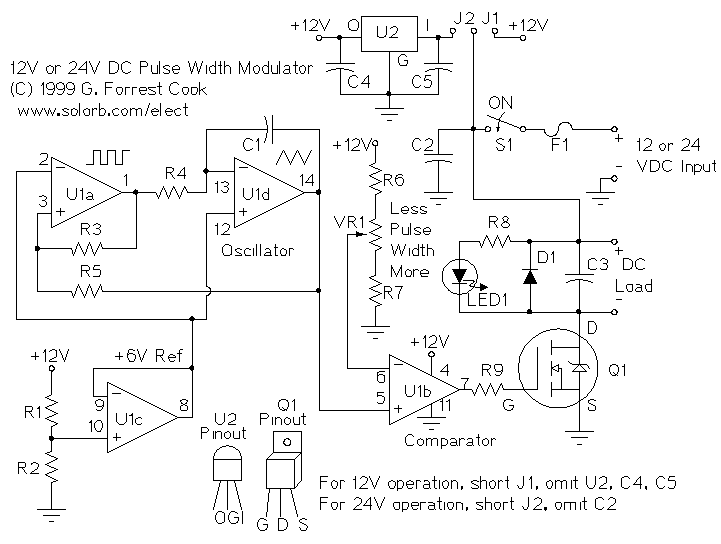
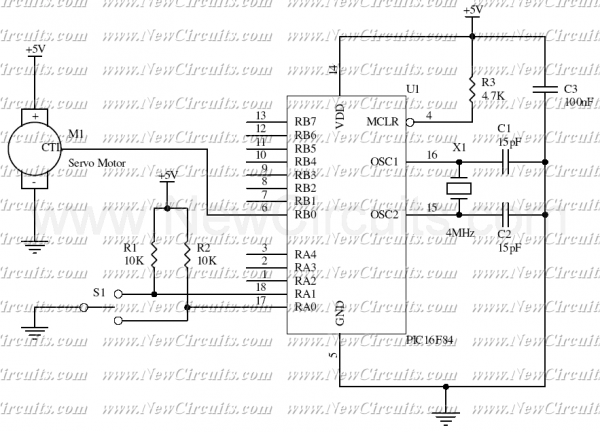
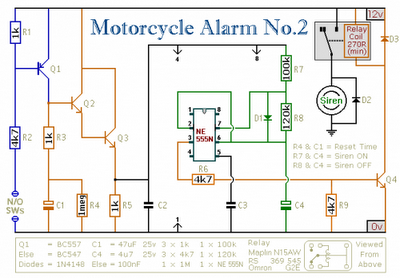
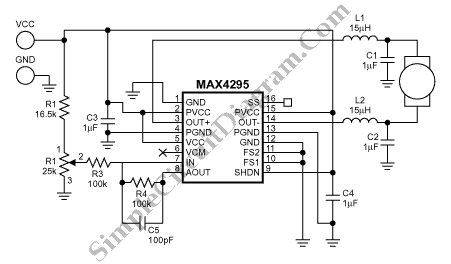
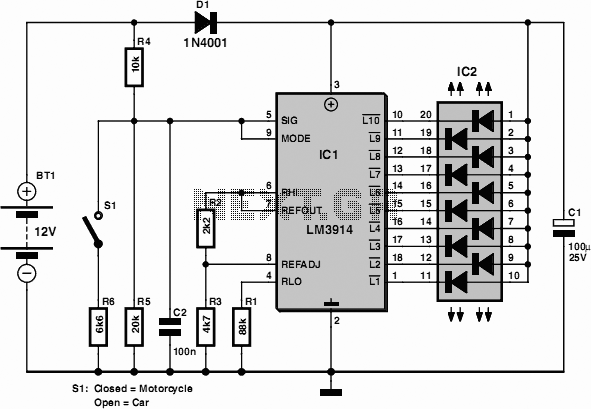
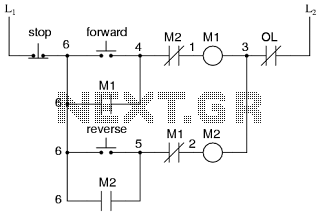
Stepper Motor Speed And Direction Controller
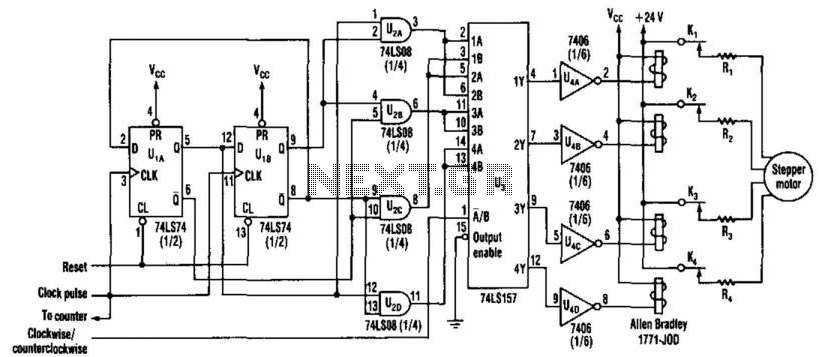
This new circuit utilizes four integrated circuits, with the option to operate with just three by combining the flip-flops and AND gates. The frequency of clock pulses dictates the revolutions per minute (RPM) of the motor. The circuit can enhance efficiency by substituting transistors for relays. It is designed to drive a stepper motor, with its speed directly proportional to the clock rate. Standard SSI LSTTL chips are employed in the design.
