PWM Motor Speed Controller
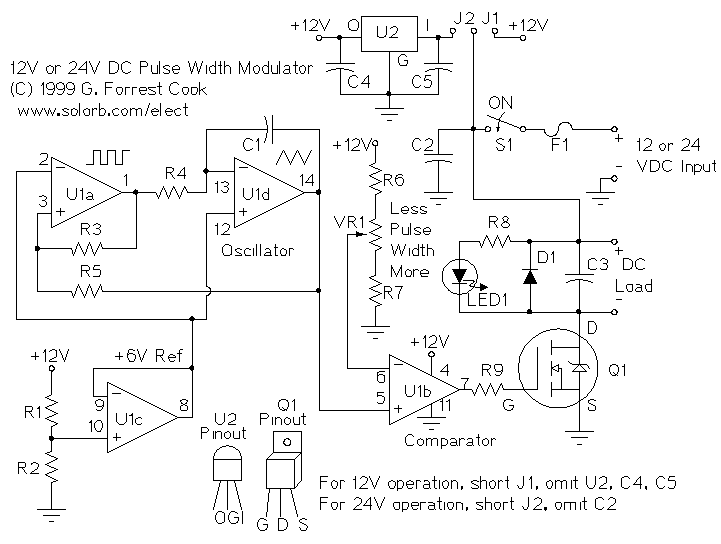
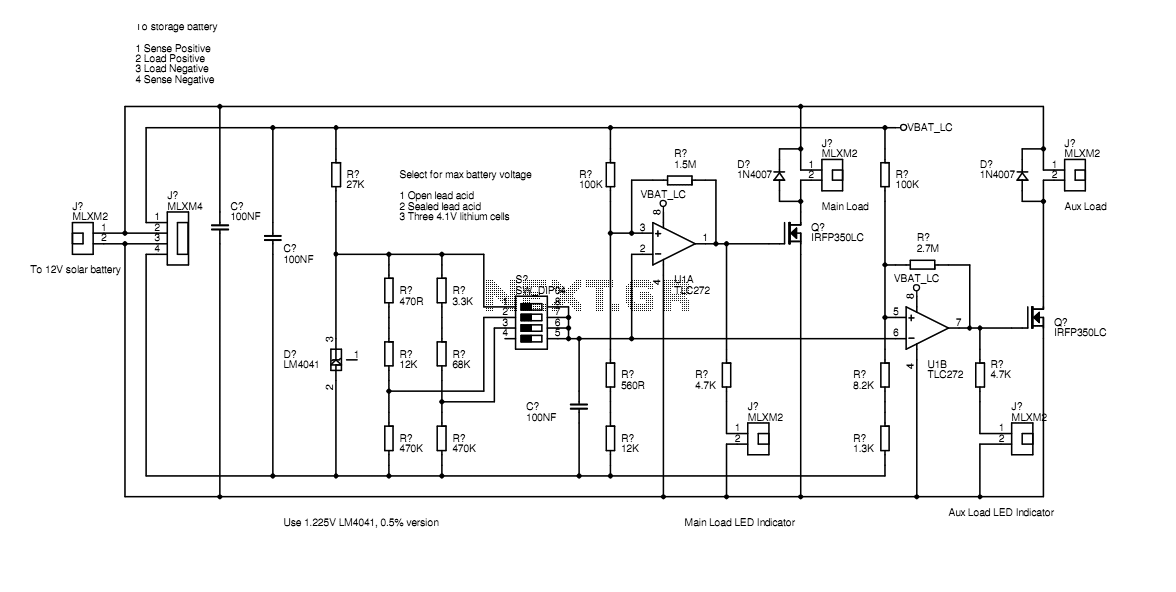
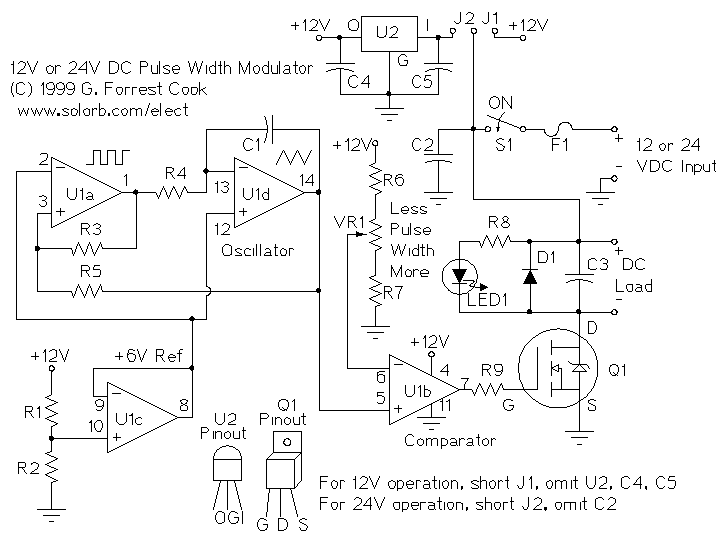
A pulse width modulator (PWM) is a device that may be used as an efficient light dimmer or DC motor speed controller. The circuit described here is for a general purpose device that can control DC devices which draw up to a few amps of current. The circuit may be used in either 12 or 24 Volt systems with only a few minor wiring changes. This device has been used to control the brightness of an automotive tail lamp and as a motor speed control for small DC fans of the type used in computer power supplies. More: A PWM circuit works by making a square wave with a variable on-to-off ratio, the average on time may be varied from 0 to 100 percent. In this manner, a variable amount of power is transferred to the load. The main advantage of a PWM circuit over a resistive.
