increasing its speed, while a lower duty cycle decreases the power and slows the motor down. This method is efficient and allows for precise control of motor speed.
The schematic diagram associated with this circuit illustrates the connections between the microcontroller, transistor, optocoupler, and the DC motor. It is essential to ensure that the components are rated appropriately for the motor's voltage and current requirements to prevent damage. Additionally, proper heat sinking should be considered for the transistor if high currents are involved.speed of the d.c. motor is controlled by using ATMEL89C52 lmicrocontroller ,feedback from optocoupler. the circuit diagram can be seen above(click on the diagram to get larger view) the motor speed is controlled by the use of transistor as control switch varying the dutycycle of the switching signal to the transistor varies the power of.. 🔗 External reference