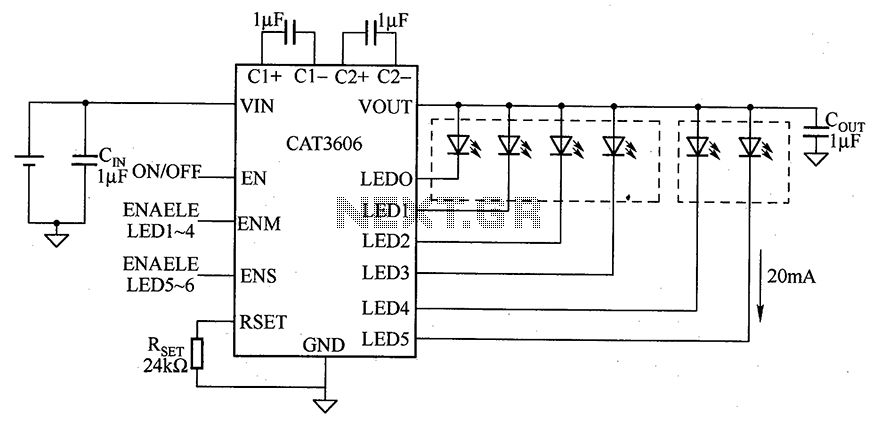
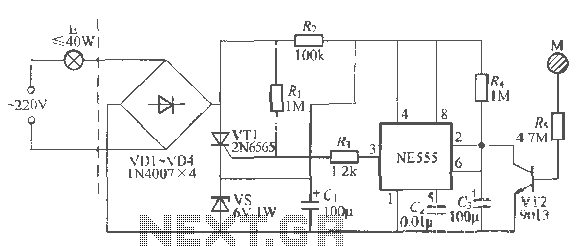
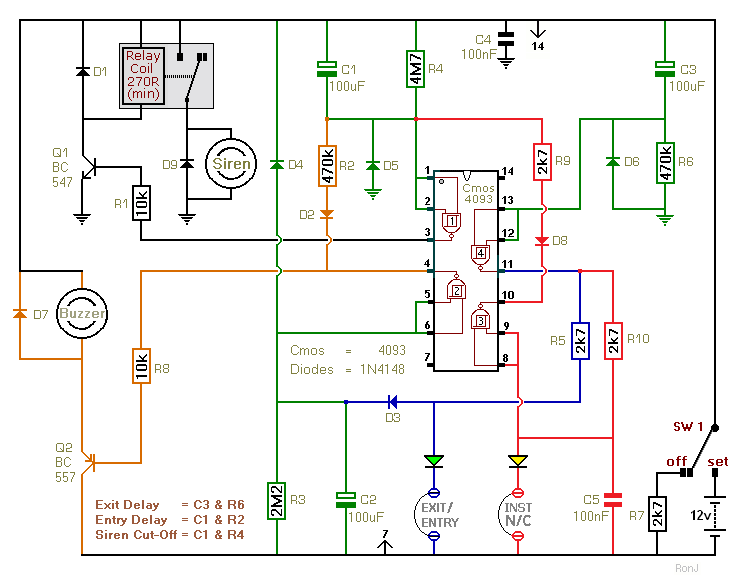
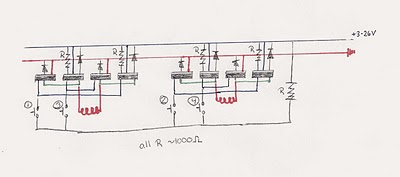
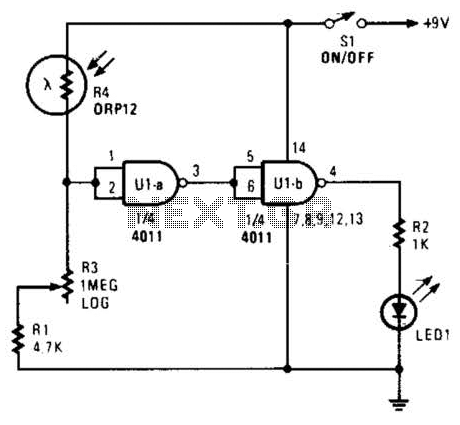
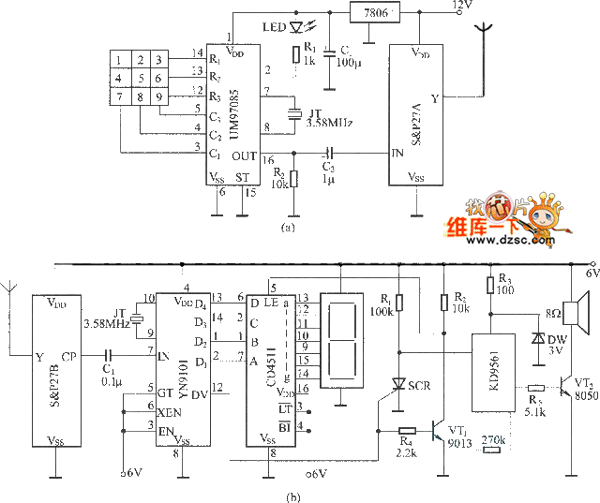
Spy RF Bug Detector Circuit
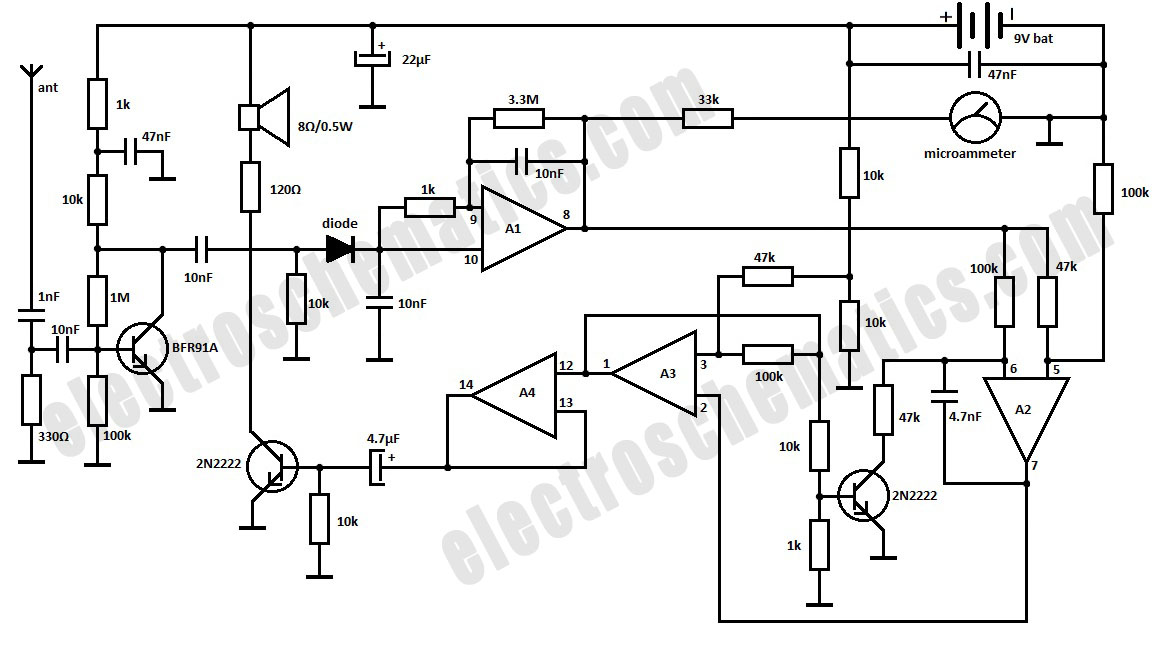
This is a simple RF bug detector designed to identify spy bugs, capable of operating up to 2 GHz. Below are some essential components required for this circuit.
The RF bug detector circuit functions by utilizing radio frequency signals to identify hidden transmitting devices. The key components of the circuit include an RF amplifier, a frequency mixer, a signal detector, and an audio output stage.
The RF amplifier is responsible for boosting weak signals received from the environment, ensuring that even low-power transmissions can be detected. The frequency mixer combines the incoming RF signals with a local oscillator signal to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. This IF signal is then processed by the signal detector, which can be a diode or a dedicated RF detector IC. The detector extracts the audio or modulation information from the IF signal, allowing the user to discern the presence of a transmitting device.
The audio output stage typically consists of an audio amplifier that converts the detected signals into audible sounds, alerting the user to the presence of a bug. Additionally, a simple LED indicator may be incorporated to provide a visual cue when a signal is detected.
Power supply considerations are essential for this circuit, as it may require a regulated voltage source, typically ranging from 5V to 12V, depending on the components used. Battery operation is also a viable option for portability, making the device suitable for field use.
In summary, the RF bug detector circuit is a straightforward yet effective tool for identifying hidden surveillance devices, employing a combination of RF amplification, signal mixing, detection, and audio output to provide feedback to the user. Proper selection of components and careful design will ensure optimal performance across the specified frequency range.Here is a simple RF bug detector that will help you detect spy bugs and can operate up to 2 GHz. Below are some essential things required for this circuit:.. 🔗 External reference