The pulse width modulation (PWM) circuit operates by generating a square wave signal whose duty cycle can be adjusted to control the amount of power delivered to a load. The circuit is typically designed to accommodate DC devices that require a current draw of several amps, making it suitable for applications such as dimming lights or controlling the speed of small DC motors.
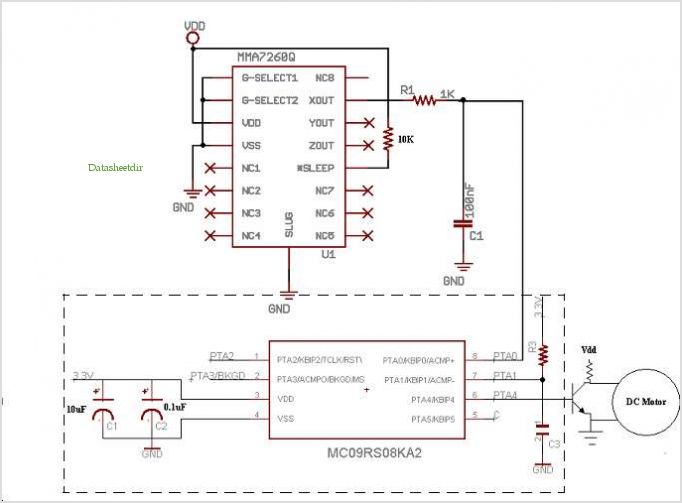
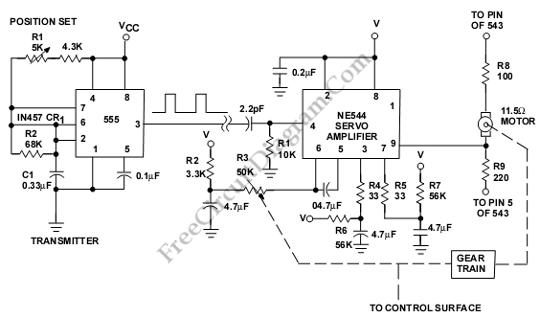
The core of the PWM circuit often includes a timer or microcontroller that produces the square wave output. The frequency of this square wave is usually fixed, while the duty cycle—the ratio of the time the signal is high (on) to the total period of the signal—can be varied. By changing the duty cycle, the average voltage and current supplied to the load can be adjusted, effectively controlling the brightness of a light or the speed of a motor.
