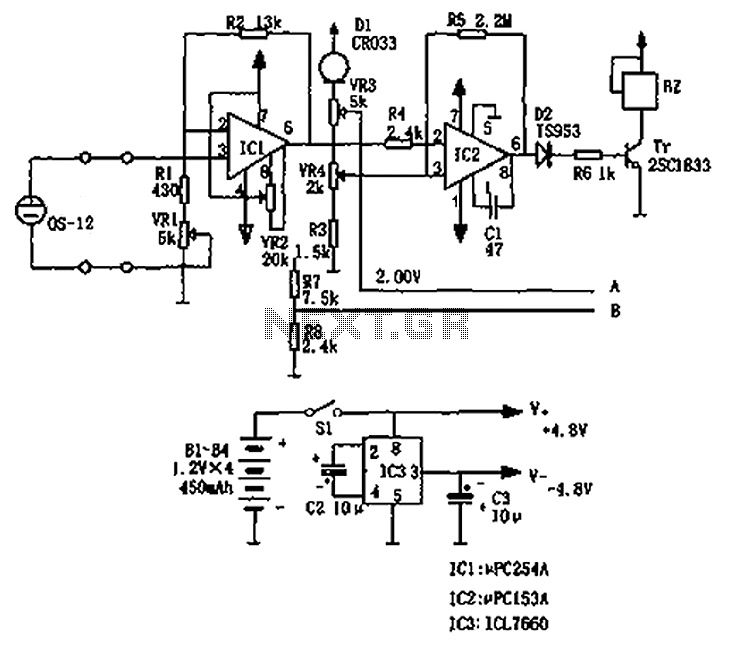
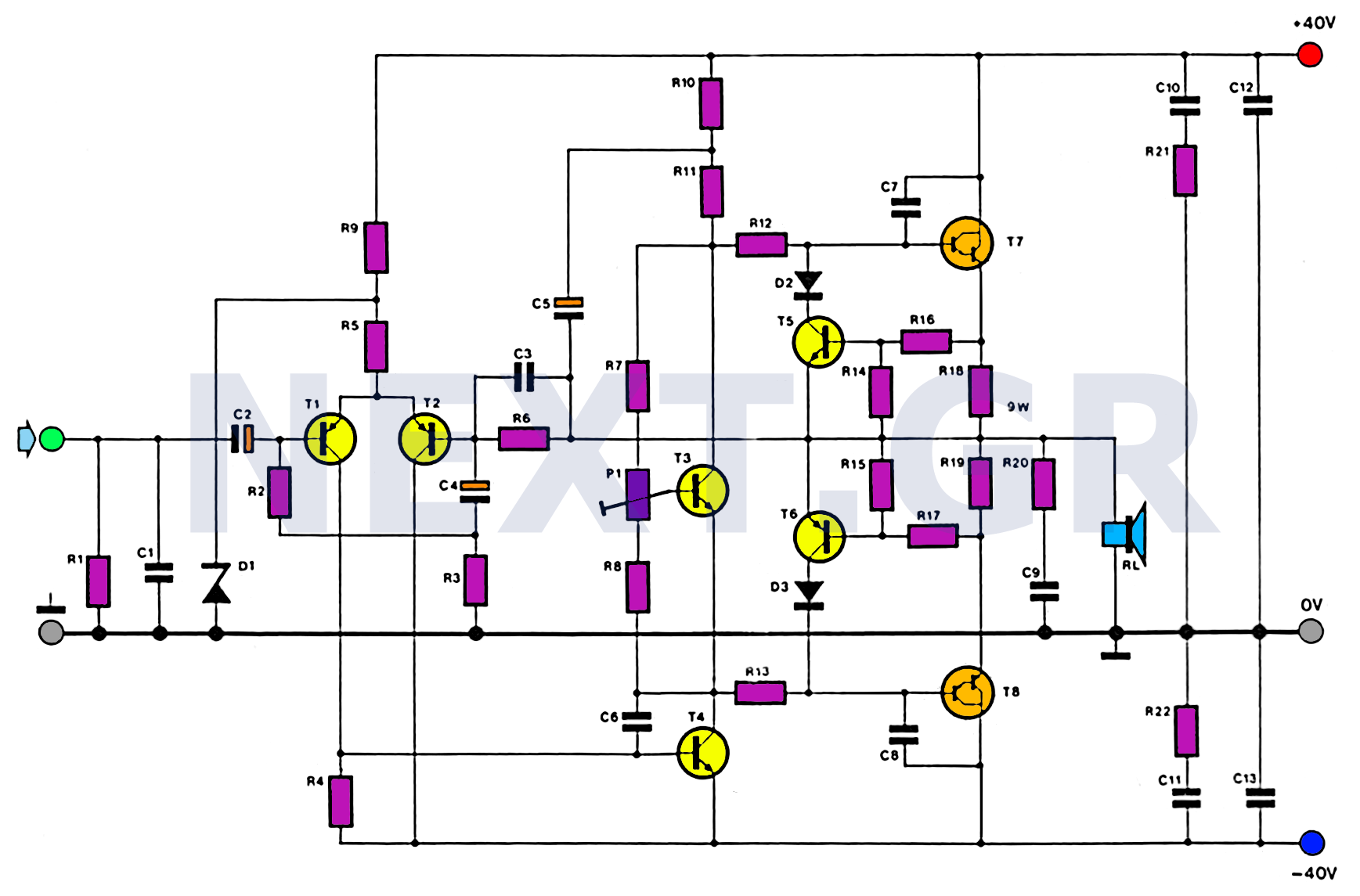
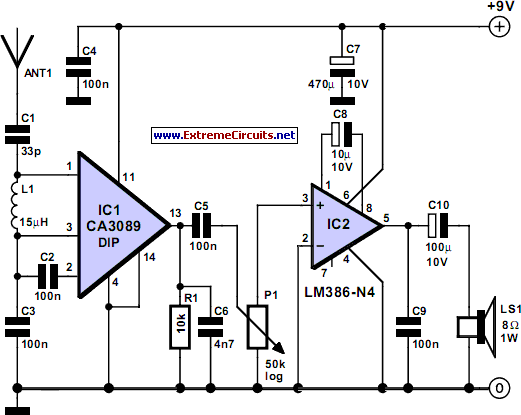
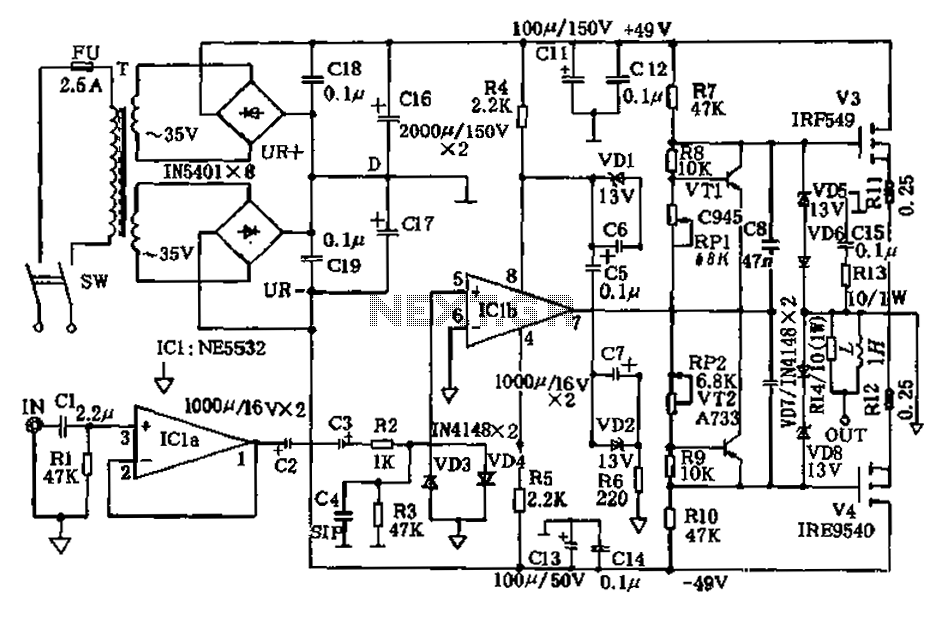
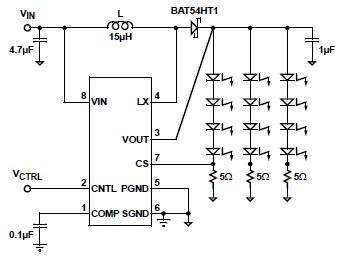
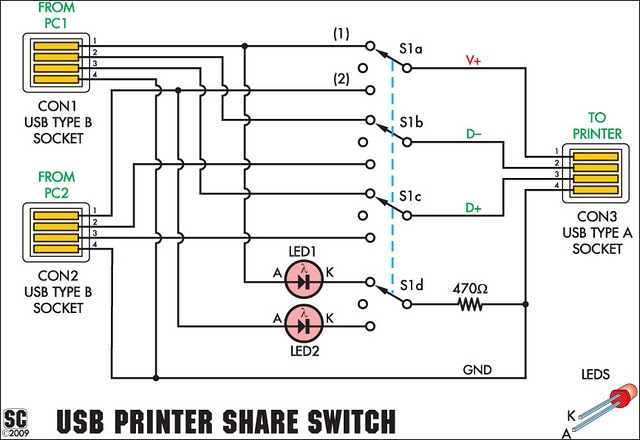
square wave oscillator circuit
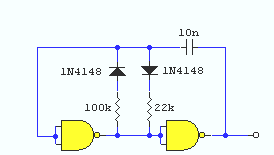
A simple square wave oscillator can be created using two gates from a CMOS 4011 NAND chip. Alternatively, a CMOS 4001 chip or a TTL equivalent can also be utilized. In this circuit, the mark-space ratio can be independently controlled by varying the resistor values. The rise and fall times of the output pulses depend on the operating voltage of the integrated circuit (IC) and the type of IC used, typically falling within the range of tens of nanoseconds.
