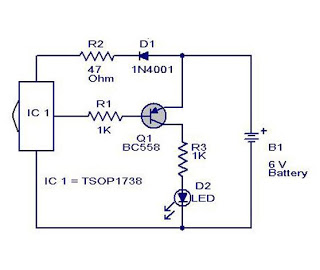
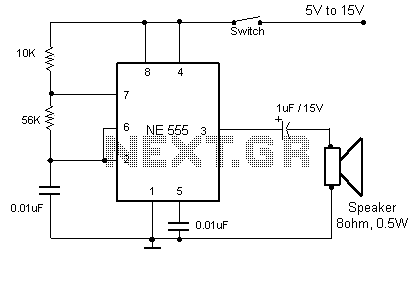
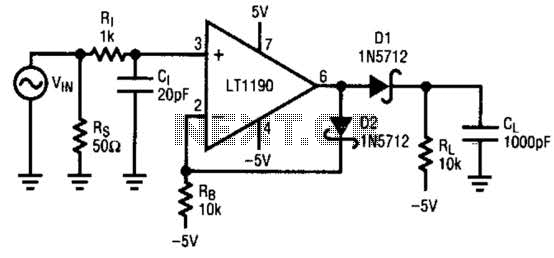
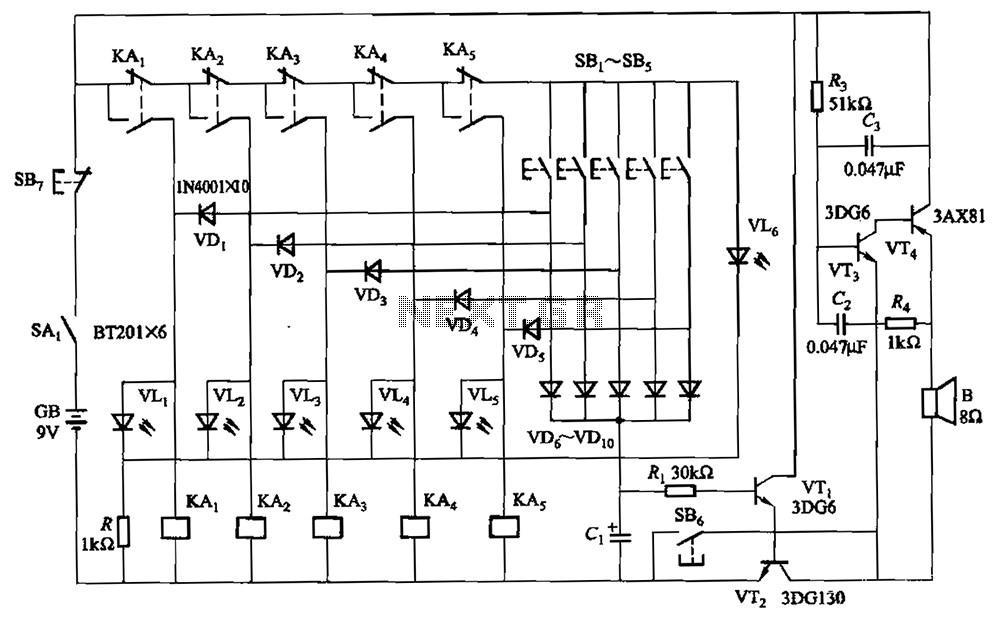
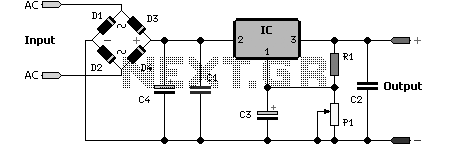
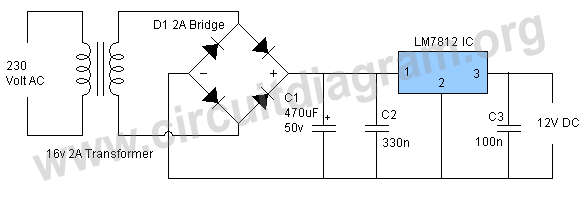
Speed-Control Switch Circuit Circuit
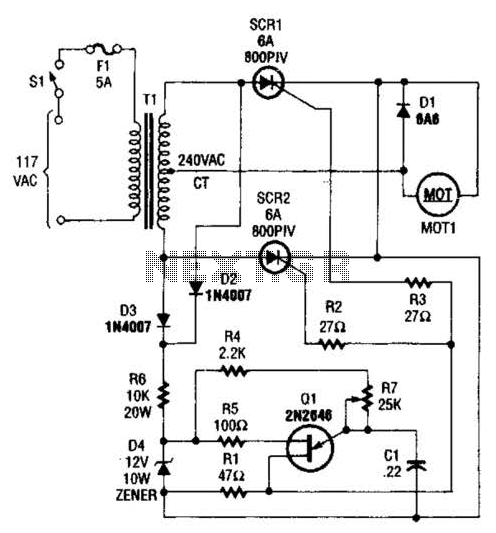
A center-tapped 240-V transformer is used with two SCR devices to provide rectified AC (pulsating DC) to MOT1. Q1 is a UJT ramp generator used to generate trigger pulses for SCR1 and SCR2.
The circuit employs a center-tapped transformer rated for 240 volts, which serves as the primary power source. This transformer splits the AC voltage into two equal halves, providing the necessary input for the two silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs). The SCRs are positioned in a configuration that allows them to rectify the AC voltage into pulsating DC, which is then supplied to the load, identified as MOT1.
The UJT (Unijunction Transistor) ramp generator, designated as Q1, is integral to the operation of the SCRs. It generates trigger pulses that are essential for the SCRs to turn on and off at specific intervals. The ramp generator operates by charging a capacitor through a resistor until a predetermined voltage level is reached, at which point a pulse is emitted. This pulse is fed into the gate terminals of SCR1 and SCR2, enabling them to conduct and control the flow of current to MOT1.
The design ensures that the SCRs are triggered in such a manner that they effectively manage the power delivered to the load, allowing for precise control over the output characteristics. The use of a center-tapped transformer in conjunction with the UJT ramp generator provides a robust solution for converting AC power into a usable form of pulsating DC, suitable for various applications. The overall circuit design emphasizes reliability and efficiency in power management. A center-tapped 240-V transformer is used with two SCR devices to provide rectified ac (pulsating dc) to MOT1. Ql is a UJT ramp generator used to generate trigger pulses for SCR1 and SCR2. 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs a center-tapped transformer rated for 240 volts, which serves as the primary power source. This transformer splits the AC voltage into two equal halves, providing the necessary input for the two silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs). The SCRs are positioned in a configuration that allows them to rectify the AC voltage into pulsating DC, which is then supplied to the load, identified as MOT1.
The UJT (Unijunction Transistor) ramp generator, designated as Q1, is integral to the operation of the SCRs. It generates trigger pulses that are essential for the SCRs to turn on and off at specific intervals. The ramp generator operates by charging a capacitor through a resistor until a predetermined voltage level is reached, at which point a pulse is emitted. This pulse is fed into the gate terminals of SCR1 and SCR2, enabling them to conduct and control the flow of current to MOT1.
The design ensures that the SCRs are triggered in such a manner that they effectively manage the power delivered to the load, allowing for precise control over the output characteristics. The use of a center-tapped transformer in conjunction with the UJT ramp generator provides a robust solution for converting AC power into a usable form of pulsating DC, suitable for various applications. The overall circuit design emphasizes reliability and efficiency in power management. A center-tapped 240-V transformer is used with two SCR devices to provide rectified ac (pulsating dc) to MOT1. Ql is a UJT ramp generator used to generate trigger pulses for SCR1 and SCR2. 🔗 External reference