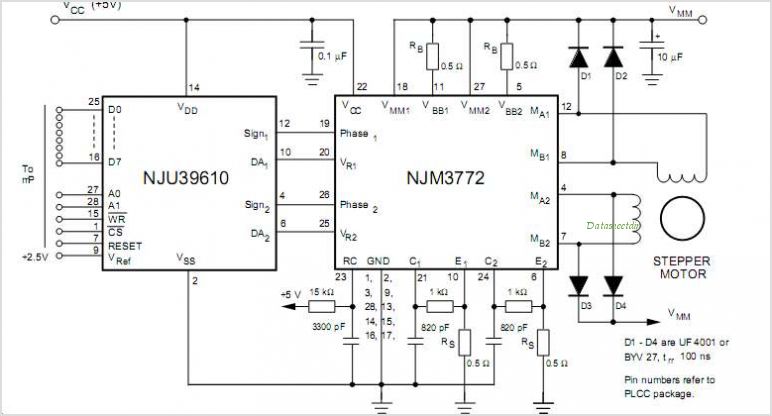
For operation in 12 or 24 Volt systems, the circuit may incorporate a few minor modifications in the wiring configuration, allowing for versatility in application. The output stage typically consists of a transistor or MOSFET capable of handling the required load current, ensuring efficient switching with minimal heat generation.
In practical applications, such as automotive lighting or cooling fans, the PWM circuit provides a smooth and efficient control method compared to traditional resistive dimming or speed control methods. By using PWM, the circuit minimizes power loss and enhances the operational lifespan of the components involved. Overall, the PWM circuit serves as a reliable solution for various DC power management needs.A pulse width modulator (PWM) is a device that may be used as an efficient light dimmer or DC motor speed controller. The circuit described here is for a general purpose device that can control DC devices which draw up to a few amps of current.
The circuit may be used in either 12 or 24 Volt systems with only a few minor wiring changes. This device has been used to control the brightness of an automotive tail lamp and as a motor speed control for small DC fans of the type used in computer power supplies. A PWM circuit works by making a square wave with a variable on-to-off ratio, the average on time may be varied from 0 to 100 percent. In this manner, a variable amount of power is transferred to the load. The main advantage of a PWM circuit over a resisti 🔗 External reference
The pulse width modulation (PWM) circuit operates by generating a square wave signal whose duty cycle can be adjusted to control the amount of power delivered to a load. The circuit is typically designed to accommodate DC devices that require a current draw of several amps, making it suitable for applications such as dimming lights or controlling the speed of small DC motors.
The core of the PWM circuit often includes a timer or microcontroller that produces the square wave output. The frequency of this square wave is usually fixed, while the duty cycle—the ratio of the time the signal is high (on) to the total period of the signal—can be varied. By changing the duty cycle, the average voltage and current supplied to the load can be adjusted, effectively controlling the brightness of a light or the speed of a motor.
For operation in 12 or 24 Volt systems, the circuit may incorporate a few minor modifications in the wiring configuration, allowing for versatility in application. The output stage typically consists of a transistor or MOSFET capable of handling the required load current, ensuring efficient switching with minimal heat generation.
In practical applications, such as automotive lighting or cooling fans, the PWM circuit provides a smooth and efficient control method compared to traditional resistive dimming or speed control methods. By using PWM, the circuit minimizes power loss and enhances the operational lifespan of the components involved. Overall, the PWM circuit serves as a reliable solution for various DC power management needs.A pulse width modulator (PWM) is a device that may be used as an efficient light dimmer or DC motor speed controller. The circuit described here is for a general purpose device that can control DC devices which draw up to a few amps of current.
The circuit may be used in either 12 or 24 Volt systems with only a few minor wiring changes. This device has been used to control the brightness of an automotive tail lamp and as a motor speed control for small DC fans of the type used in computer power supplies. A PWM circuit works by making a square wave with a variable on-to-off ratio, the average on time may be varied from 0 to 100 percent. In this manner, a variable amount of power is transferred to the load. The main advantage of a PWM circuit over a resisti 🔗 External reference