The circuit consists of four primary components: flip-flops, AND gates, a clock pulse generator, and a motor driver stage. The flip-flops serve as memory elements, maintaining the state of the motor control logic. The AND gates are used to process the signals coming from the flip-flops, enabling precise control over the motor operation based on the desired speed.
The clock pulse generator is a crucial element in this design, as it establishes the timing for the entire circuit. By adjusting the frequency of the clock pulses, the user can effectively change the RPM of the stepper motor. This allows for fine-tuned control over the motor's performance, making it suitable for applications requiring variable speed.
Incorporating switching transistors instead of traditional solid-state relays improves the circuit's efficiency. Transistors can switch on and off more rapidly than relays, resulting in faster response times and lower power consumption. This enhancement is particularly beneficial in applications where the motor speed must be adjusted frequently.
The use of standard SSI LSTTL chips ensures compatibility and ease of integration with other components in electronic systems. These chips provide reliable performance and are widely available, making them a practical choice for this circuit design.
Overall, the circuit represents a robust solution for controlling stepper motors, combining flexibility in design with enhanced operational efficiency. This new circuit uses four chips, with an option of using just three (the flip-flops and AND g ates can be combined). The rate of clock pulses determines the motor"s rpm. Switching transistors can replace the relays to increase the circuit"s efficiency. This circuit drives a stepper motor whose speed depends on clock rate. Standard SSI LSTTL chips are used. Switching transistors can be used in place of the solid-state relays to improve the circuit"s efficiency. 🔗 External reference
The circuit consists of four primary components: flip-flops, AND gates, a clock pulse generator, and a motor driver stage. The flip-flops serve as memory elements, maintaining the state of the motor control logic. The AND gates are used to process the signals coming from the flip-flops, enabling precise control over the motor operation based on the desired speed.
The clock pulse generator is a crucial element in this design, as it establishes the timing for the entire circuit. By adjusting the frequency of the clock pulses, the user can effectively change the RPM of the stepper motor. This allows for fine-tuned control over the motor's performance, making it suitable for applications requiring variable speed.
Incorporating switching transistors instead of traditional solid-state relays improves the circuit's efficiency. Transistors can switch on and off more rapidly than relays, resulting in faster response times and lower power consumption. This enhancement is particularly beneficial in applications where the motor speed must be adjusted frequently.
The use of standard SSI LSTTL chips ensures compatibility and ease of integration with other components in electronic systems. These chips provide reliable performance and are widely available, making them a practical choice for this circuit design.
Overall, the circuit represents a robust solution for controlling stepper motors, combining flexibility in design with enhanced operational efficiency. This new circuit uses four chips, with an option of using just three (the flip-flops and AND g ates can be combined). The rate of clock pulses determines the motor"s rpm. Switching transistors can replace the relays to increase the circuit"s efficiency. This circuit drives a stepper motor whose speed depends on clock rate. Standard SSI LSTTL chips are used. Switching transistors can be used in place of the solid-state relays to improve the circuit"s efficiency. 🔗 External reference