The RF bug detector circuit functions by utilizing radio frequency signals to identify hidden transmitting devices. The key components of the circuit include an RF amplifier, a frequency mixer, a signal detector, and an audio output stage.
The RF amplifier is responsible for boosting weak signals received from the environment, ensuring that even low-power transmissions can be detected. The frequency mixer combines the incoming RF signals with a local oscillator signal to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. This IF signal is then processed by the signal detector, which can be a diode or a dedicated RF detector IC. The detector extracts the audio or modulation information from the IF signal, allowing the user to discern the presence of a transmitting device.
The audio output stage typically consists of an audio amplifier that converts the detected signals into audible sounds, alerting the user to the presence of a bug. Additionally, a simple LED indicator may be incorporated to provide a visual cue when a signal is detected.
Power supply considerations are essential for this circuit, as it may require a regulated voltage source, typically ranging from 5V to 12V, depending on the components used. Battery operation is also a viable option for portability, making the device suitable for field use.
In summary, the RF bug detector circuit is a straightforward yet effective tool for identifying hidden surveillance devices, employing a combination of RF amplification, signal mixing, detection, and audio output to provide feedback to the user. Proper selection of components and careful design will ensure optimal performance across the specified frequency range.Here is a simple RF bug detector that will help you detect spy bugs and can operate up to 2 GHz. Below are some essential things required for this circuit:.. 🔗 External reference