The circuit design for the square wave oscillator employs two NAND gates configured in a feedback loop. The first NAND gate is used to generate a basic pulse signal, while the second NAND gate provides feedback to establish oscillation. The configuration allows for the adjustment of the mark-space ratio by changing the resistor values connected to the gates.
In this configuration, the resistors are connected to the inputs of the NAND gates, influencing the timing characteristics of the output waveform. The timing components determine how long the output remains high versus low, effectively controlling the frequency of the oscillation.
The performance of the oscillator is influenced by the supply voltage applied to the IC. Higher voltages generally lead to faster rise and fall times, which can be critical for applications requiring precise timing. The choice of IC also impacts the output characteristics; for instance, CMOS devices typically have lower power consumption compared to their TTL counterparts, making them suitable for battery-operated applications.
When designing the circuit, it is essential to consider the load connected to the output. The output stage of the NAND gates can drive a variety of loads, but excessive loading may affect the rise and fall times. Proper decoupling capacitors should be included near the power supply pins of the IC to enhance stability and reduce noise.
In summary, this simple square wave oscillator circuit utilizing CMOS NAND gates provides flexibility in frequency generation and offers the ability to control the mark-space ratio through resistor adjustments. The circuit is suitable for various applications, including clock generation, signal modulation, and waveform shaping.Using two gates from a CMOS 4011 NAND chip, a simple Squarewave oscillator can br made. Alternatively a CMOS 4001 chip can also be used, or a TTL equivalent. In this circuit the mark space ratio can also be independently controlled by varying the value of the resistors. The rise and fall times of the output pulses depend on the operating voltage o f the IC and type of IC, but will be typically in the order on tens of nanoseconds. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design for the square wave oscillator employs two NAND gates configured in a feedback loop. The first NAND gate is used to generate a basic pulse signal, while the second NAND gate provides feedback to establish oscillation. The configuration allows for the adjustment of the mark-space ratio by changing the resistor values connected to the gates.
In this configuration, the resistors are connected to the inputs of the NAND gates, influencing the timing characteristics of the output waveform. The timing components determine how long the output remains high versus low, effectively controlling the frequency of the oscillation.
The performance of the oscillator is influenced by the supply voltage applied to the IC. Higher voltages generally lead to faster rise and fall times, which can be critical for applications requiring precise timing. The choice of IC also impacts the output characteristics; for instance, CMOS devices typically have lower power consumption compared to their TTL counterparts, making them suitable for battery-operated applications.
When designing the circuit, it is essential to consider the load connected to the output. The output stage of the NAND gates can drive a variety of loads, but excessive loading may affect the rise and fall times. Proper decoupling capacitors should be included near the power supply pins of the IC to enhance stability and reduce noise.
In summary, this simple square wave oscillator circuit utilizing CMOS NAND gates provides flexibility in frequency generation and offers the ability to control the mark-space ratio through resistor adjustments. The circuit is suitable for various applications, including clock generation, signal modulation, and waveform shaping.Using two gates from a CMOS 4011 NAND chip, a simple Squarewave oscillator can br made. Alternatively a CMOS 4001 chip can also be used, or a TTL equivalent. In this circuit the mark space ratio can also be independently controlled by varying the value of the resistors. The rise and fall times of the output pulses depend on the operating voltage o f the IC and type of IC, but will be typically in the order on tens of nanoseconds. 🔗 External reference